Meningioma
Mehr erfahren2.231,25 €*
Artikel in Produktion, lieferbar vorauss. in 2-3 Wochen
Produktnummer:
MP2004
Artikelnummer: MP2004
Produktinformationen "Meningioma"
Clinical History
A 68-year-old female presented with recent onset of seizures and was diagnosed with epilepsy. Collateral history revealed a gradual change in the patient’s personality. She subsequently died several months later from a myocardial infarction.
Pathology
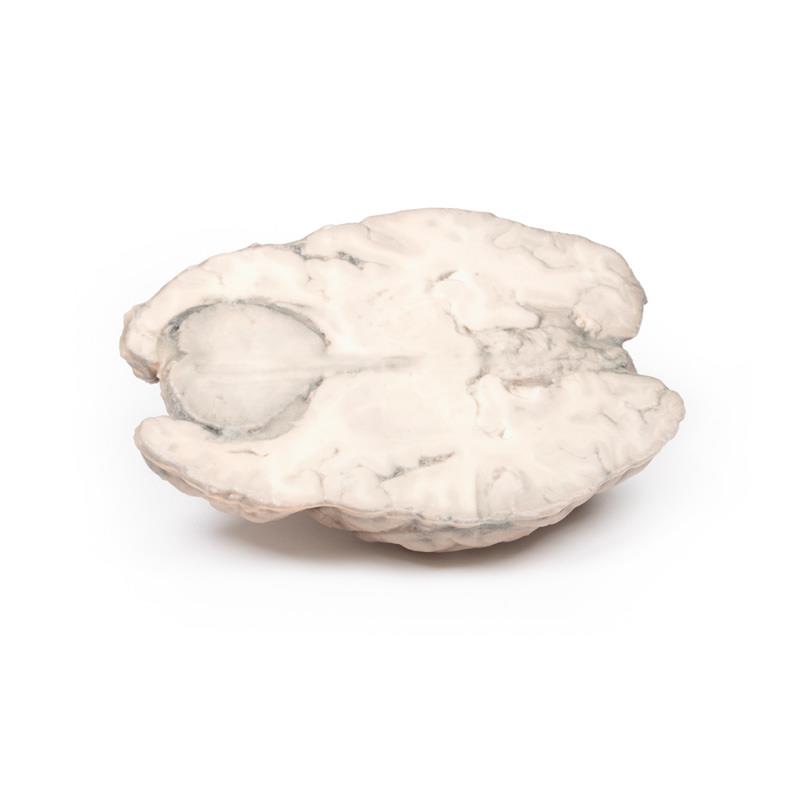
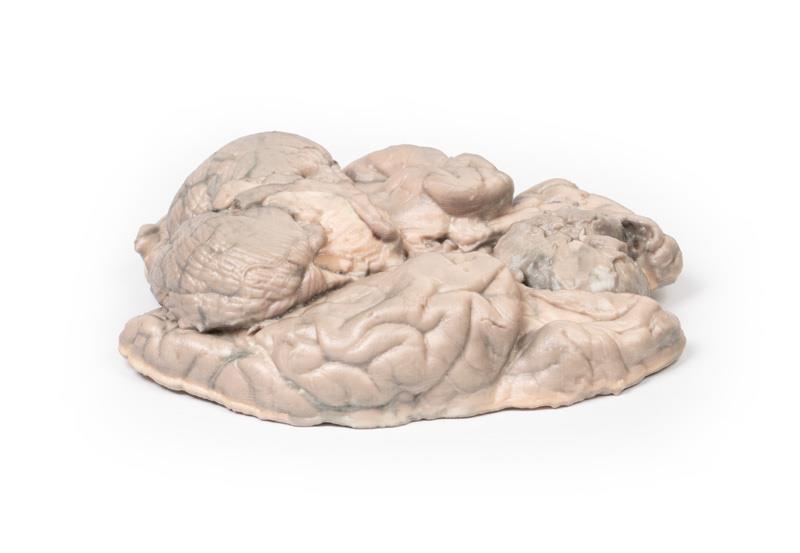
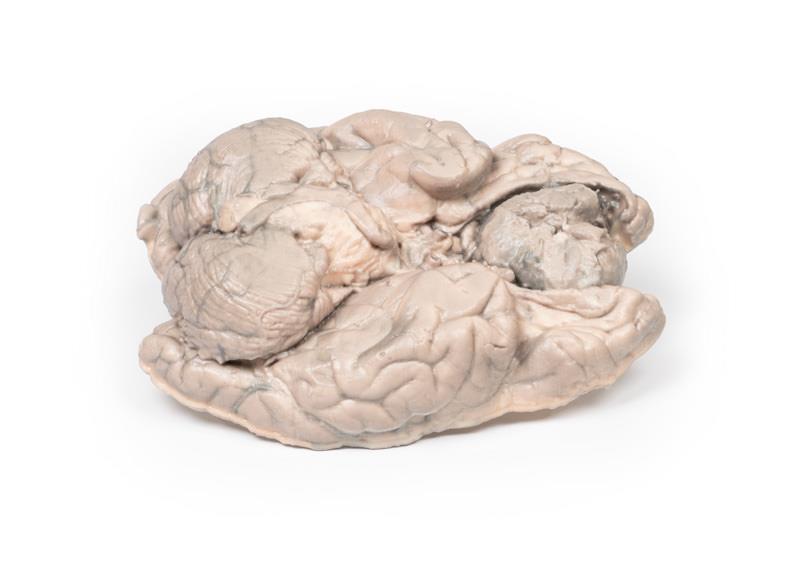
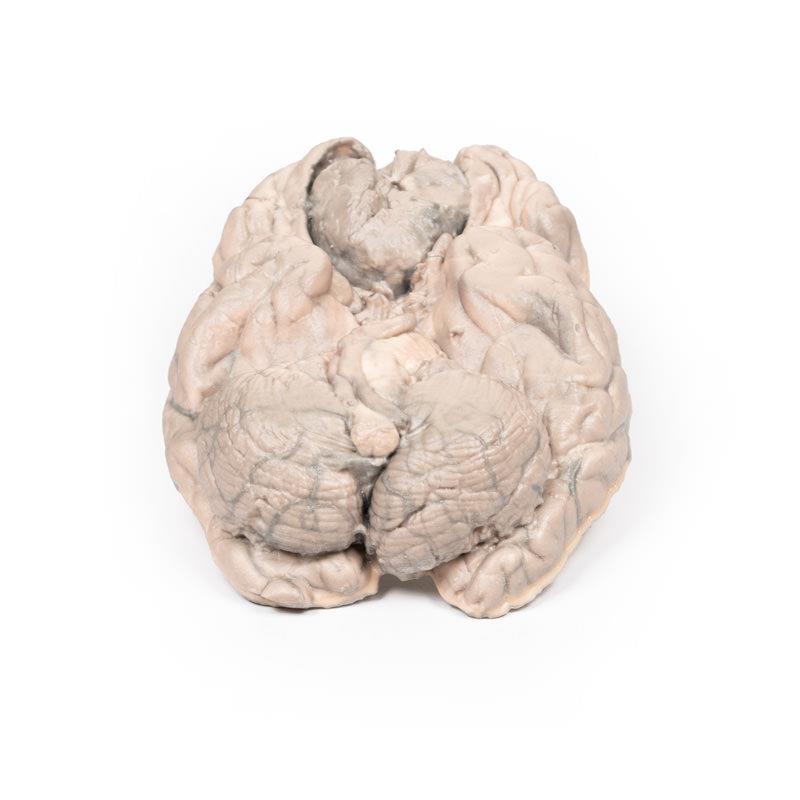
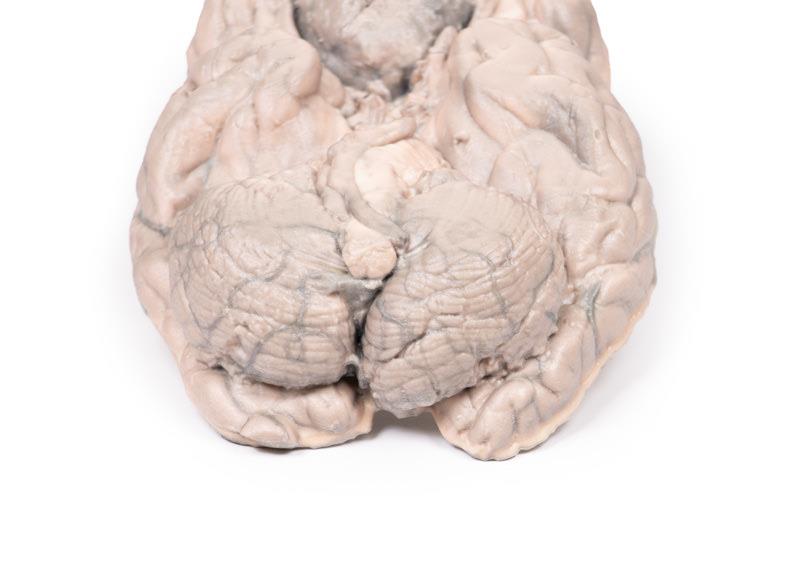
This brain specimen has been sliced horizontally. A well-circumscribed 6cm tumour is evident in between the two frontal lobes. The tumour is compressing the frontal lobes. It has a pinkish cut surface with some yellow areas indicating necrosis. It was attached to the dura mater anteriorly. This is an example of a meningioma.
Further Information
Meningiomas are often said to be the most common tumours of the central nervous system (CNS); however, in fact they arise in the meninges (dura, arachnoid and pia), which are strictly speaking not part of the CNS per se. They arise from arachnoid cells closely associated with the dura; hence, these tumours can be associated with the dura or dural folds (falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli). Meningiomas are predominantly slow growing benign tumours. Symptoms are determined by the tumour location and the speed of growth. Symptoms include seizures, change of mental state, vision, hearing- or smell alterations, and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure. Meningiomas are frequently asymptomatic. Treatment includes observation, surgery or radiotherapy, depending on the clinical context and tumour morphology.
Meningiomas are rare in children with a median age of 65 years at diagnosis. There is a 3:2 female predominance. Exposure to ionising radiation, including cranial radiotherapy, increases the risk of development meningiomas. The greatest genetic predisposition for development is seen in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). NF2 is an autosomal dominant disease caused by mutations in the NF2 gene on Chromosome 22 leading to multiple tumours associated with the nervous system.
A 68-year-old female presented with recent onset of seizures and was diagnosed with epilepsy. Collateral history revealed a gradual change in the patient’s personality. She subsequently died several months later from a myocardial infarction.
Pathology
This brain specimen has been sliced horizontally. A well-circumscribed 6cm tumour is evident in between the two frontal lobes. The tumour is compressing the frontal lobes. It has a pinkish cut surface with some yellow areas indicating necrosis. It was attached to the dura mater anteriorly. This is an example of a meningioma.
Further Information
Meningiomas are often said to be the most common tumours of the central nervous system (CNS); however, in fact they arise in the meninges (dura, arachnoid and pia), which are strictly speaking not part of the CNS per se. They arise from arachnoid cells closely associated with the dura; hence, these tumours can be associated with the dura or dural folds (falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli). Meningiomas are predominantly slow growing benign tumours. Symptoms are determined by the tumour location and the speed of growth. Symptoms include seizures, change of mental state, vision, hearing- or smell alterations, and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure. Meningiomas are frequently asymptomatic. Treatment includes observation, surgery or radiotherapy, depending on the clinical context and tumour morphology.
Meningiomas are rare in children with a median age of 65 years at diagnosis. There is a 3:2 female predominance. Exposure to ionising radiation, including cranial radiotherapy, increases the risk of development meningiomas. The greatest genetic predisposition for development is seen in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). NF2 is an autosomal dominant disease caused by mutations in the NF2 gene on Chromosome 22 leading to multiple tumours associated with the nervous system.