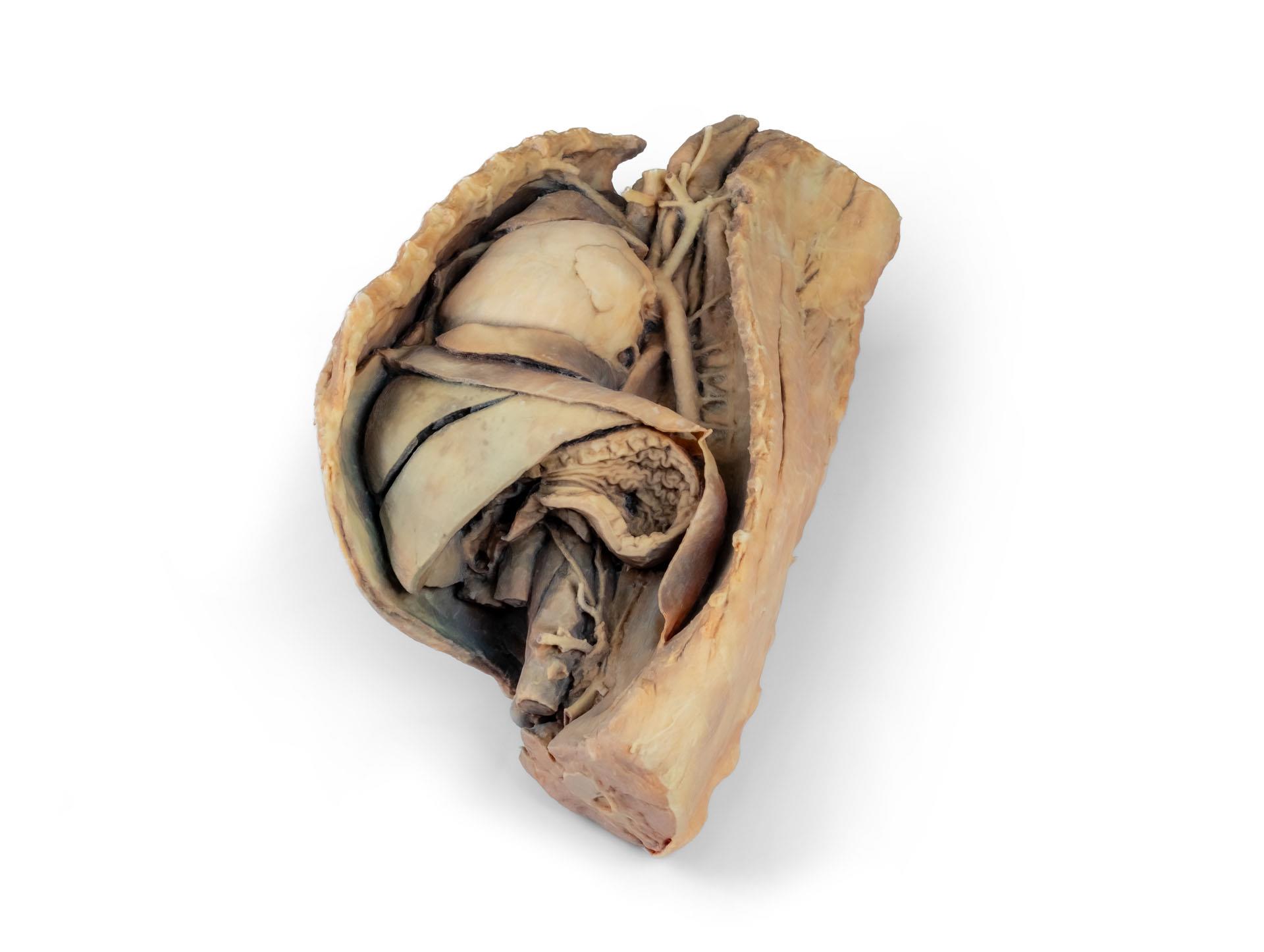
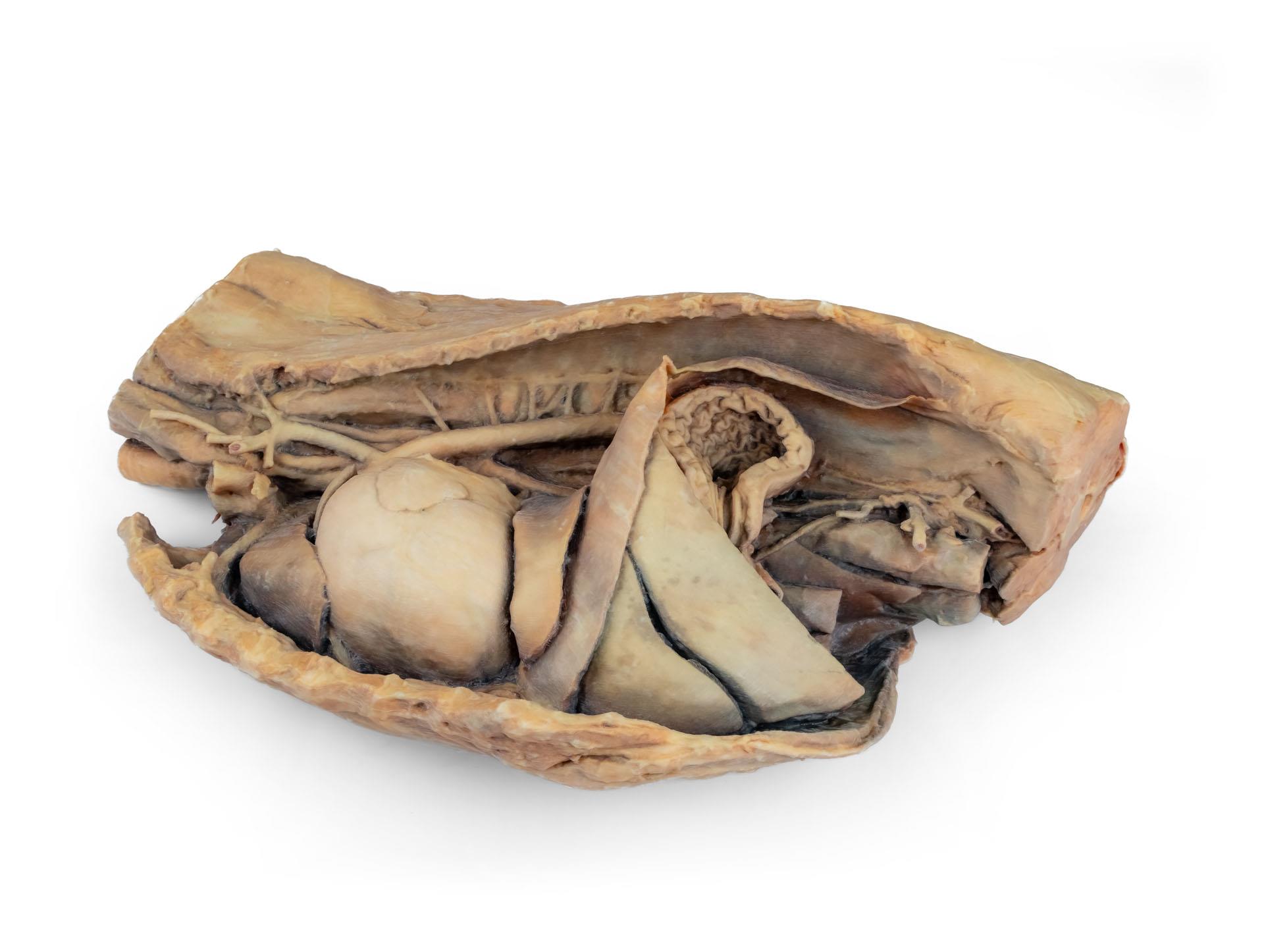
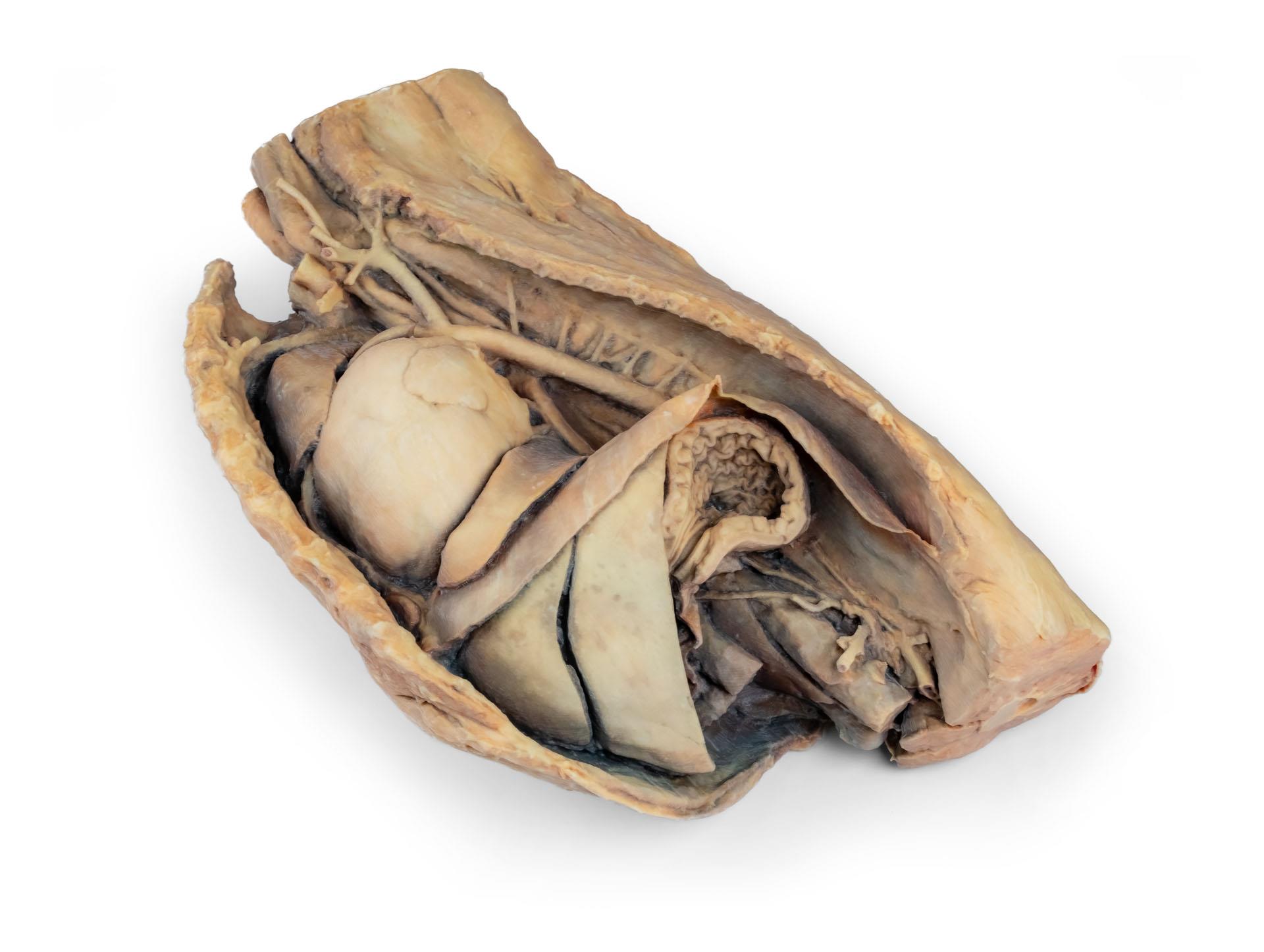
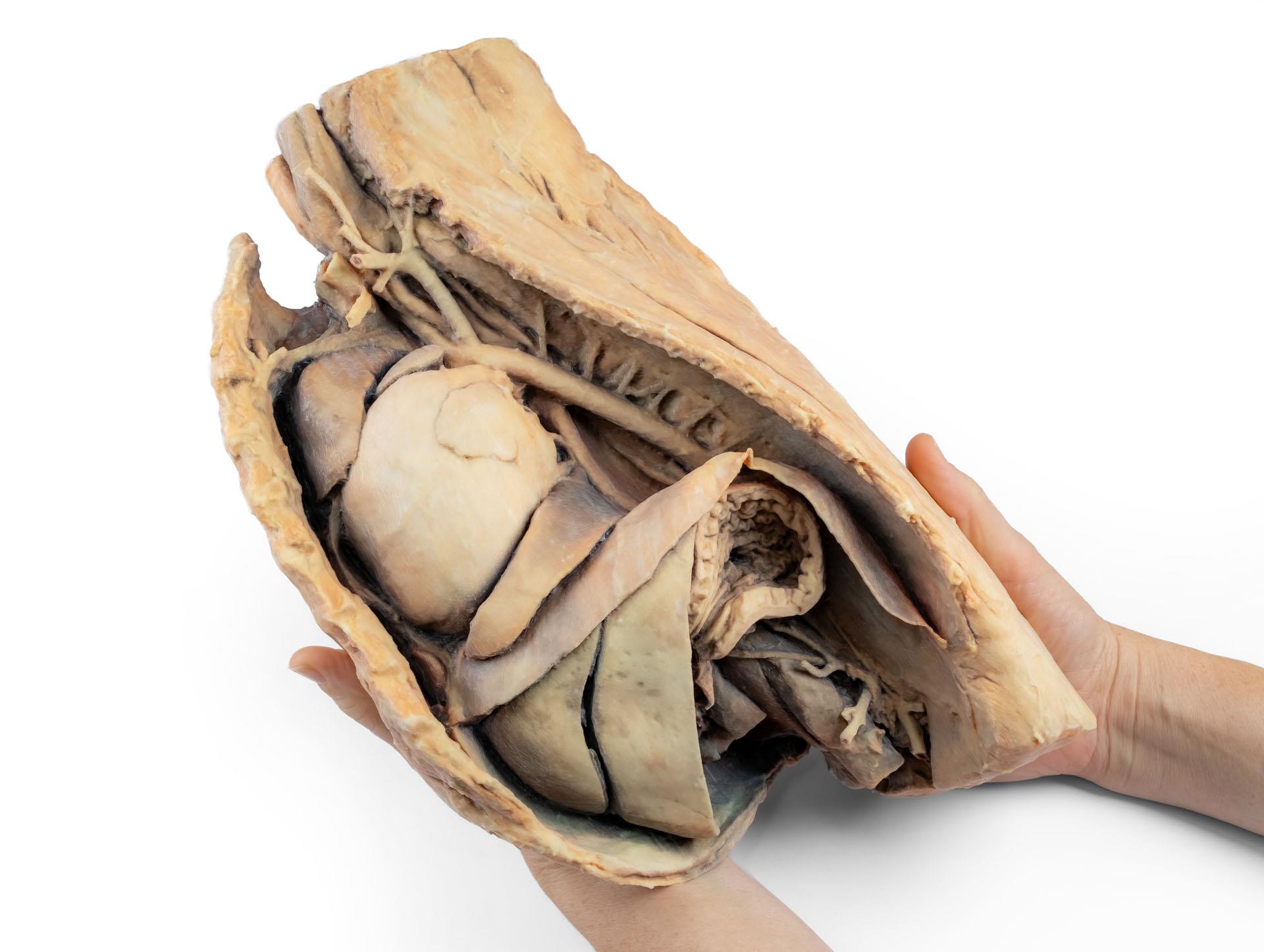
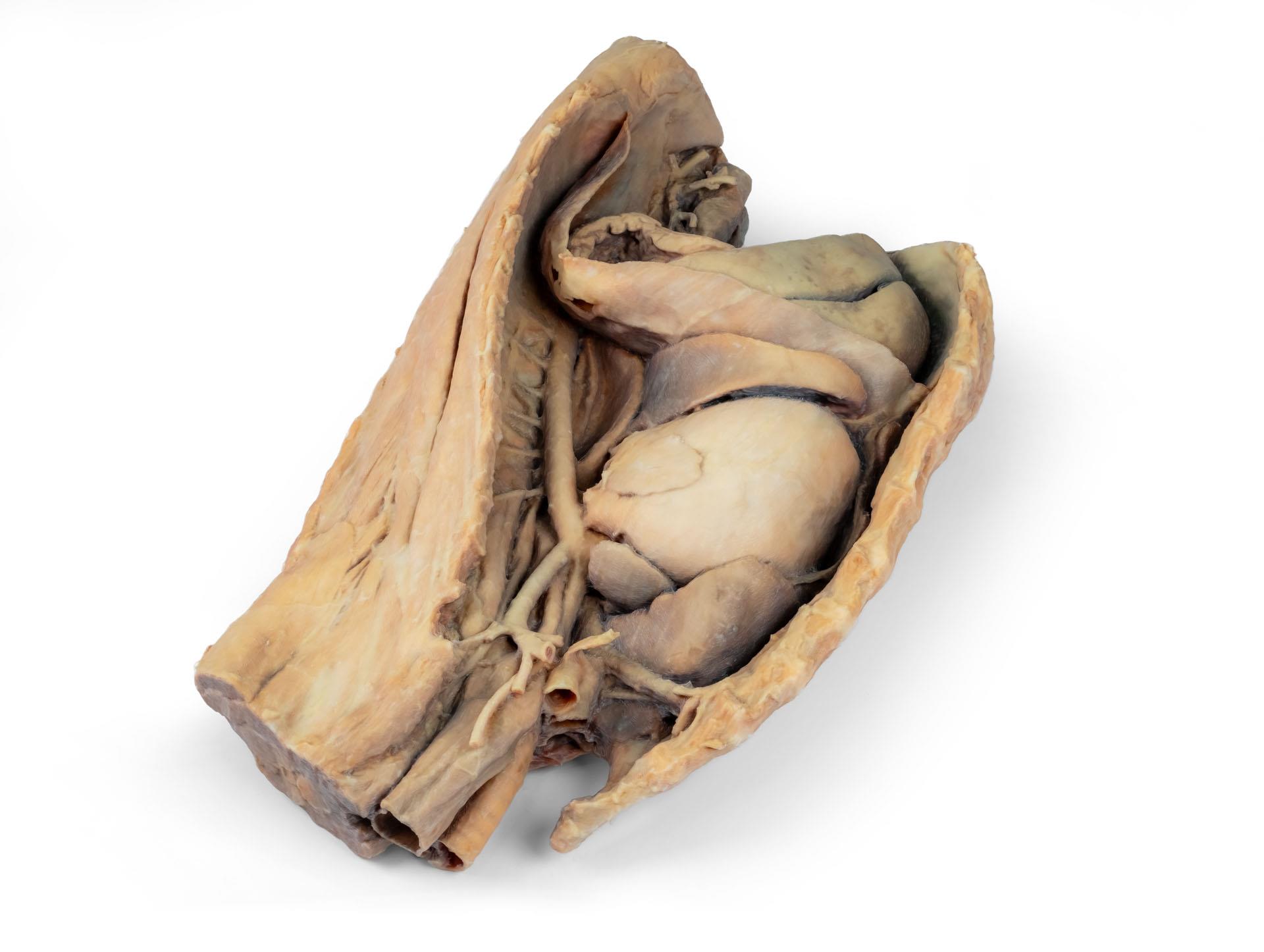
Cavité thoracique canine côté gauche
3 973,41 €*
Article en production, livraison prévue dans 2-3 semaines
Réf. produit :
VP9050
Numéro d'article: VP9050
Informations sur le produit "Cavité thoracique canine côté gauche"
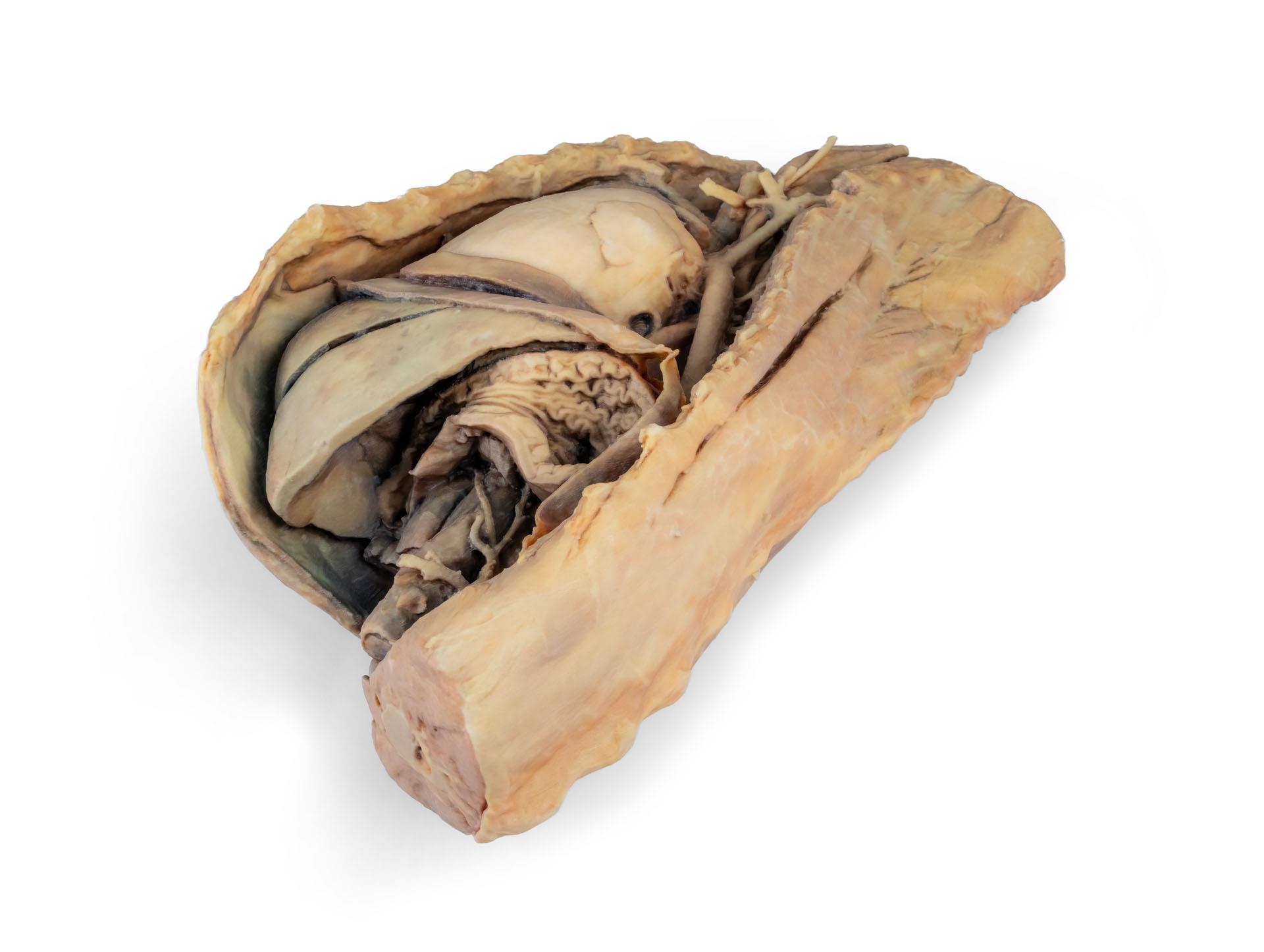
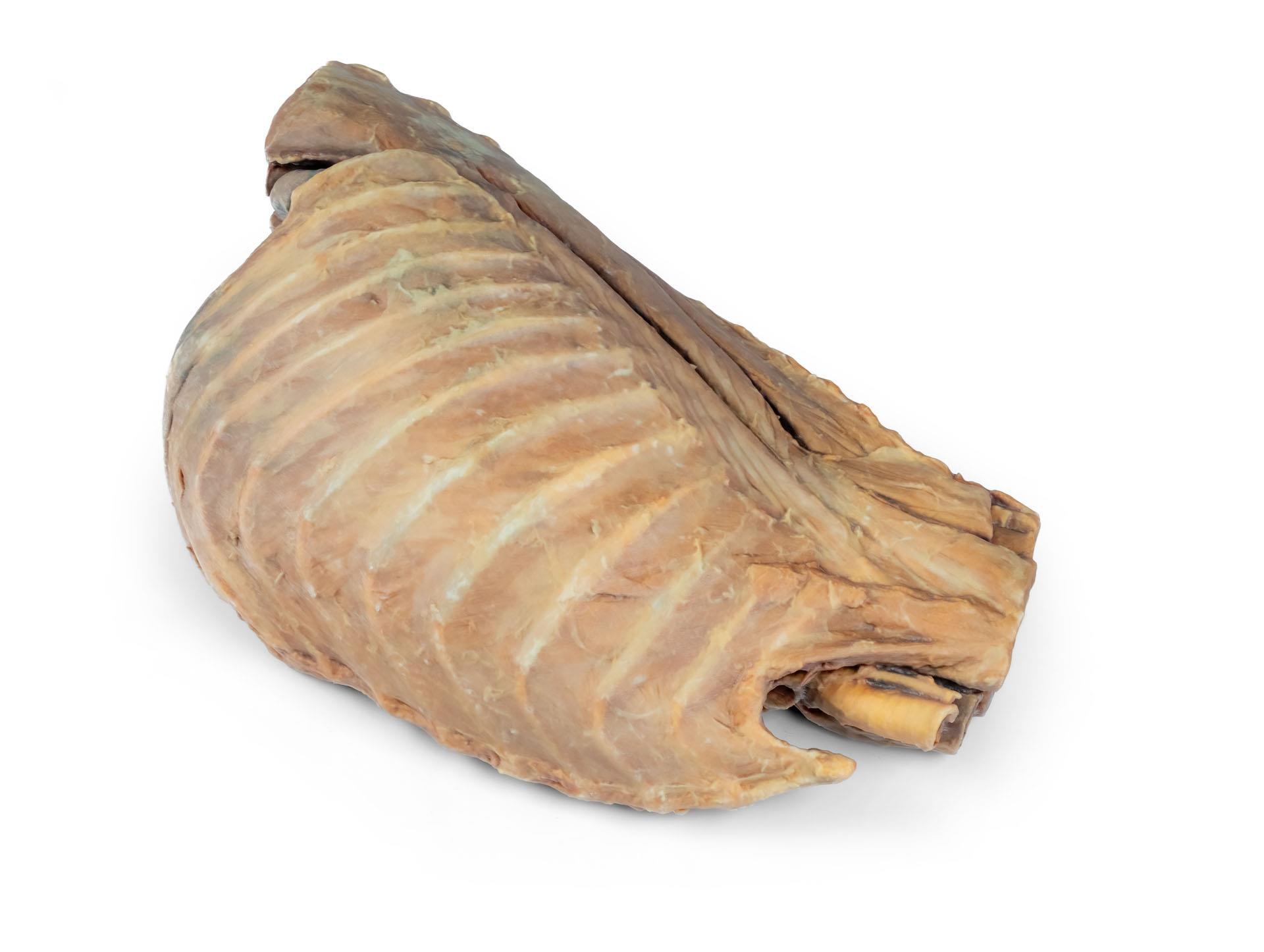
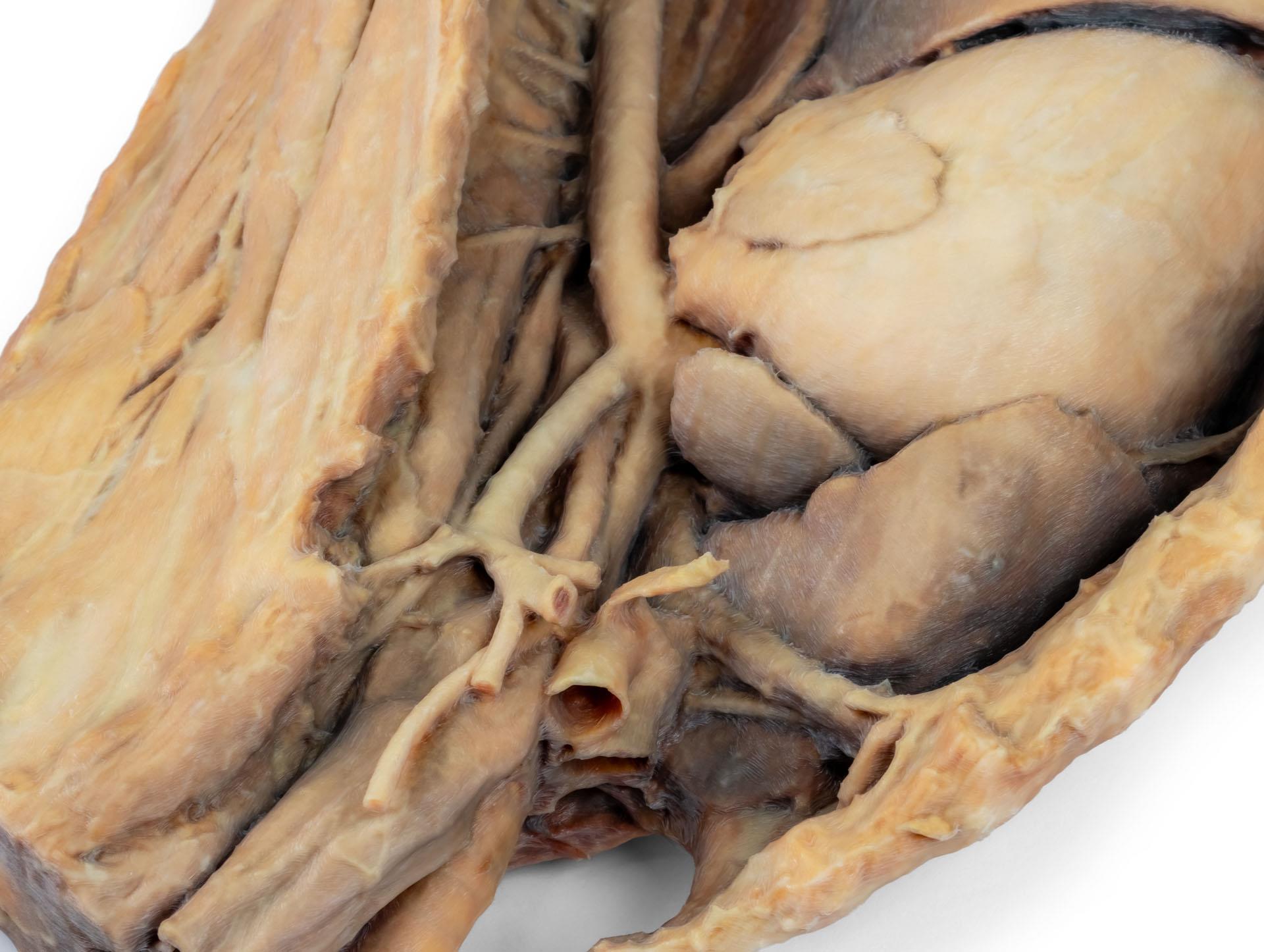
Ce spécimen représente la topographie du cœur après l'ablation du poumon gauche lors d'une dissection de la cavité thoracique et de l'abdomen crânien d'un chien abordé par le côté gauche. Les lobes crâniens et accessoires du poumon droit restent in situ et servent de points de référence anatomiques. Dans le médiastin crânien, le tronc brachiocéphalique et l'artère sous-clavière gauche sont identifiables en tant que branches principales issues de l'arc aortique.
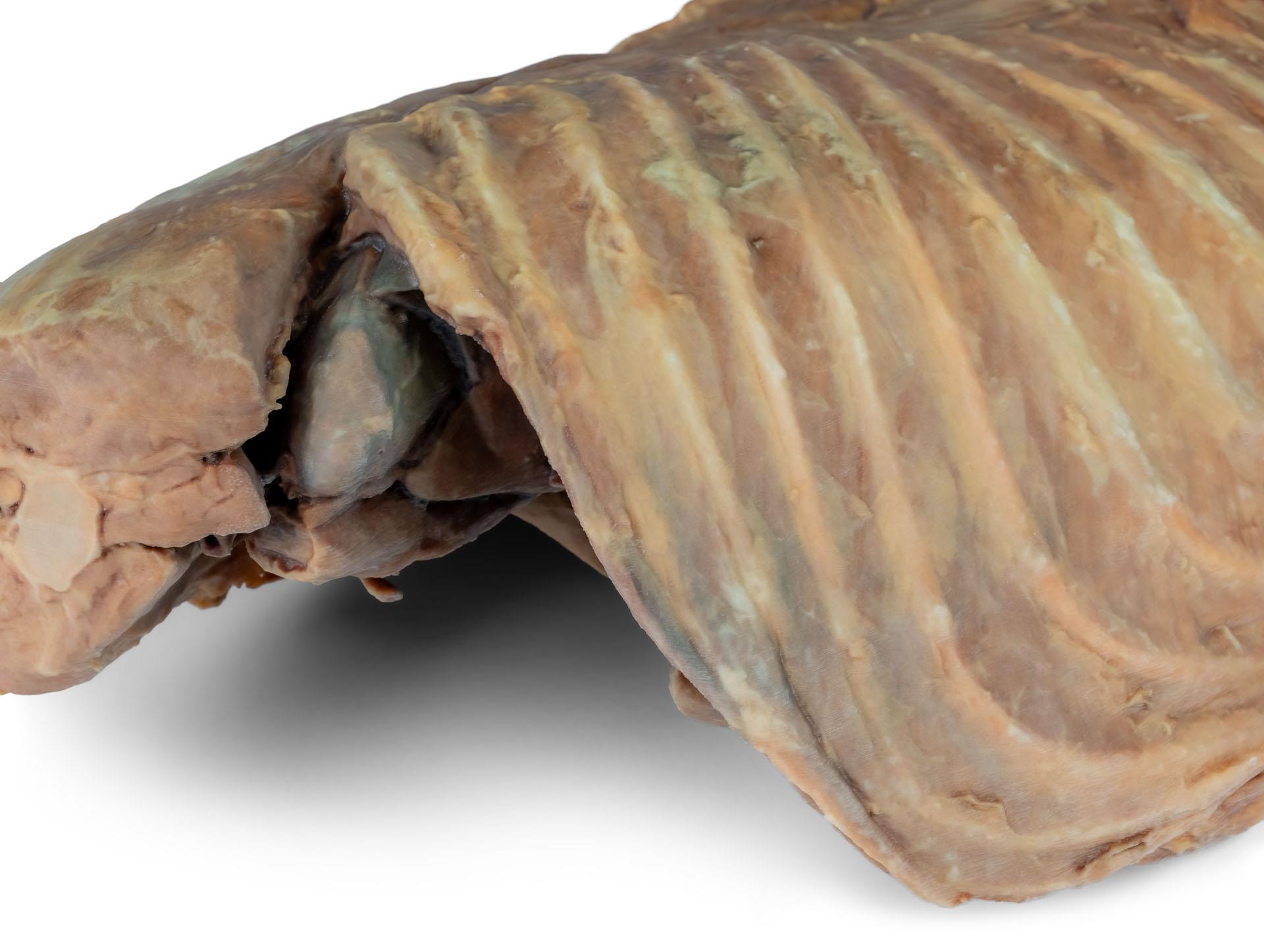
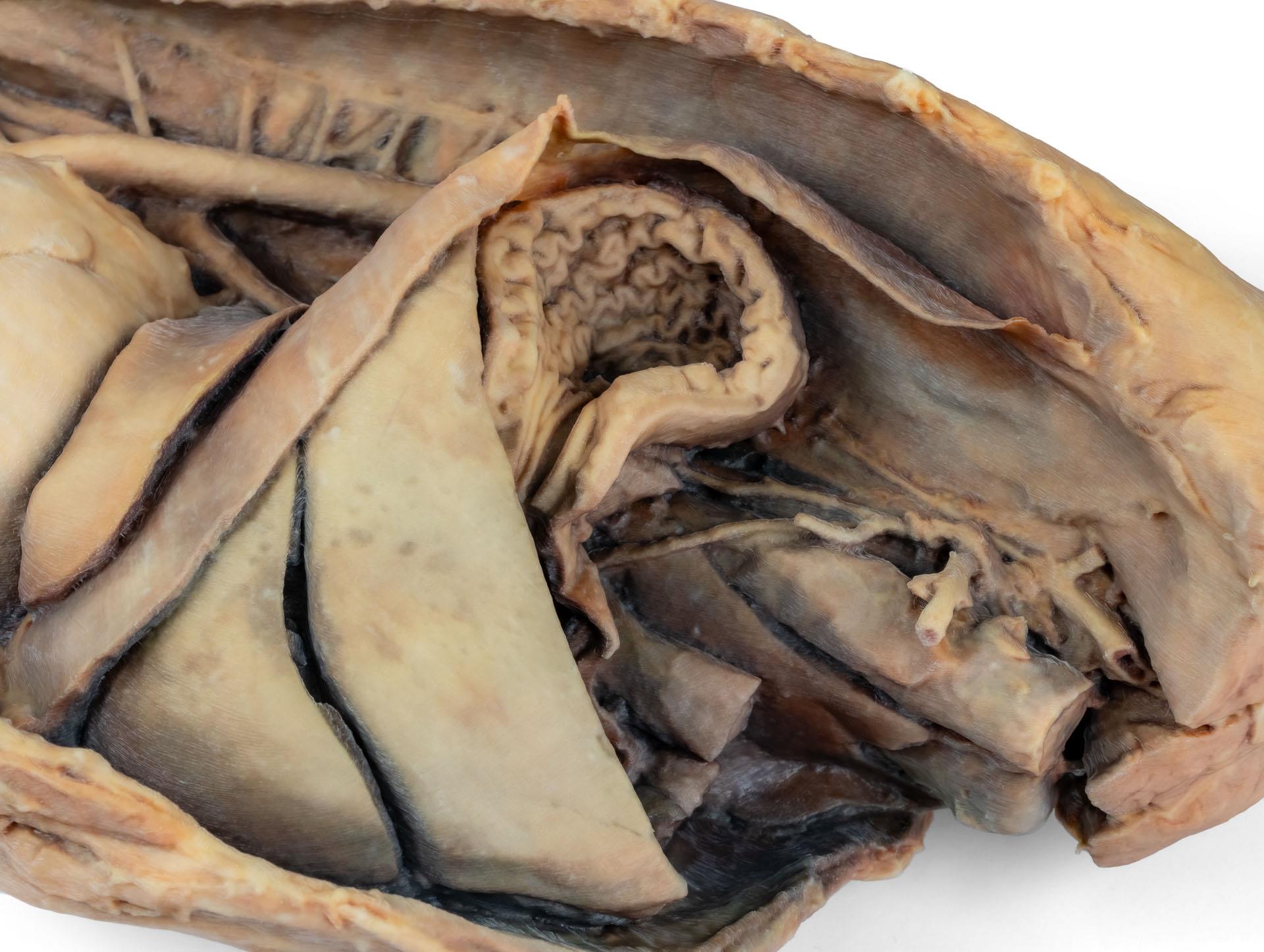
La partie thoracique de l'œsophage traverse le médiastin en direction craniocaudale. Le diaphragme a été préservé pour servir de repère aux organes rétrodiaphragmatiques tels que le foie et l'estomac.Les crêtes diaphragmatiques et leur relation avec le hiatus aortique sont conservées, de même que les branches viscérales initiales de l'aorte abdominale, à savoir le tronc cœliaque et l'artère mésentérique crâniale. Une partie de la paroi auriculaire droite a été enlevée pour exposer la valve auriculo-ventriculaire droite (tricuspide), y compris les muscles chordaetendineae et papillaires.
En outre, la trabécule septomarginale (bande modératrice) est visible dans le ventricule droit, ainsi que la trajectoire du ventricule vers le tronc pulmonaire. La paroi auriculaire gauche est également ouverte pour montrer sa lumière.
La partie thoracique de l'œsophage traverse le médiastin en direction craniocaudale. Le diaphragme a été préservé pour servir de repère aux organes rétrodiaphragmatiques tels que le foie et l'estomac.Les crêtes diaphragmatiques et leur relation avec le hiatus aortique sont conservées, de même que les branches viscérales initiales de l'aorte abdominale, à savoir le tronc cœliaque et l'artère mésentérique crâniale. Une partie de la paroi auriculaire droite a été enlevée pour exposer la valve auriculo-ventriculaire droite (tricuspide), y compris les muscles chordaetendineae et papillaires.
En outre, la trabécule septomarginale (bande modératrice) est visible dans le ventricule droit, ainsi que la trajectoire du ventricule vers le tronc pulmonaire. La paroi auriculaire gauche est également ouverte pour montrer sa lumière.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.