Product information "Popliteal Fossa distal thigh and proximal leg"
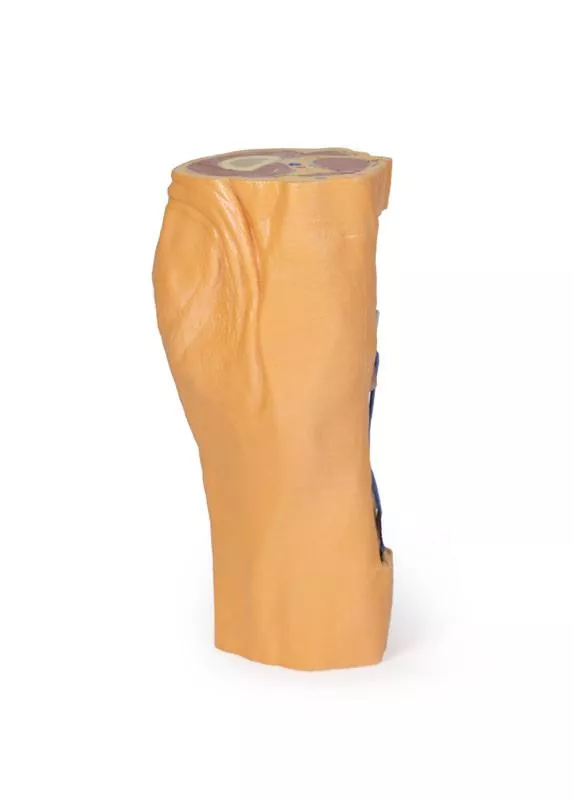
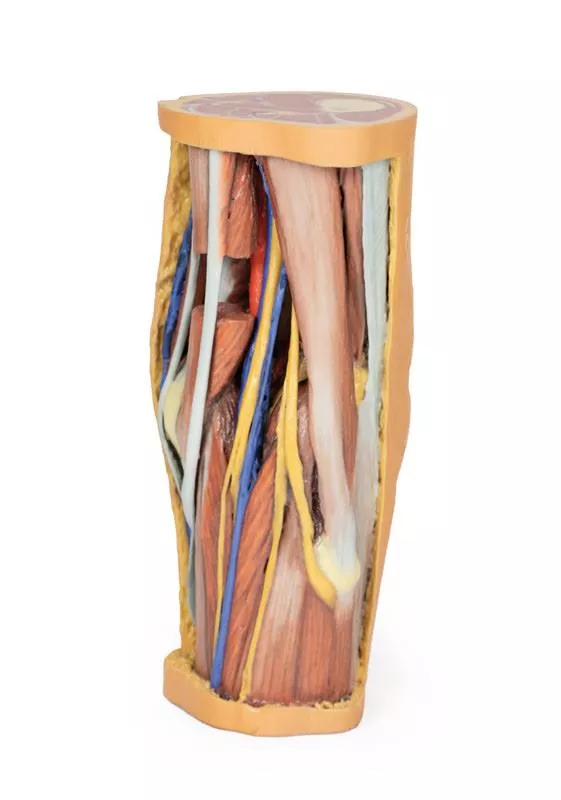
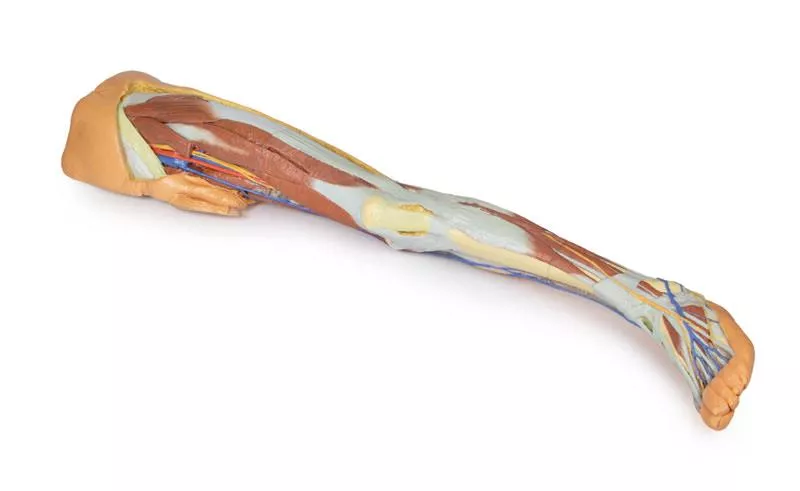
This 3D printed specimen preserves the distal thigh and proximal leg, dissected posteriorly to highlight the popliteal fossa and surrounding structures.
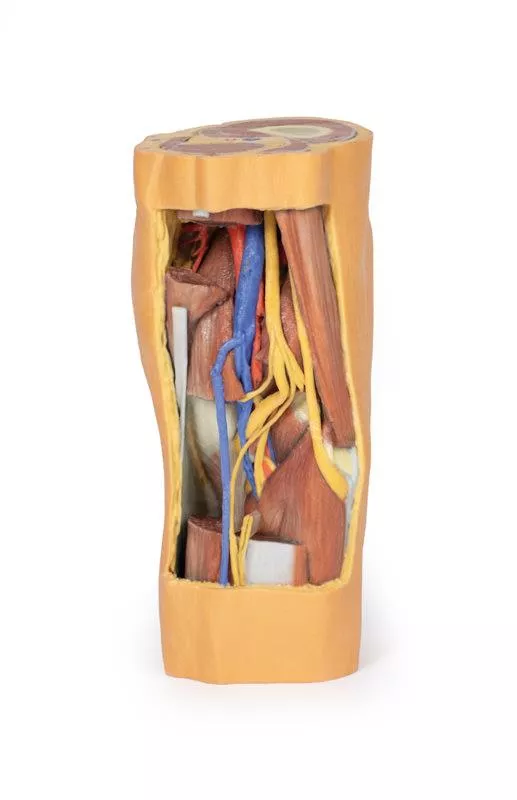
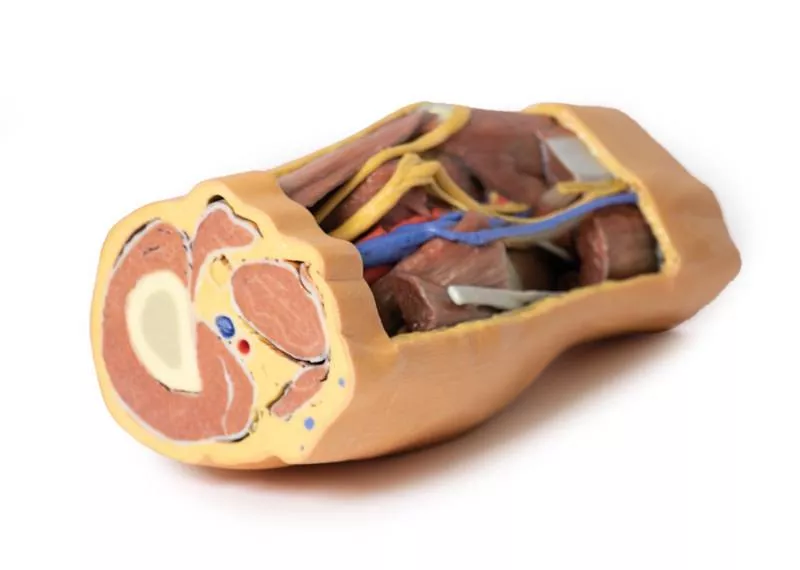
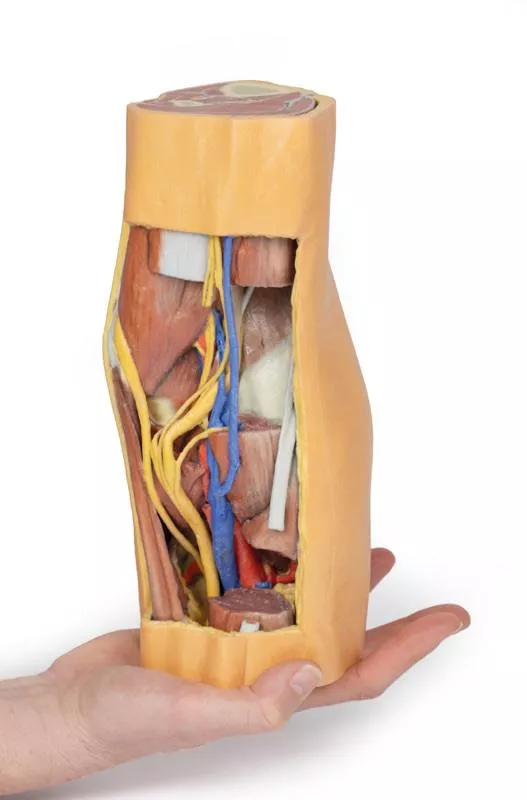
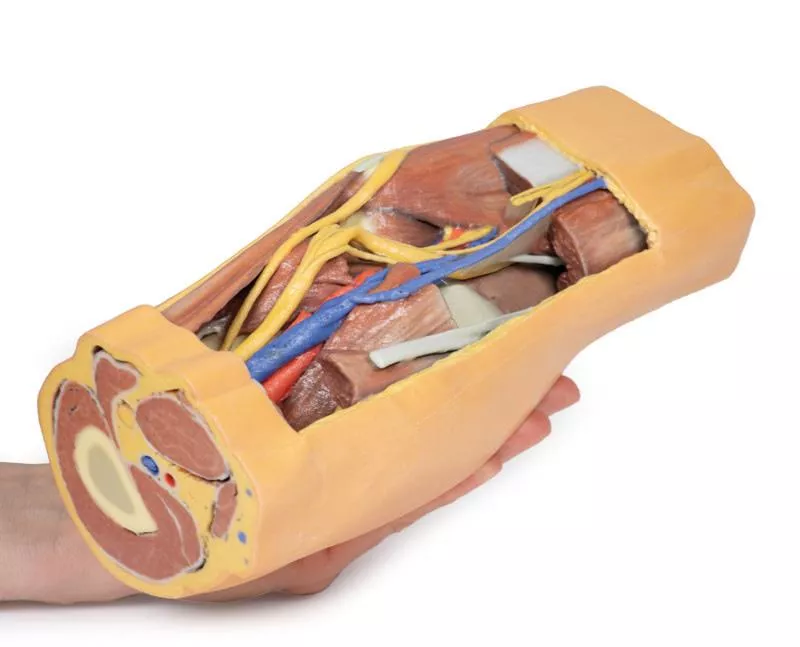
Proximal Cross-Section: Compartments and Vessels
The proximal cross-section displays the anterior, posterior, and medial compartment muscles, with the popliteal artery and vein entering the fossa via the adductor hiatus. The sciatic nerve and great saphenous vein are also visible. Posteriorly, the skin, superficial fascia, fascia lata, and crural fascia have been removed to clearly demonstrate the course of the popliteal vessels, tibial nerve, and common peroneal nerve. Medial sectioning of the semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles reveals the superior medial genicular artery and the medial head of the gastrocnemius, while distal sectioning exposes the popliteus muscle and the tendon of the plantaris.
Popliteal Vessels and Nerves
The popliteal artery and vein can be traced through the fossa to their passage deep to the soleus muscle, accompanied by the tibial nerve. With the lateral head of the gastrocnemius removed, several tibial nerve branches and the medial sural cutaneous nerve are visible. The common peroneal nerve runs parallel, descending laterally over the exposed soleus to the fibular neck, just distal to the biceps femoris. Deep to the biceps femoris, the superior lateral genicular branch passes toward the anterior compartment.
Distal Cross-Section: Leg Neurovascular Structures
The distal cross-section shows the continuation of the popliteal contents and branches. The great and small saphenous veins and sural nerves are visible within the superficial fascia. Between the posterior, lateral, and anterior compartment muscles, the neurovascular bundles of the leg can be observed, including the posterior tibial artery and veins with tibial nerve, the peroneal artery and veins, and the anterior tibial artery, veins, and deep peroneal nerve.
Proximal Cross-Section: Compartments and Vessels
The proximal cross-section displays the anterior, posterior, and medial compartment muscles, with the popliteal artery and vein entering the fossa via the adductor hiatus. The sciatic nerve and great saphenous vein are also visible. Posteriorly, the skin, superficial fascia, fascia lata, and crural fascia have been removed to clearly demonstrate the course of the popliteal vessels, tibial nerve, and common peroneal nerve. Medial sectioning of the semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles reveals the superior medial genicular artery and the medial head of the gastrocnemius, while distal sectioning exposes the popliteus muscle and the tendon of the plantaris.
Popliteal Vessels and Nerves
The popliteal artery and vein can be traced through the fossa to their passage deep to the soleus muscle, accompanied by the tibial nerve. With the lateral head of the gastrocnemius removed, several tibial nerve branches and the medial sural cutaneous nerve are visible. The common peroneal nerve runs parallel, descending laterally over the exposed soleus to the fibular neck, just distal to the biceps femoris. Deep to the biceps femoris, the superior lateral genicular branch passes toward the anterior compartment.
Distal Cross-Section: Leg Neurovascular Structures
The distal cross-section shows the continuation of the popliteal contents and branches. The great and small saphenous veins and sural nerves are visible within the superficial fascia. Between the posterior, lateral, and anterior compartment muscles, the neurovascular bundles of the leg can be observed, including the posterior tibial artery and veins with tibial nerve, the peroneal artery and veins, and the anterior tibial artery, veins, and deep peroneal nerve.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.