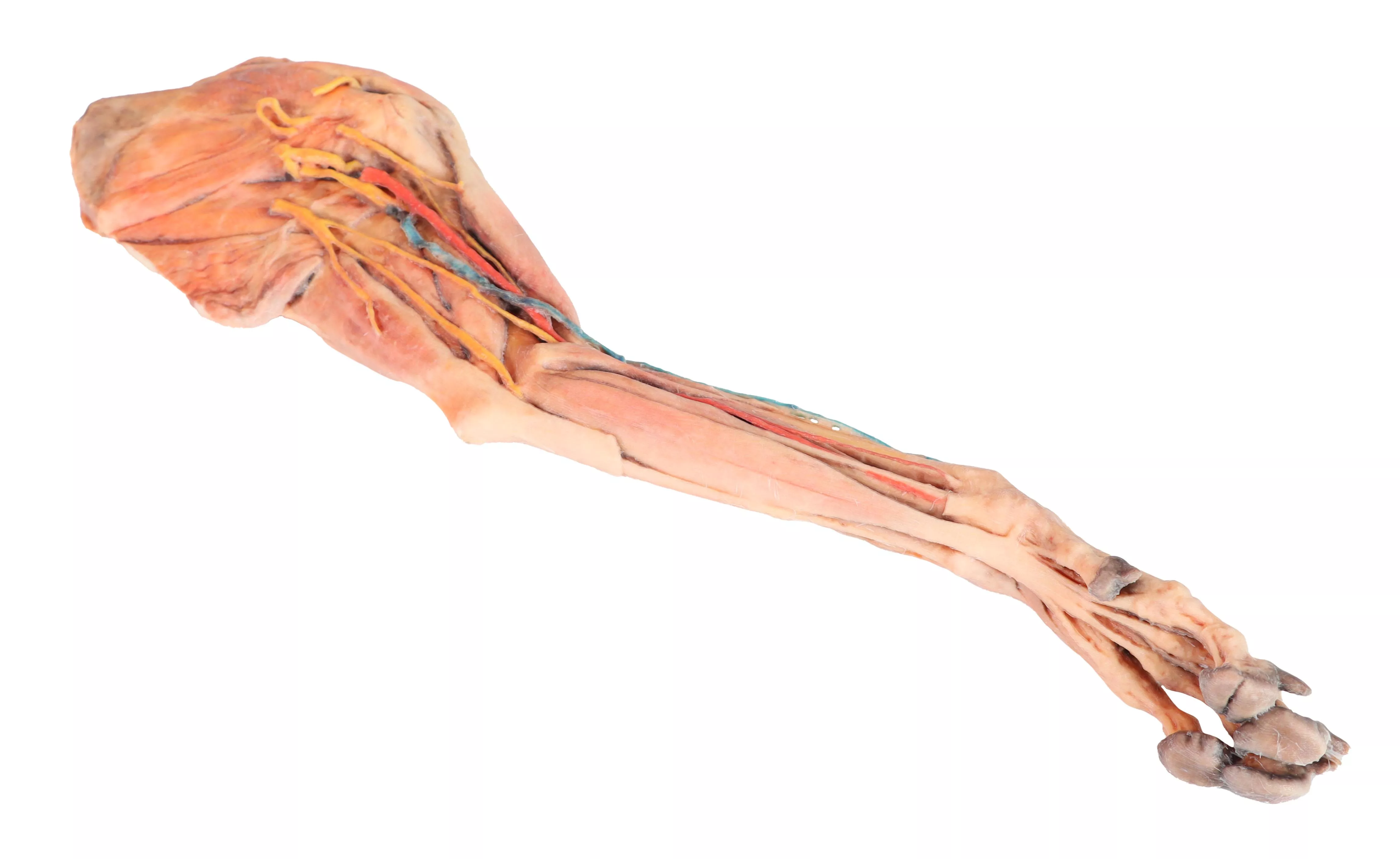
Brusthöhle des Hundes, linke Seite
3.973,41 €*
Artikel in Produktion, lieferbar vorauss. in 2-3 Wochen
Produktnummer:
VP9050
Artikelnummer: VP9050
Produktinformationen "Brusthöhle des Hundes, linke Seite"
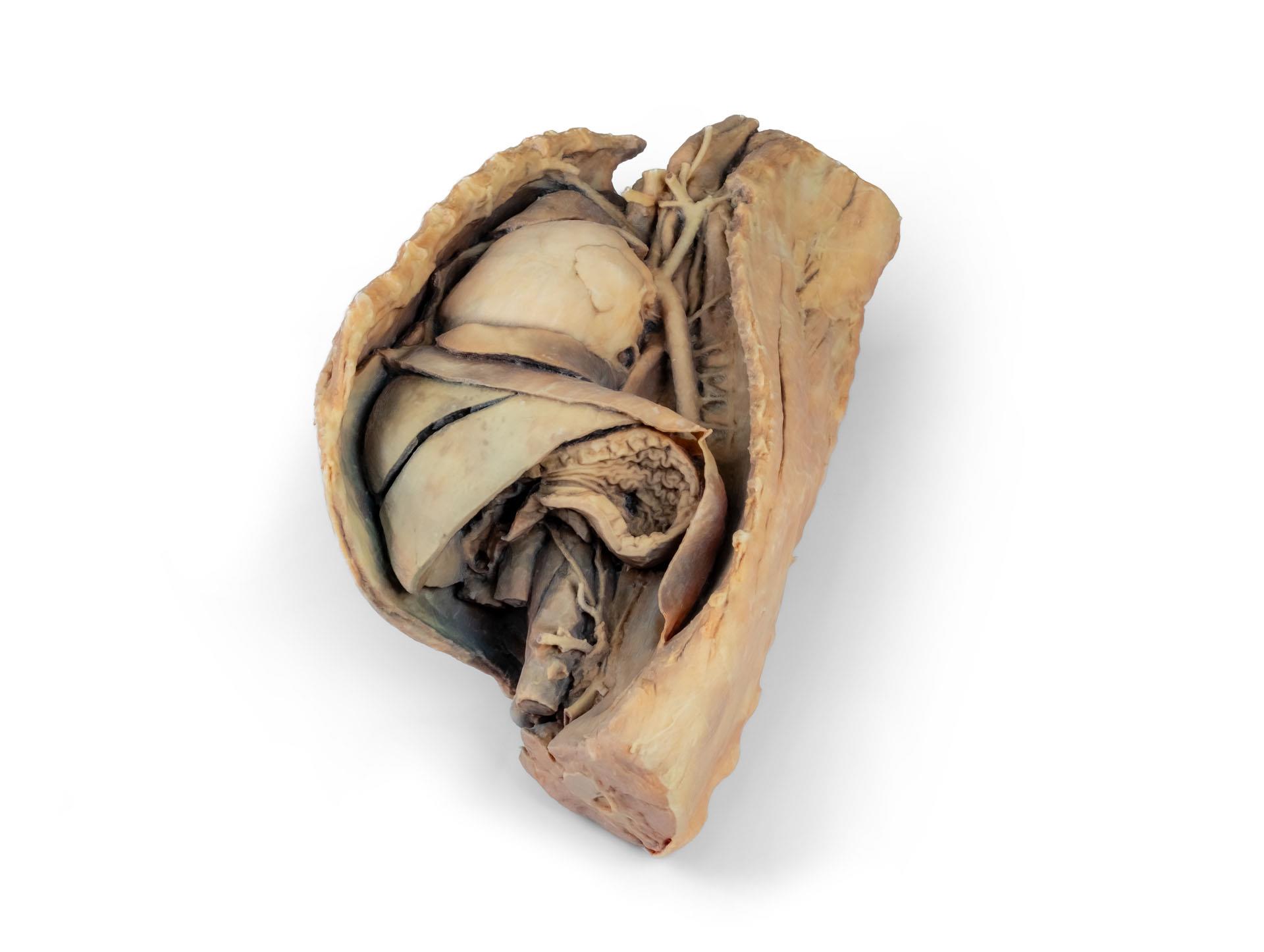
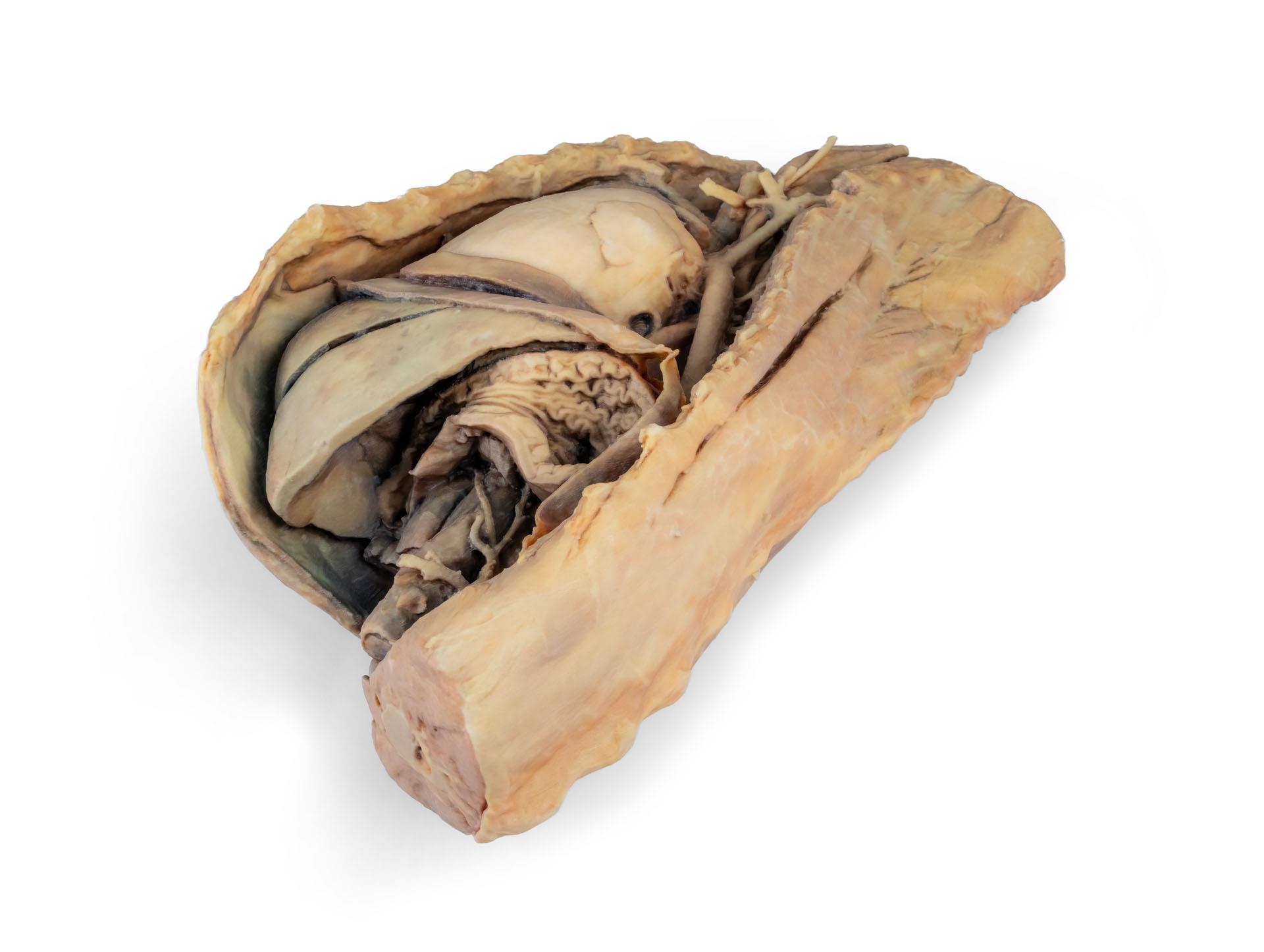
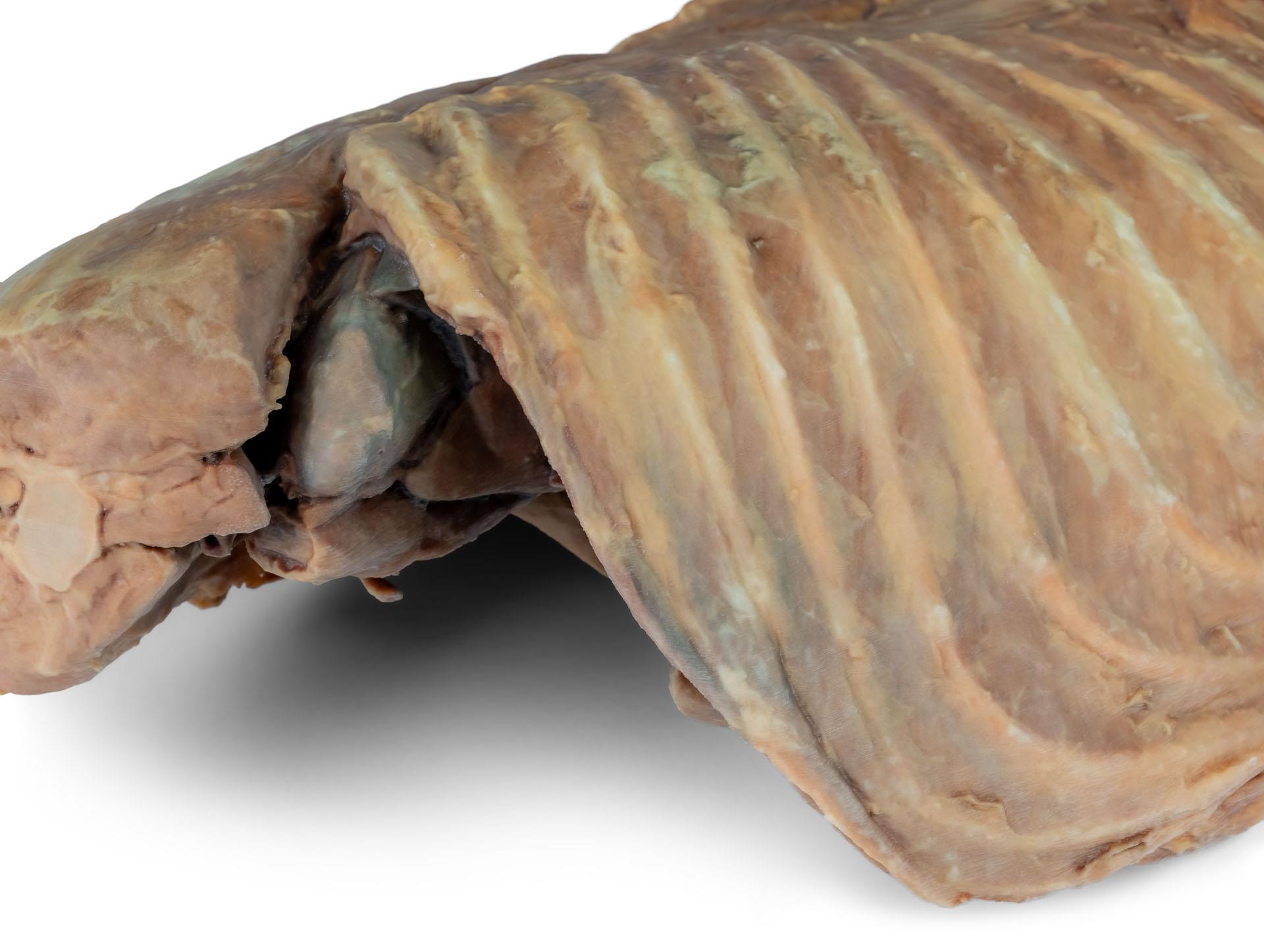
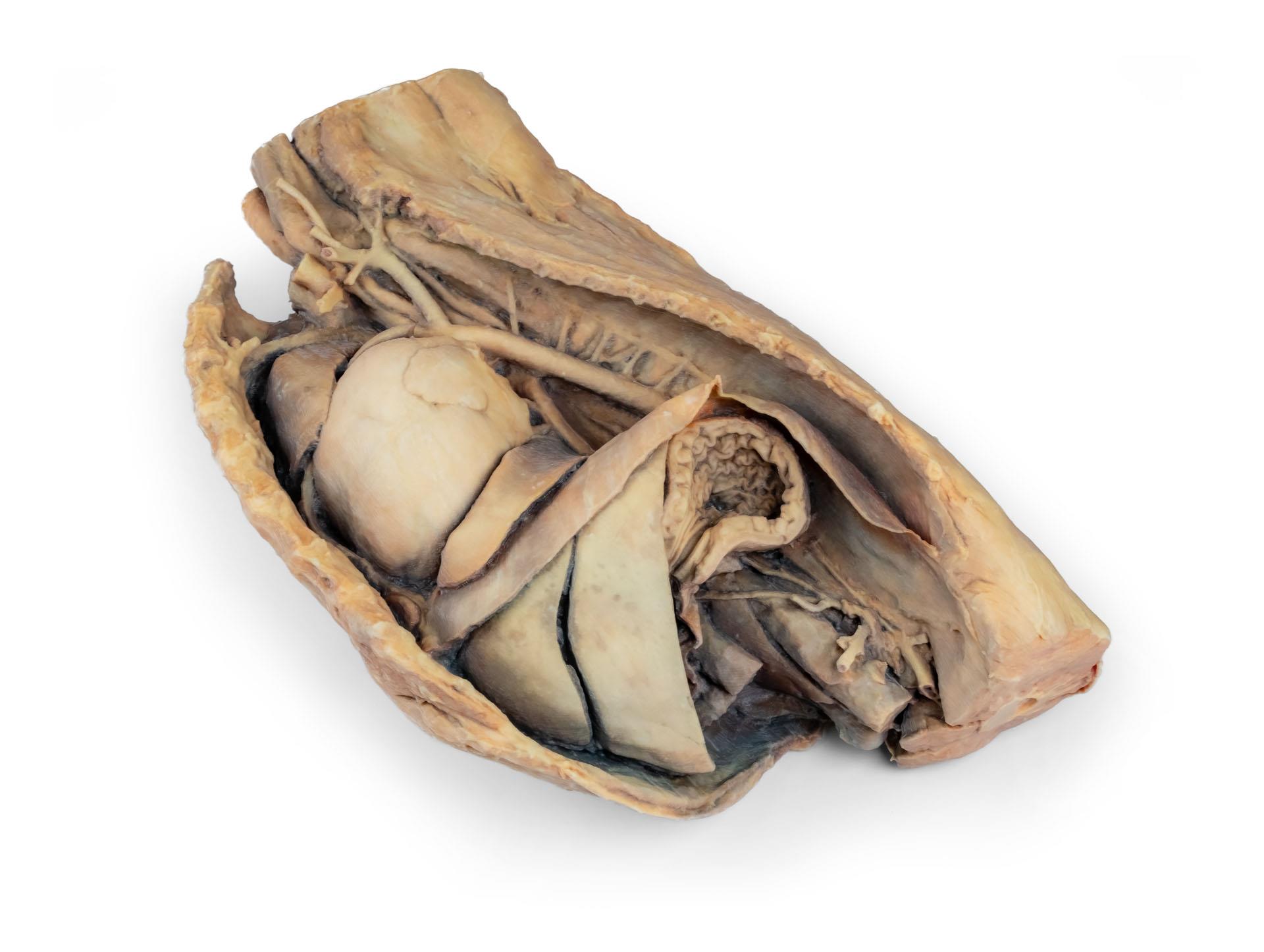
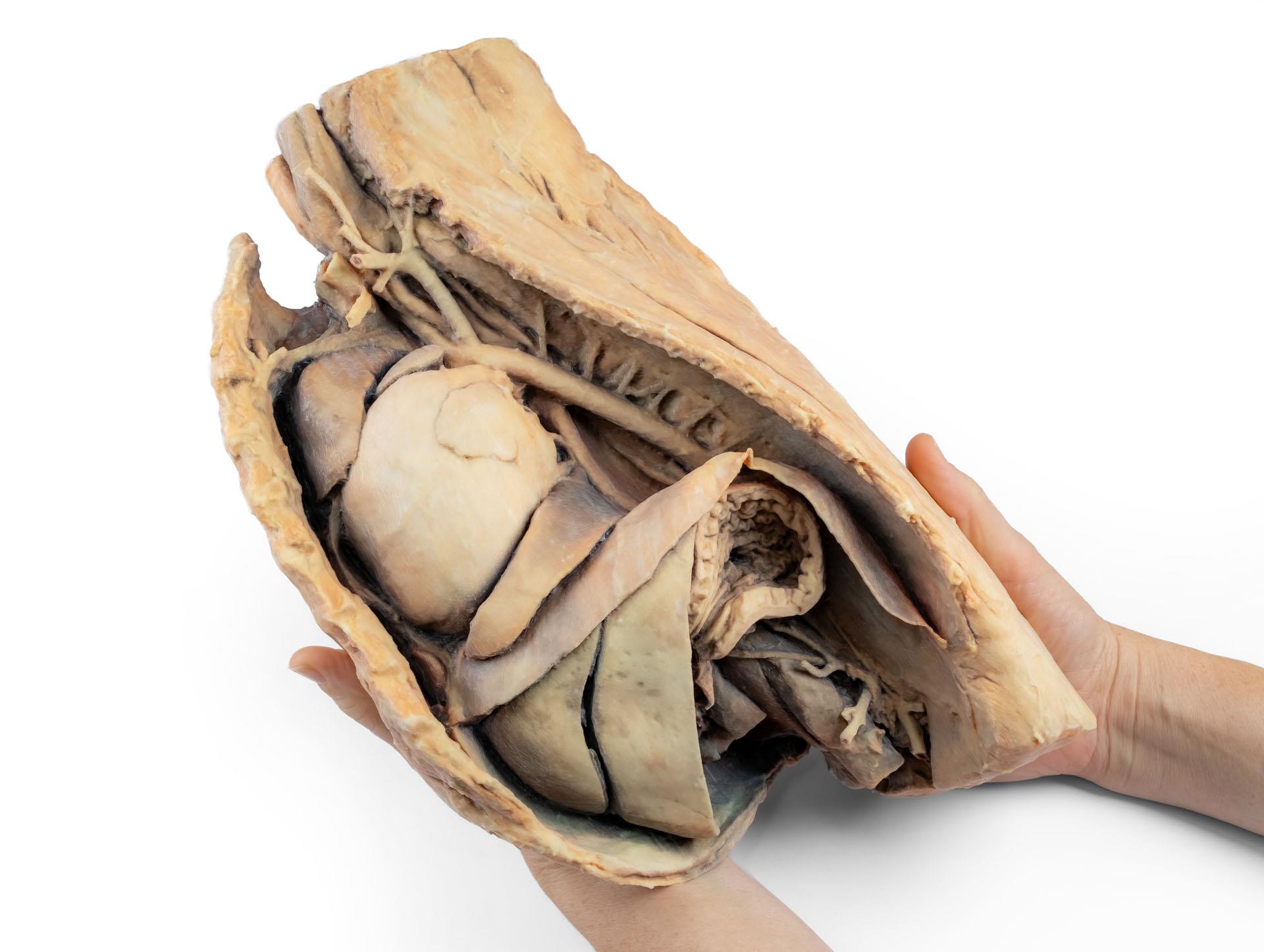
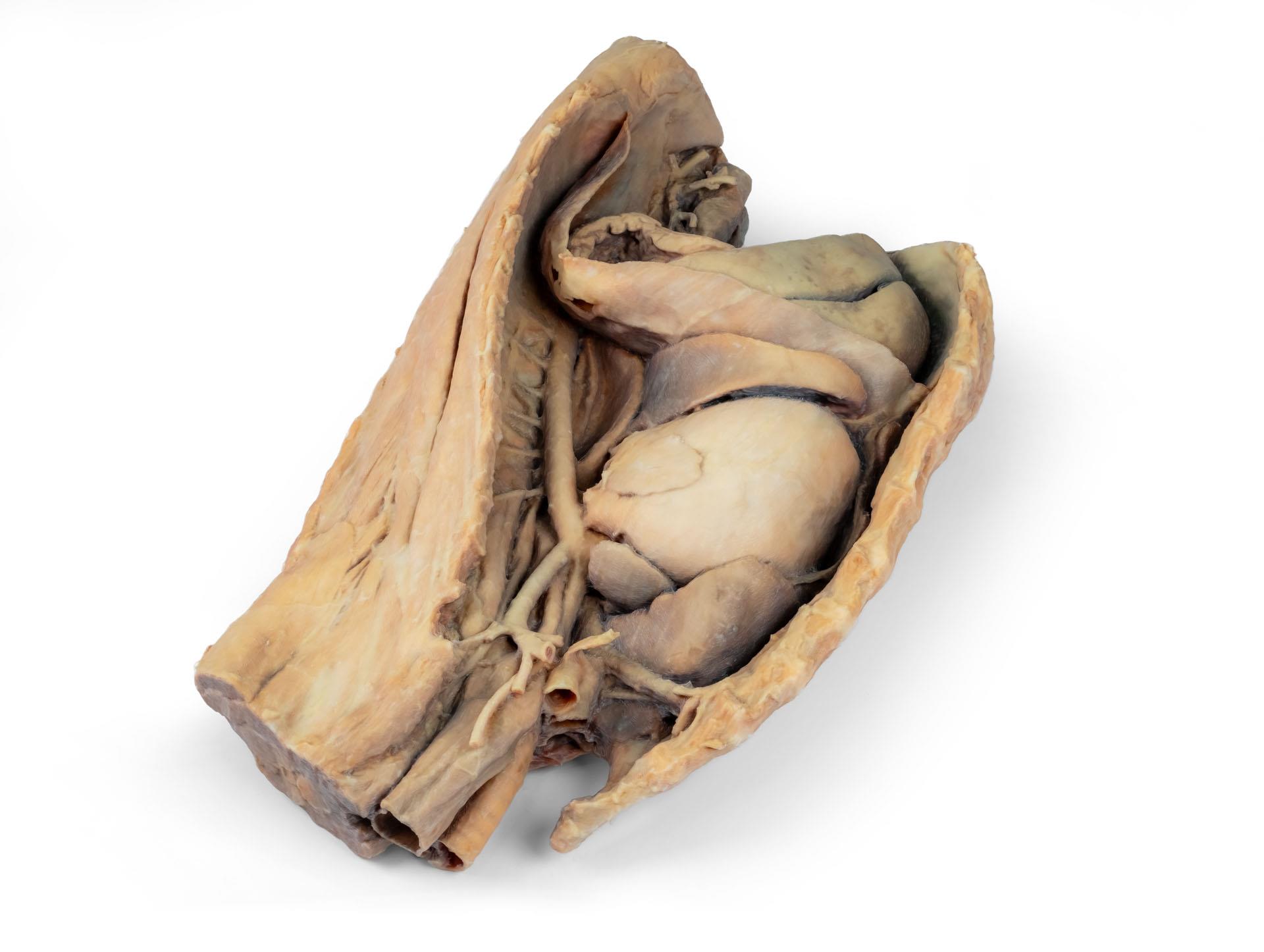
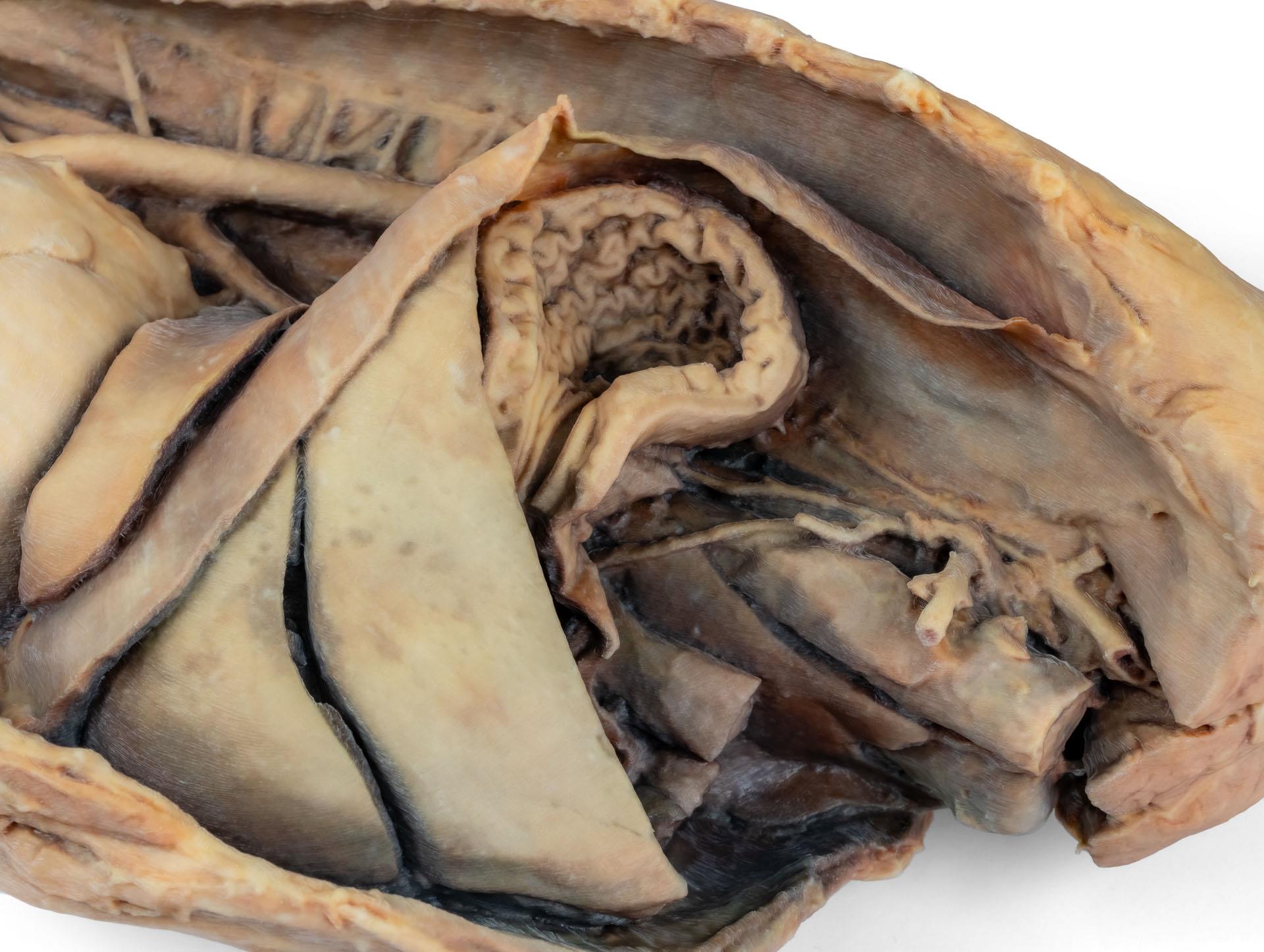
Dieses Präparat zeigt die Topographie des Herzens nach Entfernung des linken Lungenflügels bei der Dissektion der Brusthöhle und des kranialen Abdomens eines Hundes, der von der linken Seite betrachtet wird. Der kraniale und der akzessorische Lappen des rechten Lungenflügels bleiben in situ und dienen als anatomische Referenzpunkte. Im kranialen Mediastinum sind der Truncus brachiocephalicus und die linke Arteria subclavia als Hauptäste des Aortenbogens identifizierbar.
Der thorakale Teil der Speiseröhre verläuft durch das Mediastinum in kraniokaudaler Richtung. Das Zwerchfell ist erhalten geblieben und dient als Orientierungshilfe für retrodiaphragmatische Organe wie Leber und Magen.
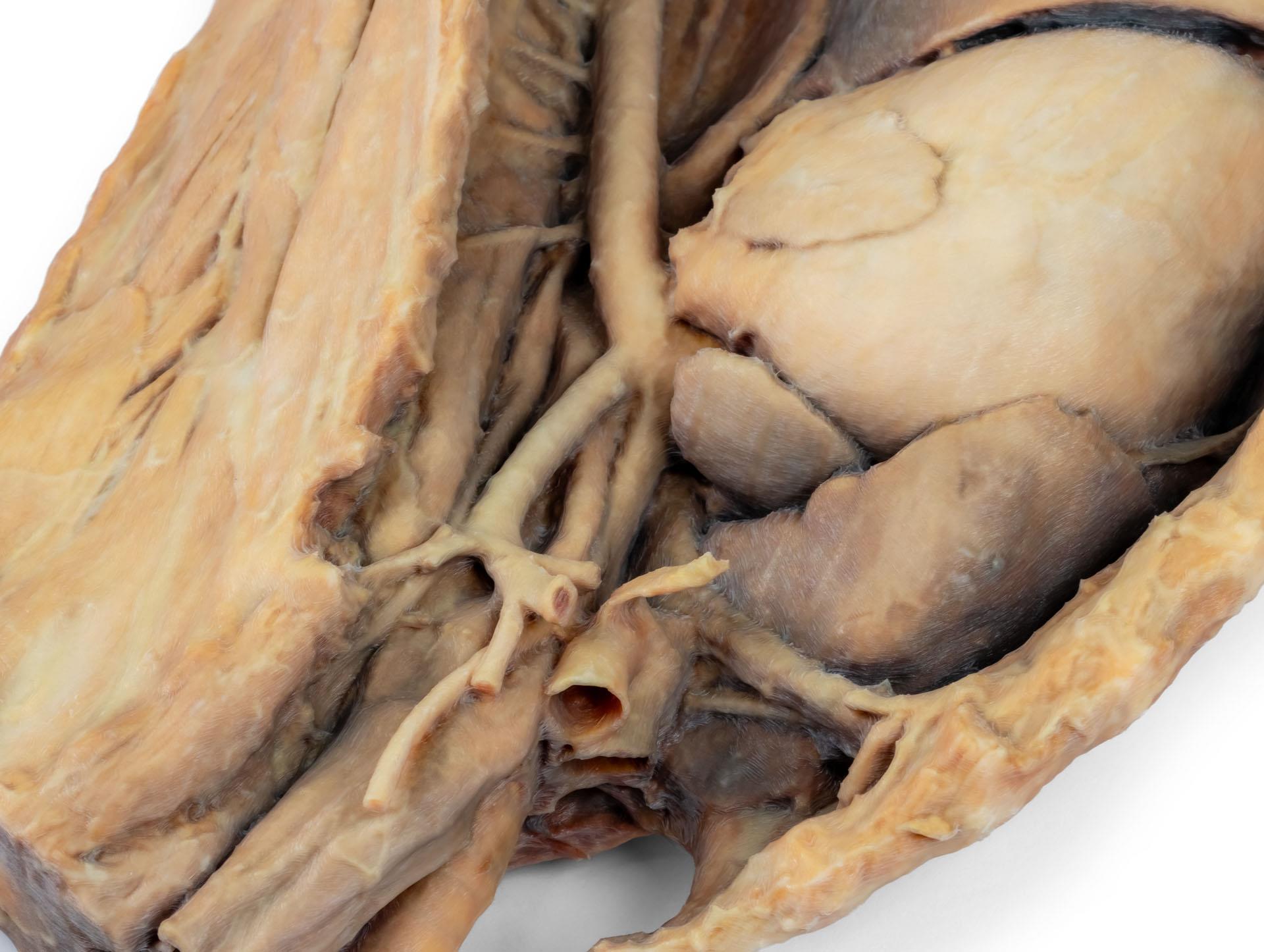
Die Crura diaphragmatica und ihre Beziehung zum Hiatus aorticus bleiben erhalten, ebenso wie die ersten viszeralen Äste der abdominalen Aorta, insbesondere der Truncus celiacus und die kraniale Mesenterialarterie.
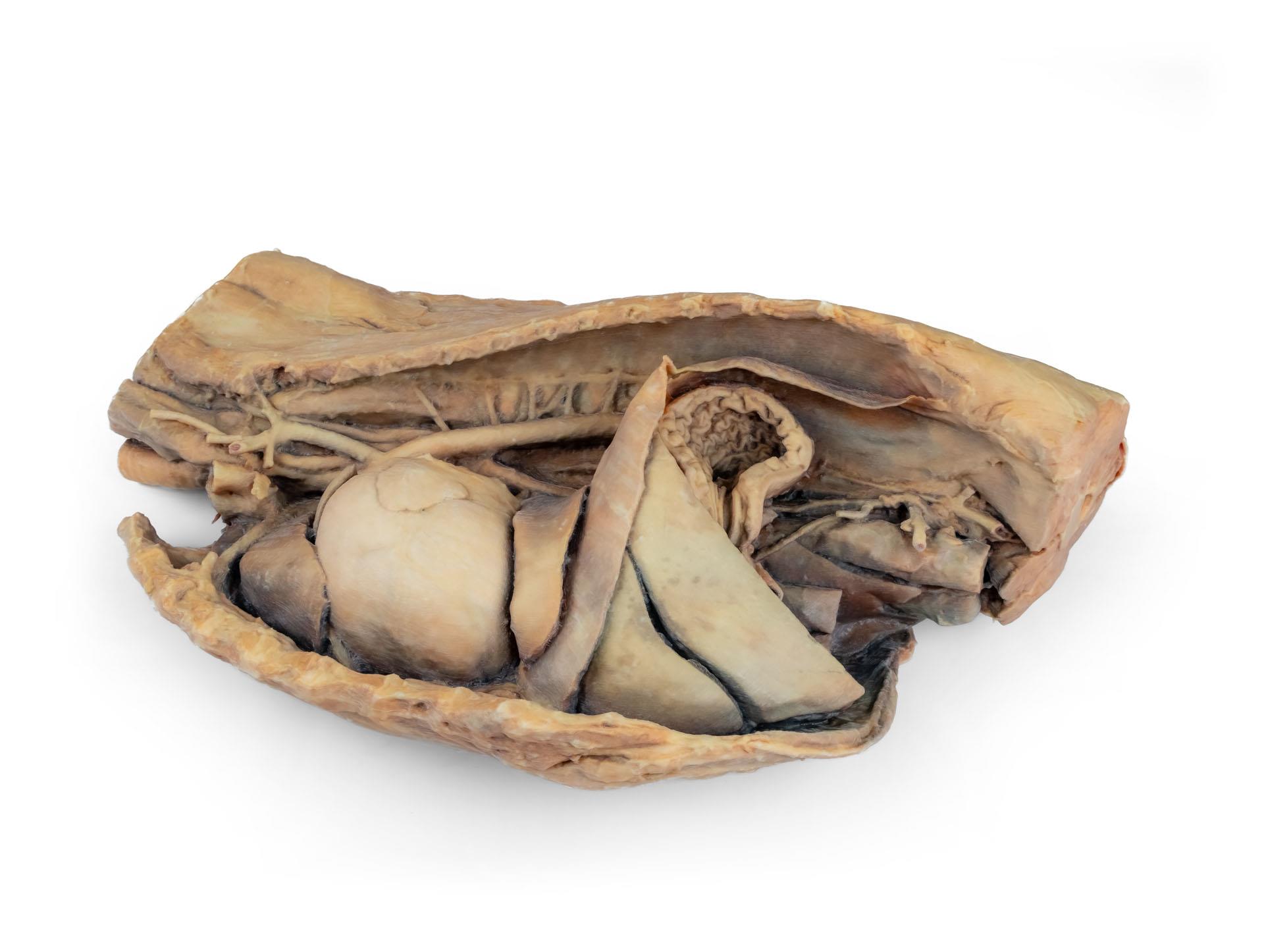
Ein Teil der rechten Vorhofwand wurde entfernt, um die rechte atrioventrikuläre (trikuspidale) Klappe einschließlich der Chordaetendineae und Papillarmuskeln freizulegen.
Darüber hinaus ist das Septomarginaltrabekel (Moderatorenband) innerhalb der rechten Herzkammer sichtbar, ebenso wie der Weg von der Herzkammer zum Truncus pulmonalis.Die linke Vorhofwand ist ebenfalls geöffnet, um ihr Lumen zu zeigen.
Der thorakale Teil der Speiseröhre verläuft durch das Mediastinum in kraniokaudaler Richtung. Das Zwerchfell ist erhalten geblieben und dient als Orientierungshilfe für retrodiaphragmatische Organe wie Leber und Magen.
Die Crura diaphragmatica und ihre Beziehung zum Hiatus aorticus bleiben erhalten, ebenso wie die ersten viszeralen Äste der abdominalen Aorta, insbesondere der Truncus celiacus und die kraniale Mesenterialarterie.
Ein Teil der rechten Vorhofwand wurde entfernt, um die rechte atrioventrikuläre (trikuspidale) Klappe einschließlich der Chordaetendineae und Papillarmuskeln freizulegen.
Darüber hinaus ist das Septomarginaltrabekel (Moderatorenband) innerhalb der rechten Herzkammer sichtbar, ebenso wie der Weg von der Herzkammer zum Truncus pulmonalis.Die linke Vorhofwand ist ebenfalls geöffnet, um ihr Lumen zu zeigen.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.