Product information "Multinodular goitre"
Clinical History
A 53-year-old female presented with an abnormal neck swelling and persistent cough. She also experienced lethargy and weight gain over several years. During investigations, she died months later from unrelated cardiovascular disease.
Pathology
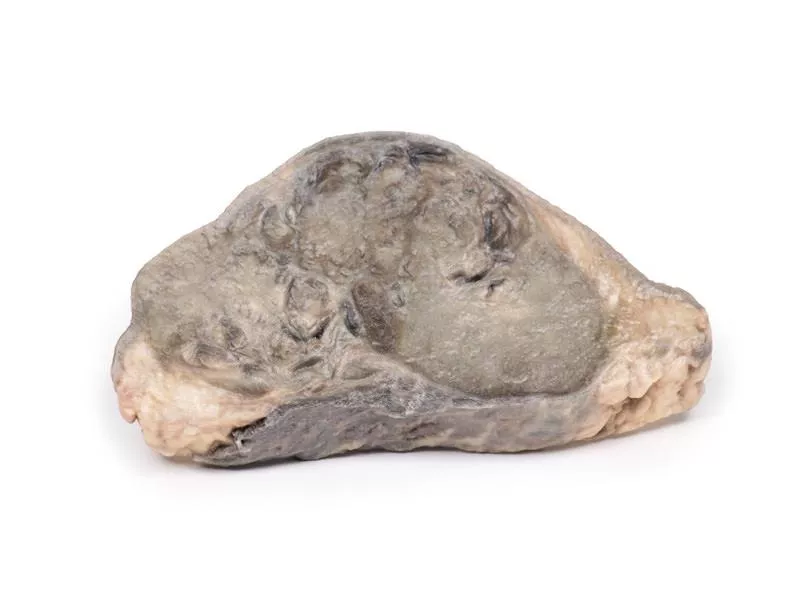
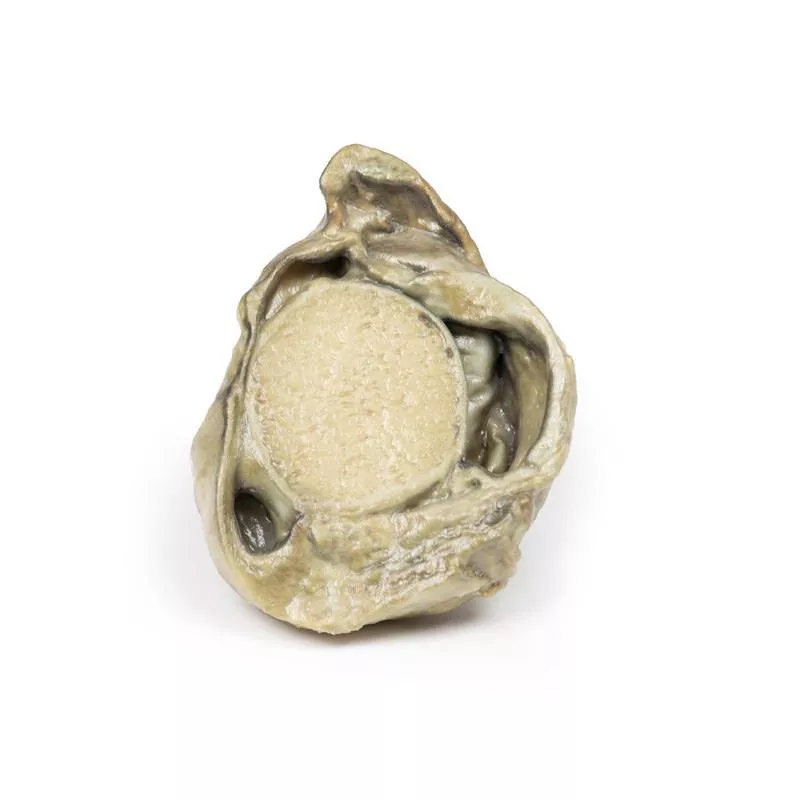
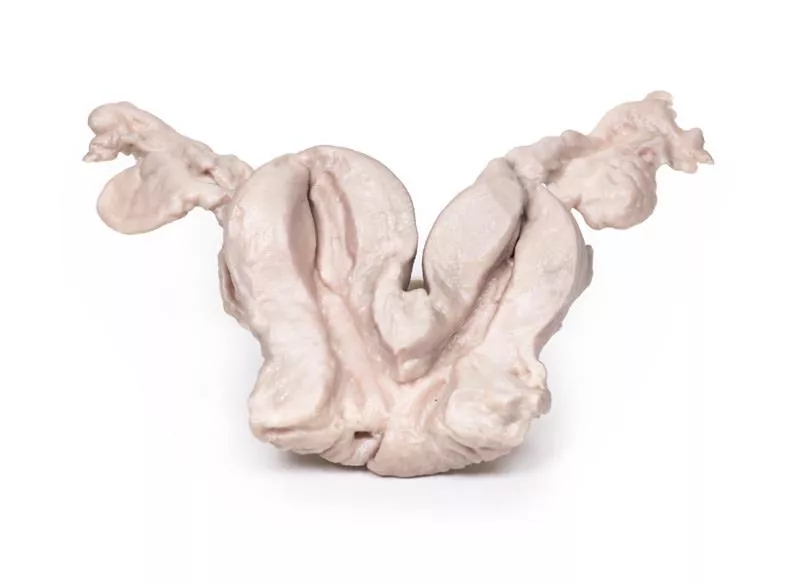
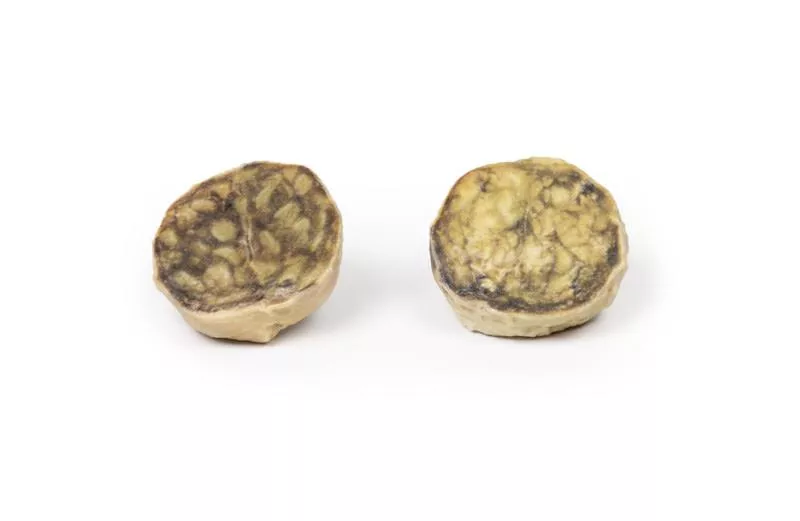
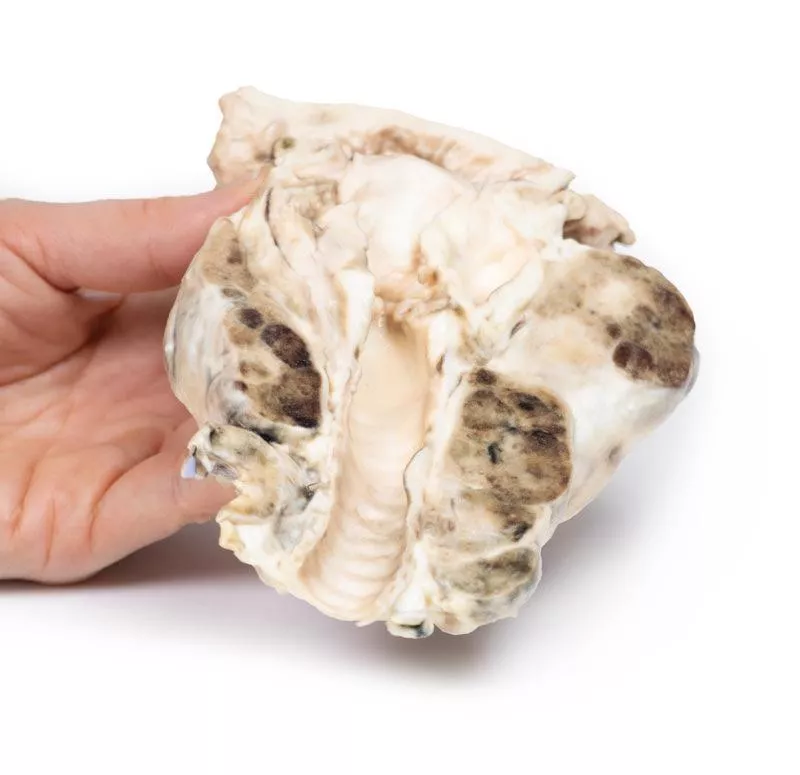
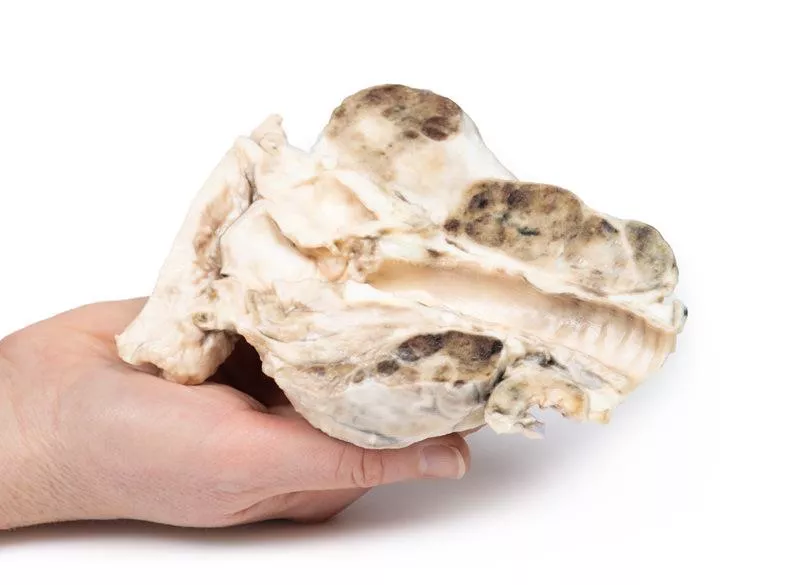
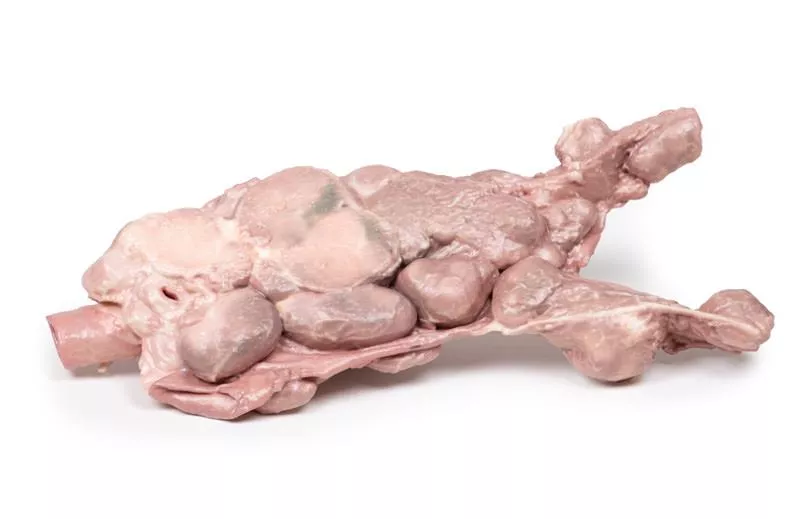
The post-mortem specimen includes the base of the tongue, larynx, and trachea. The thyroid gland is grossly enlarged, especially the right lobe, extending beyond its normal boundaries. The cut surfaces show multiple hyper- and hypopigmented nodules and cystic areas in both lobes. The tongue base, larynx, and trachea appear normal.
Further Information
Nodular goitre is usually detected as a neck swelling. Depending on size and location, it can cause pressure symptoms like difficulty breathing, dysphagia, cough, or hoarseness. Rarely, recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis occurs. Sudden growth or tenderness can result from cystic expansion or hemorrhage within nodules.
Causes include autoimmune diseases (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Grave’s disease), thyroid nodules, and iodine deficiency. Goitre develops when thyroid hormone synthesis is reduced—due to biosynthetic defects or iodine shortage—leading to increased TSH stimulation and thyroid growth. In Hashimoto’s, elevated TSH combined with fibrosis enlarges the thyroid. In Grave’s disease, stimulation by TSH receptor antibodies causes the goitre.
A 53-year-old female presented with an abnormal neck swelling and persistent cough. She also experienced lethargy and weight gain over several years. During investigations, she died months later from unrelated cardiovascular disease.
Pathology
The post-mortem specimen includes the base of the tongue, larynx, and trachea. The thyroid gland is grossly enlarged, especially the right lobe, extending beyond its normal boundaries. The cut surfaces show multiple hyper- and hypopigmented nodules and cystic areas in both lobes. The tongue base, larynx, and trachea appear normal.
Further Information
Nodular goitre is usually detected as a neck swelling. Depending on size and location, it can cause pressure symptoms like difficulty breathing, dysphagia, cough, or hoarseness. Rarely, recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis occurs. Sudden growth or tenderness can result from cystic expansion or hemorrhage within nodules.
Causes include autoimmune diseases (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Grave’s disease), thyroid nodules, and iodine deficiency. Goitre develops when thyroid hormone synthesis is reduced—due to biosynthetic defects or iodine shortage—leading to increased TSH stimulation and thyroid growth. In Hashimoto’s, elevated TSH combined with fibrosis enlarges the thyroid. In Grave’s disease, stimulation by TSH receptor antibodies causes the goitre.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.