Product information "Temporal Bone Model, Set of 3"
This 3-part 3D printed model, derived from CT data, highlights the complex anatomy of the temporal bone, including ossicles, canals, chambers, foramina, and air spaces. Internal casts (endocasts) reveal the intricate internal structure, aiding visualization of the auditory and vestibular apparatus.
Part 1: Skull Preparation
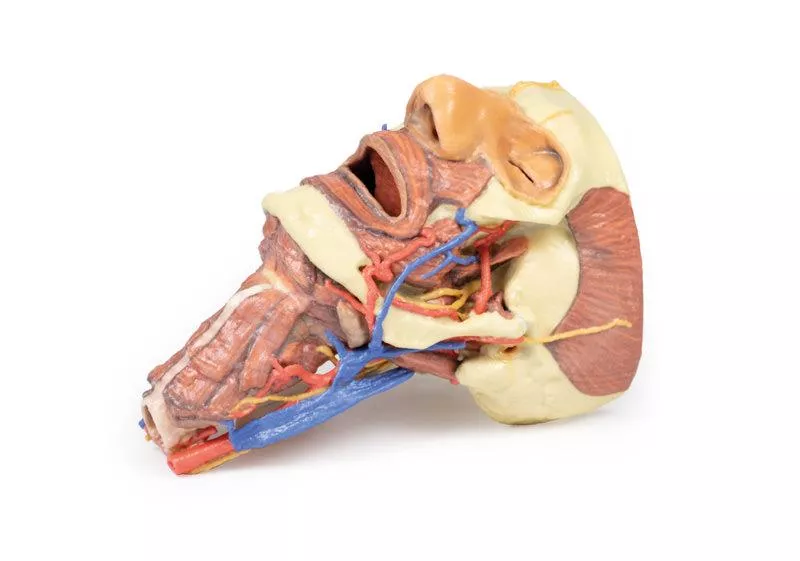
The model exposes the posterior quadrant of the skull, including the posterior and middle cranial fossa. The temporal bone and its relationship with the sphenoid, parietal, and occipital bones are clearly visible.
The middle ear (orange) shows the tympanum, aditus, antrum, and pharyngotympanic tube. The bony labyrinth of the inner ear (green) displays the semicircular canals and cochlea. The facial nerve (CN VII) is shown in yellow, tracing its course to the stylomastoid foramen. Mastoid air cells (blue) and the temporomandibular joint are also demonstrated.
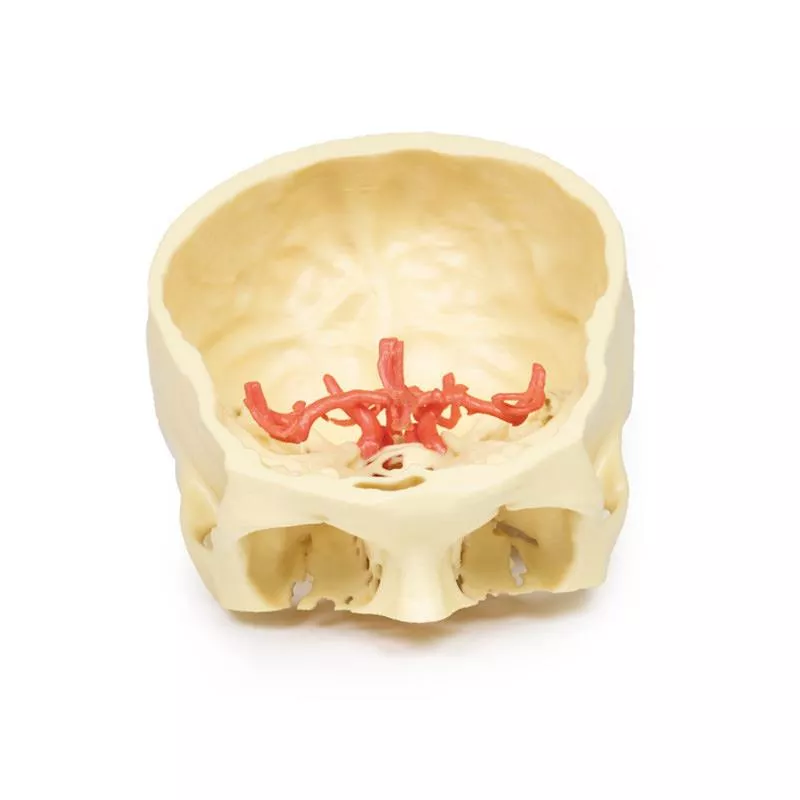
The model highlights key vascular structures, including the internal carotid artery, transverse and sigmoidal dural venous sinuses, and the jugular foramen, along with the foramen magnum and first three cervical vertebrae.
Part 2: Petrous Part of the Temporal Bone
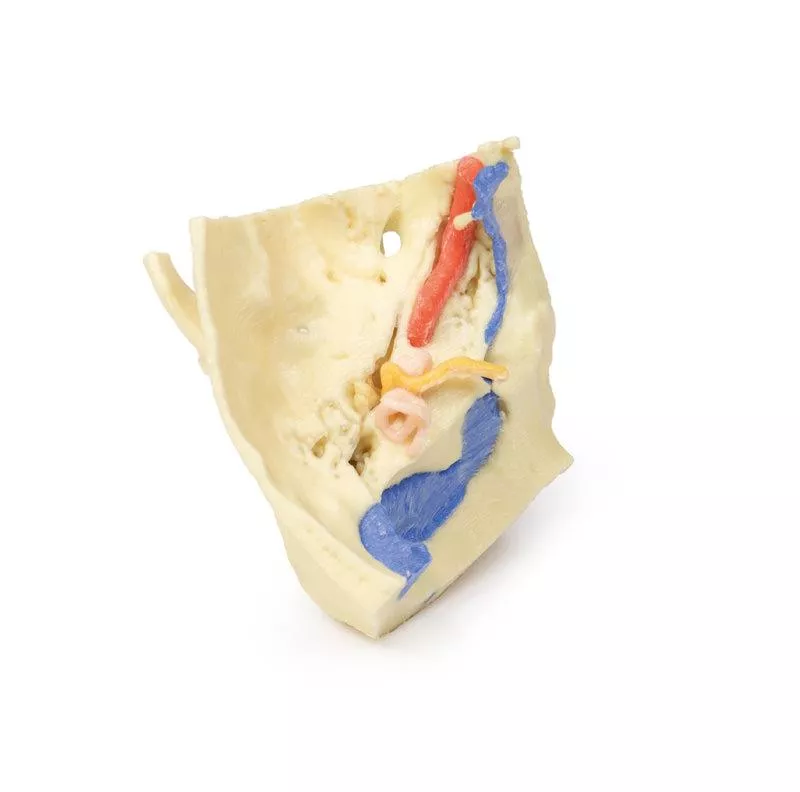
Enlarged x3, this section emphasizes the detailed internal architecture of the petrous temporal bone, including the middle ear ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes), mastoid air cells, and bony canal of the internal carotid artery.
The facial nerve and chorda tympani nerve are traced through the tympanic cavity, illustrating their relationship with the auditory structures. The model highlights connections between the tympanum and mastoid air cells via the aditus and antrum.
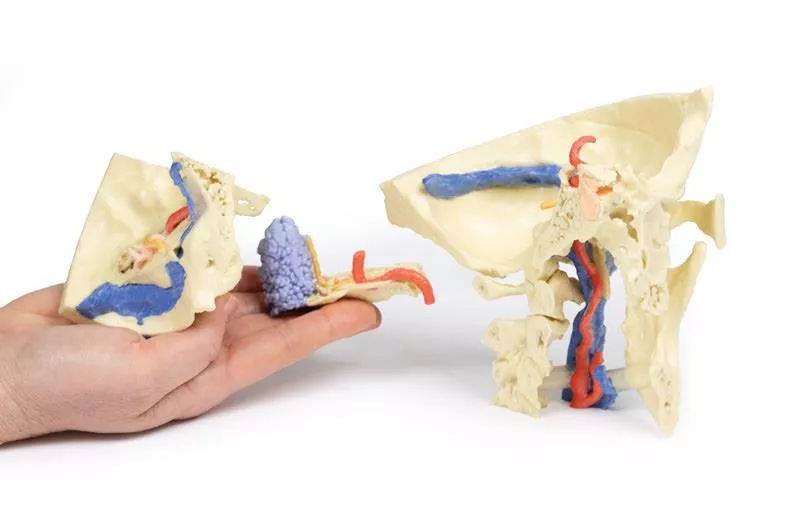
Part 3: Auditory and Vestibular Apparatus
Also enlarged x3, this model section focuses on the auditory and vestibular apparatus and their relation to surrounding otological structures. The bony labyrinth, ossicles, and tympanic connections to the nasopharynx are clearly shown.
The model demonstrates the passage of the facial (CN VII) and vestibulocochlear (CN VIII) nerves through the temporal bone, including the cochlear nerve, geniculate ganglion, and chorda tympani. The spatial relationship between these nerves, the internal carotid artery, and dural venous sinuses is accurately represented.
Part 1: Skull Preparation
The model exposes the posterior quadrant of the skull, including the posterior and middle cranial fossa. The temporal bone and its relationship with the sphenoid, parietal, and occipital bones are clearly visible.
The middle ear (orange) shows the tympanum, aditus, antrum, and pharyngotympanic tube. The bony labyrinth of the inner ear (green) displays the semicircular canals and cochlea. The facial nerve (CN VII) is shown in yellow, tracing its course to the stylomastoid foramen. Mastoid air cells (blue) and the temporomandibular joint are also demonstrated.
The model highlights key vascular structures, including the internal carotid artery, transverse and sigmoidal dural venous sinuses, and the jugular foramen, along with the foramen magnum and first three cervical vertebrae.
Part 2: Petrous Part of the Temporal Bone
Enlarged x3, this section emphasizes the detailed internal architecture of the petrous temporal bone, including the middle ear ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes), mastoid air cells, and bony canal of the internal carotid artery.
The facial nerve and chorda tympani nerve are traced through the tympanic cavity, illustrating their relationship with the auditory structures. The model highlights connections between the tympanum and mastoid air cells via the aditus and antrum.
Part 3: Auditory and Vestibular Apparatus
Also enlarged x3, this model section focuses on the auditory and vestibular apparatus and their relation to surrounding otological structures. The bony labyrinth, ossicles, and tympanic connections to the nasopharynx are clearly shown.
The model demonstrates the passage of the facial (CN VII) and vestibulocochlear (CN VIII) nerves through the temporal bone, including the cochlear nerve, geniculate ganglion, and chorda tympani. The spatial relationship between these nerves, the internal carotid artery, and dural venous sinuses is accurately represented.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.