Dog head - superficial and deep dissections
€4,001.97*
Article in production, available in about 2-3 weeks
Product number:
VP9000
Item number: VP9000
Product information "Dog head - superficial and deep dissections"
Superficial anatomical structures:
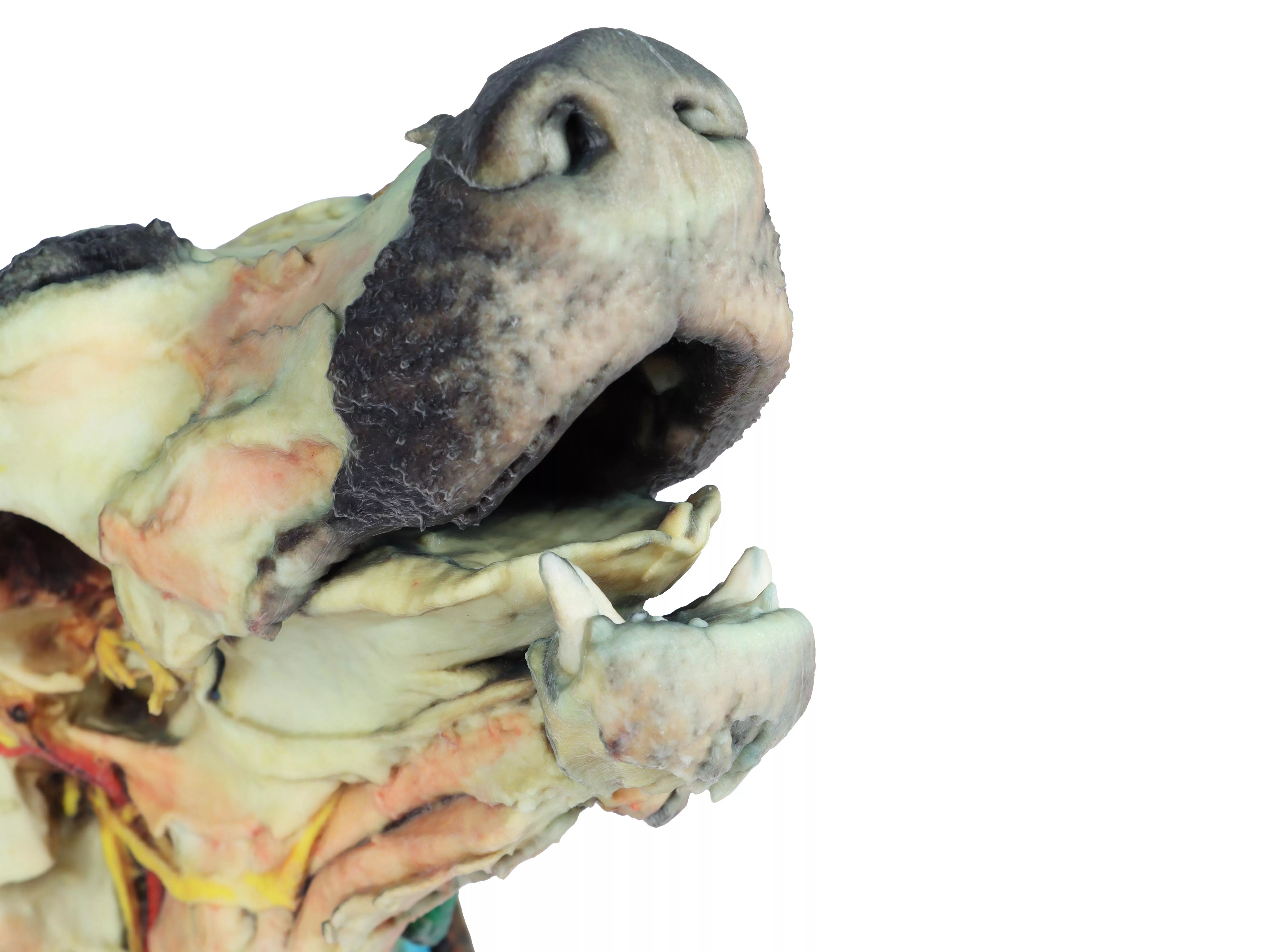
Tip of the nose (Apez nasi)
Right and left wings of the nose (Alae nasi)
Nonglandular skin on the tip of the nose (Planun nasale)
Superficial disscetion on the left side:
On the left side, the skin has been removed to identify the main anatomical structures,
which are described grouped below.
Muscles of the facial neuromuscular system:
• M. nasolabial levator (M. levator nasolabialis)
• M. canine (M. caninus)
• M. buccinator (M. buccinator)
• M. Zygoma9c (M. zygoma:cus)
• M. parodidoauricularis
Muscles of the mandibular neuromuscular system (mas9cators):
• M. masseter (M. masseter)
• M. Temporary (M.temporalis)
Nerves:
• Facial nerve: (N . facialis)
• Dorsal buccal Branch (Rami buccales)
• Ventral buccal Branch (Rami buccales)
• Bucolabial branches (Rami buccolabiales)
• N. Auriculopalpebral (N. Auriculopalpebralis)
Vascular:
• Facial artery (Arteria facialis)
• External jugular vein: (V. Jugularis externa)
o Maxillary vein (V. Maxillaris)
o Linguofacial vein (V. Linguofacialis)
Salivary glands:
• Parotid gland and paro9d duct (Glandula parotis) (Ductus parotideus)
• Mandibular gland Glandula mandibularis
Lymph nodes:
• N. L. mandibular (Lymphonodi mandubulares)
Deep dissection on the right side:
On this right side mandible has been removed to see deeper anatomical structures. You can see the surfaces of the temporal bone for the temporomandibular joint (Articulatio Temporomandibularis). The medial pterygoid muscle (M. pterygoideus medialis) is identified and sectioned in its insertion area to the ramus of the mandible (Ramus mandibulae). Next to this muscle, the branches of the mandibular nerve (N. mandibularis) are identified, as well as the maxillary nerve (nevus maxillaris) and the maxillary artery (arteria maxillaris). Near the external acoustic meatus (Meatus acusticus externus), the facial nerve (N . facialis) has been maintained, with one of its branches,
the auriculopalpebral nerve (N. Auriculopalpebralis), running parallel to the zygomatic arch (Arcus zygomaticus), visible atier removing the parotd salivary gland (Glandula parotis). The tongue is identified in its entire caudal extension, and the styloglossus (M. stylogossus), genioglossus (M. genioglossus) and genihyoid (M. geniohydeus) muscles reach it. Next to these muscles, the hypoglossal nerve (N. hypoglossus) is identified. In relation to the pharynx (Pharynx), the constrictor muscles of the pharynx (Mm. constrictors phyngis caudalis) are identified. In the most caudal area, in relation to the neck, the course of the common caro9d artery (arteria caarotis communis) and the vagosympathetic trunk nerve (Truncus vagosympathicus) are identified.
Tip of the nose (Apez nasi)
Right and left wings of the nose (Alae nasi)
Nonglandular skin on the tip of the nose (Planun nasale)
Superficial disscetion on the left side:
On the left side, the skin has been removed to identify the main anatomical structures,
which are described grouped below.
Muscles of the facial neuromuscular system:
• M. nasolabial levator (M. levator nasolabialis)
• M. canine (M. caninus)
• M. buccinator (M. buccinator)
• M. Zygoma9c (M. zygoma:cus)
• M. parodidoauricularis
Muscles of the mandibular neuromuscular system (mas9cators):
• M. masseter (M. masseter)
• M. Temporary (M.temporalis)
Nerves:
• Facial nerve: (N . facialis)
• Dorsal buccal Branch (Rami buccales)
• Ventral buccal Branch (Rami buccales)
• Bucolabial branches (Rami buccolabiales)
• N. Auriculopalpebral (N. Auriculopalpebralis)
Vascular:
• Facial artery (Arteria facialis)
• External jugular vein: (V. Jugularis externa)
o Maxillary vein (V. Maxillaris)
o Linguofacial vein (V. Linguofacialis)
Salivary glands:
• Parotid gland and paro9d duct (Glandula parotis) (Ductus parotideus)
• Mandibular gland Glandula mandibularis
Lymph nodes:
• N. L. mandibular (Lymphonodi mandubulares)
Deep dissection on the right side:
On this right side mandible has been removed to see deeper anatomical structures. You can see the surfaces of the temporal bone for the temporomandibular joint (Articulatio Temporomandibularis). The medial pterygoid muscle (M. pterygoideus medialis) is identified and sectioned in its insertion area to the ramus of the mandible (Ramus mandibulae). Next to this muscle, the branches of the mandibular nerve (N. mandibularis) are identified, as well as the maxillary nerve (nevus maxillaris) and the maxillary artery (arteria maxillaris). Near the external acoustic meatus (Meatus acusticus externus), the facial nerve (N . facialis) has been maintained, with one of its branches,
the auriculopalpebral nerve (N. Auriculopalpebralis), running parallel to the zygomatic arch (Arcus zygomaticus), visible atier removing the parotd salivary gland (Glandula parotis). The tongue is identified in its entire caudal extension, and the styloglossus (M. stylogossus), genioglossus (M. genioglossus) and genihyoid (M. geniohydeus) muscles reach it. Next to these muscles, the hypoglossal nerve (N. hypoglossus) is identified. In relation to the pharynx (Pharynx), the constrictor muscles of the pharynx (Mm. constrictors phyngis caudalis) are identified. In the most caudal area, in relation to the neck, the course of the common caro9d artery (arteria caarotis communis) and the vagosympathetic trunk nerve (Truncus vagosympathicus) are identified.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.