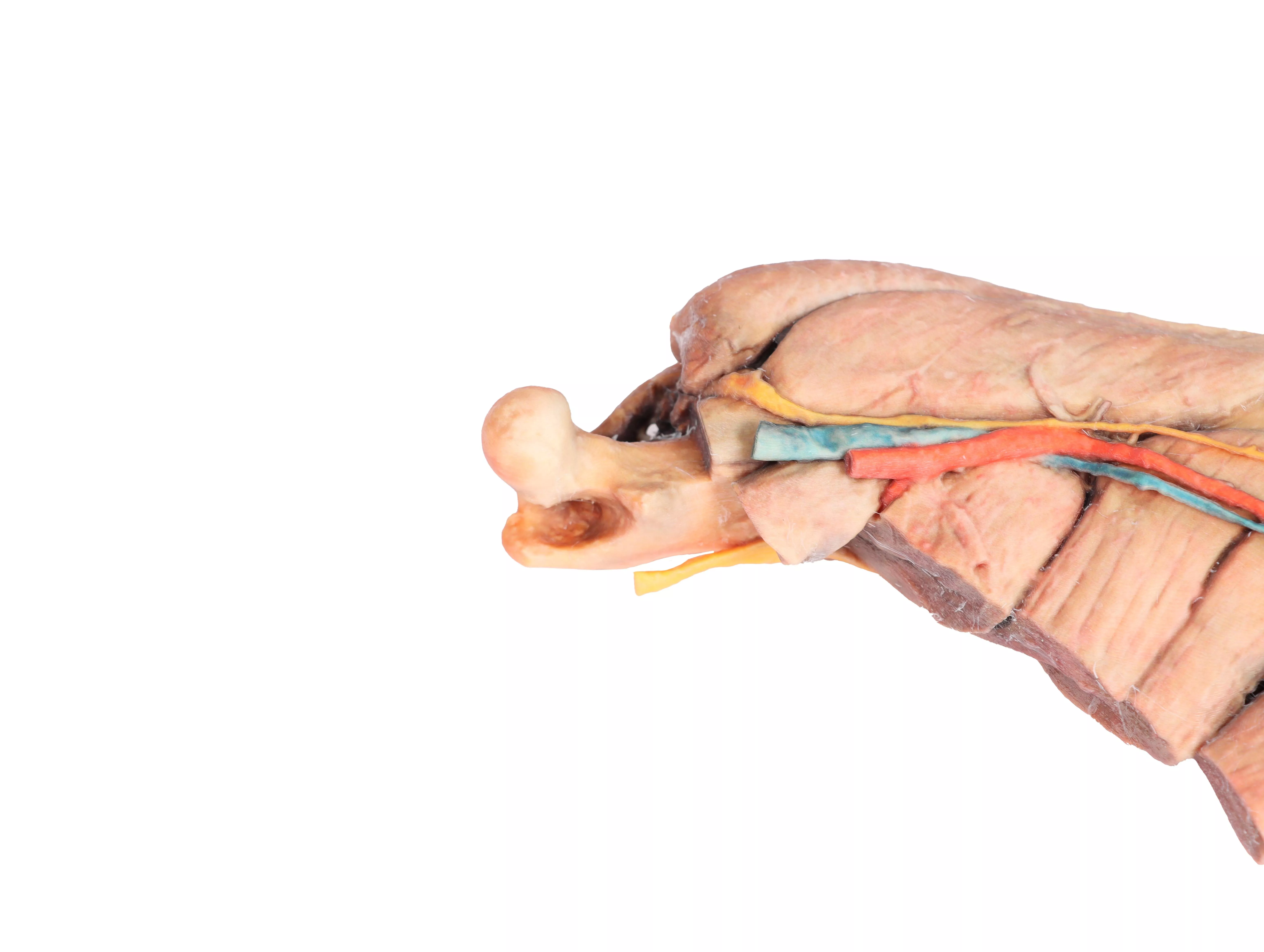
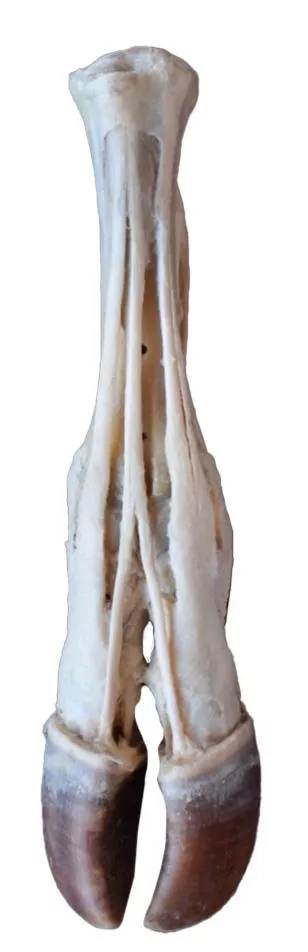
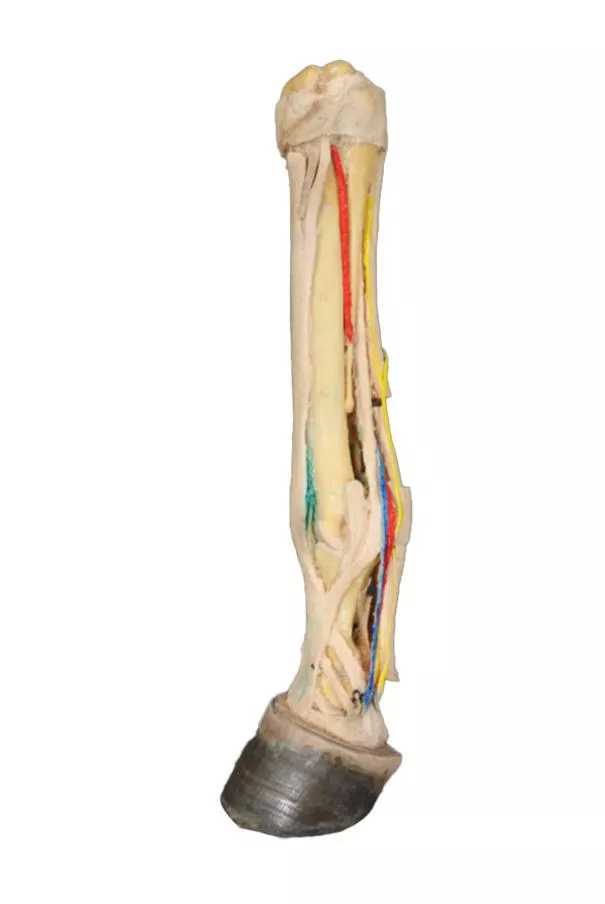
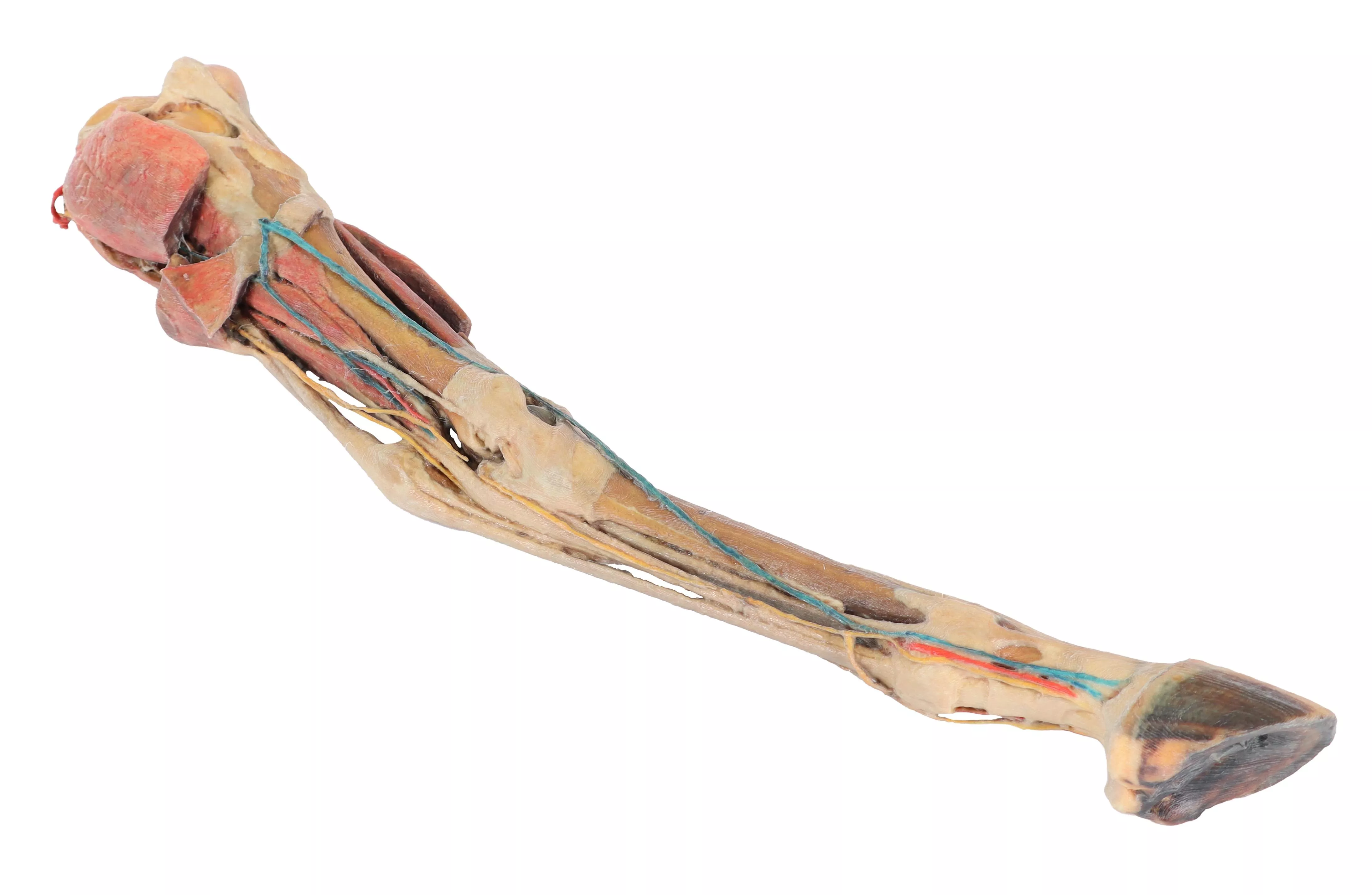
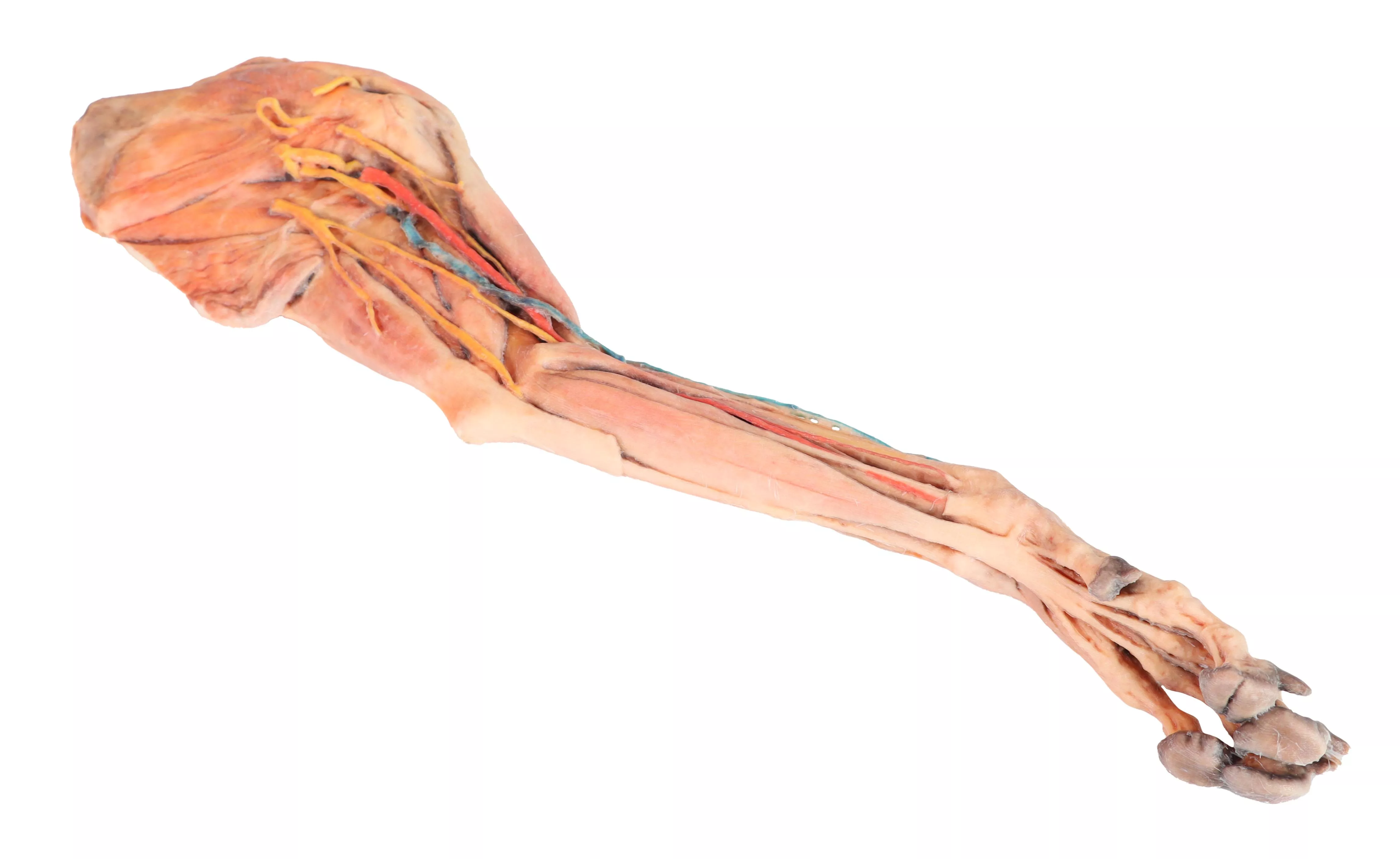
Hinterbein des Hundes – Muskeln, Sehnen, Bänder, Gefäße und Nerven, distal zum Kniegelenk
2.258,62 €*
Artikel in Produktion, lieferbar vorauss. in 2-3 Wochen
Produktnummer:
VP9015
Artikelnummer: VP9015
Produktinformationen "Hinterbein des Hundes – Muskeln, Sehnen, Bänder, Gefäße und Nerven, distal zum Kniegelenk"
This specimen preserves a superficial dissection of the lower hindlimb musculature from the mid-thigh to the foot, as well as nerves and vessels of the femoral canal and popliteal fossa.
The insertions of the muscles of the thigh in the stifle joint and tibial bone are visible. The capsule of the stifle joint has been opened to demonstrate the menisci and the collateral
ligaments. Extensor and flexor muscles of the tarsus and fingers are exposed. The dissection preserves the topography of the lateral saphenous vein on the foot surface and caudal aspect of the leg Dorsal and palmar anatomical structures of the foot are dissected. Detailed anatomical description on request.
The insertions of the muscles of the thigh in the stifle joint and tibial bone are visible. The capsule of the stifle joint has been opened to demonstrate the menisci and the collateral
ligaments. Extensor and flexor muscles of the tarsus and fingers are exposed. The dissection preserves the topography of the lateral saphenous vein on the foot surface and caudal aspect of the leg Dorsal and palmar anatomical structures of the foot are dissected. Detailed anatomical description on request.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.