Product information "Cerebral Arterio-Venous Malformation"
Clinical History
This 58-year-old patient died due to post-operative complications following transurethral resection of the prostate. He had experienced two episodes of transient neurological deficits at the ages of 28 and 35. At 50, he developed a permanent hemiparesis affecting the left leg, primarily the ankle.
Pathology
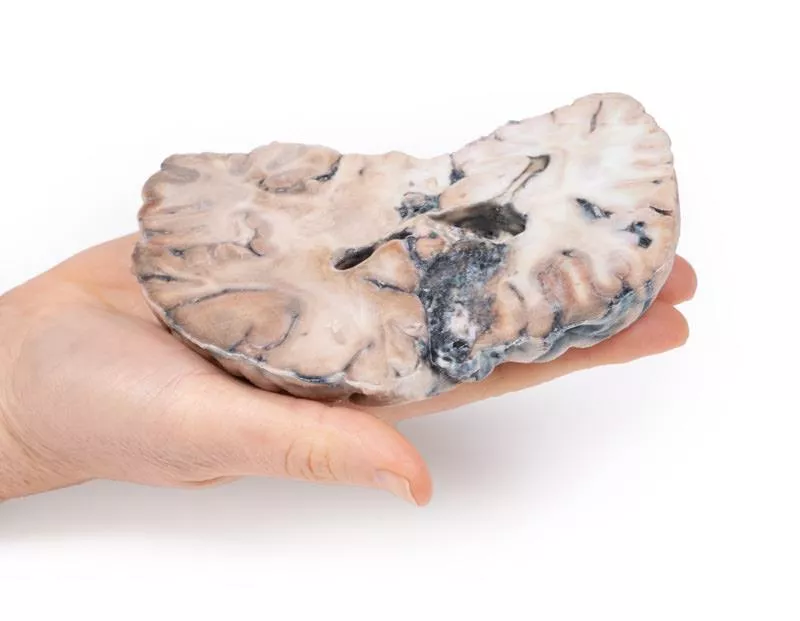
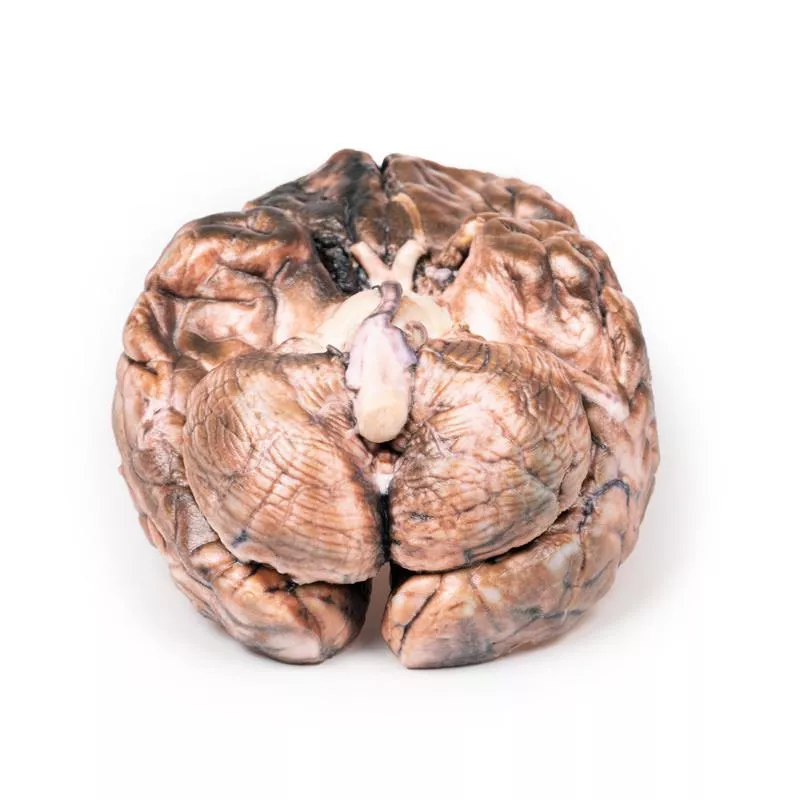
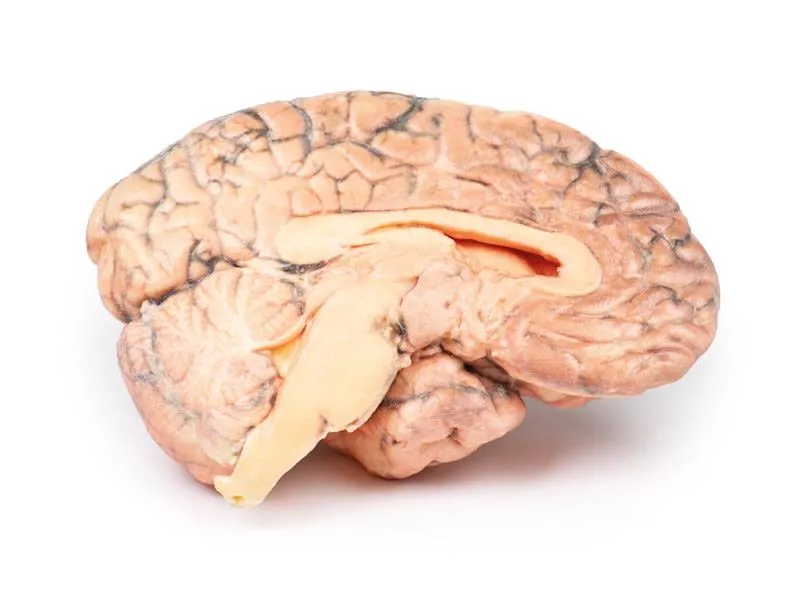
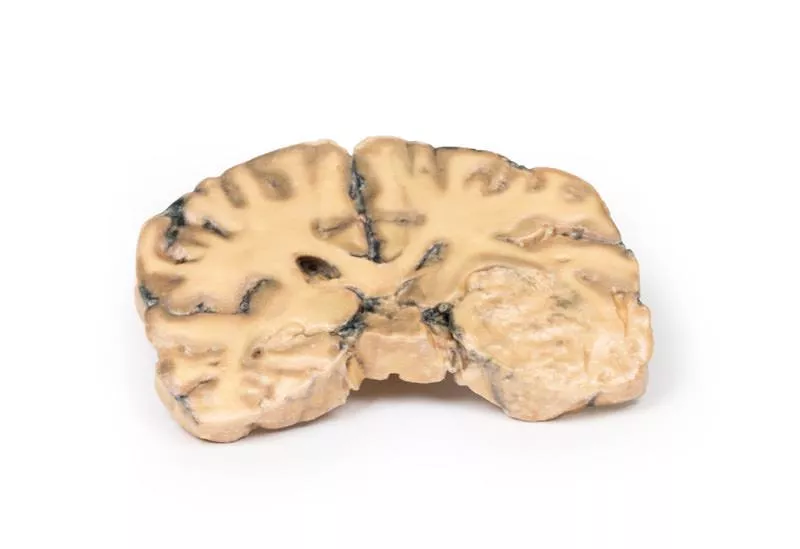
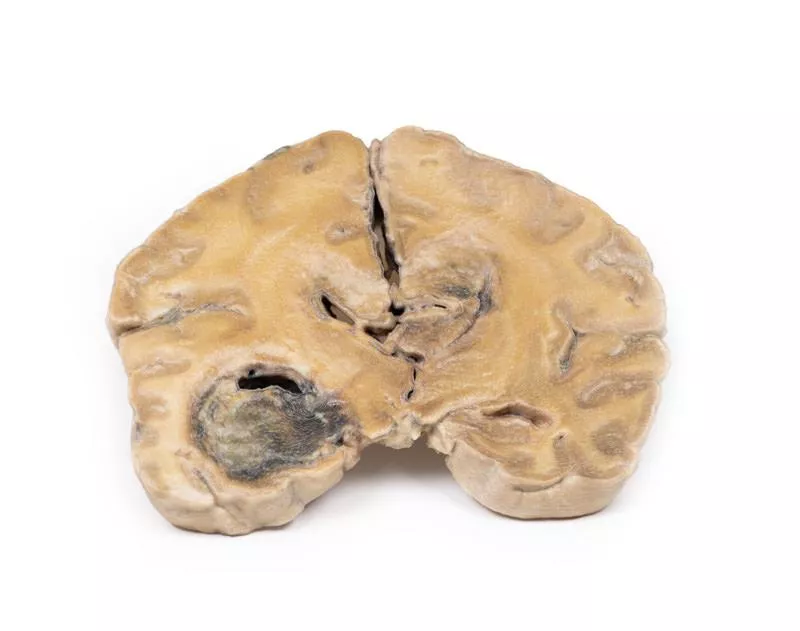
This coronal brain slice through the parietal lobes reveals a 4 cm lesion in the medial right hemisphere, extending from the cortical surface to the lateral ventricle. The abnormal area consists of tortuous vascular channels and interspersed tissue. Histology confirmed an arteriovenous malformation (AVM) with glial tissue surrounding vessels of both arterial and venous character.
Further Information
Cerebral AVMs can cause a range of symptoms such as headaches, seizures, and cranial nerve deficits, though some patients remain asymptomatic. In serious cases, vessel rupture may lead to intracranial haemorrhage, resulting in loss of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, and vision problems. Neurological deficits like hemiparesis or aphasia may occur depending on the bleed location. Ruptured AVMs carry significant risks of both mortality and long-term disability.
This 58-year-old patient died due to post-operative complications following transurethral resection of the prostate. He had experienced two episodes of transient neurological deficits at the ages of 28 and 35. At 50, he developed a permanent hemiparesis affecting the left leg, primarily the ankle.
Pathology
This coronal brain slice through the parietal lobes reveals a 4 cm lesion in the medial right hemisphere, extending from the cortical surface to the lateral ventricle. The abnormal area consists of tortuous vascular channels and interspersed tissue. Histology confirmed an arteriovenous malformation (AVM) with glial tissue surrounding vessels of both arterial and venous character.
Further Information
Cerebral AVMs can cause a range of symptoms such as headaches, seizures, and cranial nerve deficits, though some patients remain asymptomatic. In serious cases, vessel rupture may lead to intracranial haemorrhage, resulting in loss of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, and vision problems. Neurological deficits like hemiparesis or aphasia may occur depending on the bleed location. Ruptured AVMs carry significant risks of both mortality and long-term disability.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.