Canine heart with dissection
€565.25*
Article in production, available in about 2-3 weeks
Product number:
VP9030
Item number: VP9030
Product information "Canine heart with dissection"
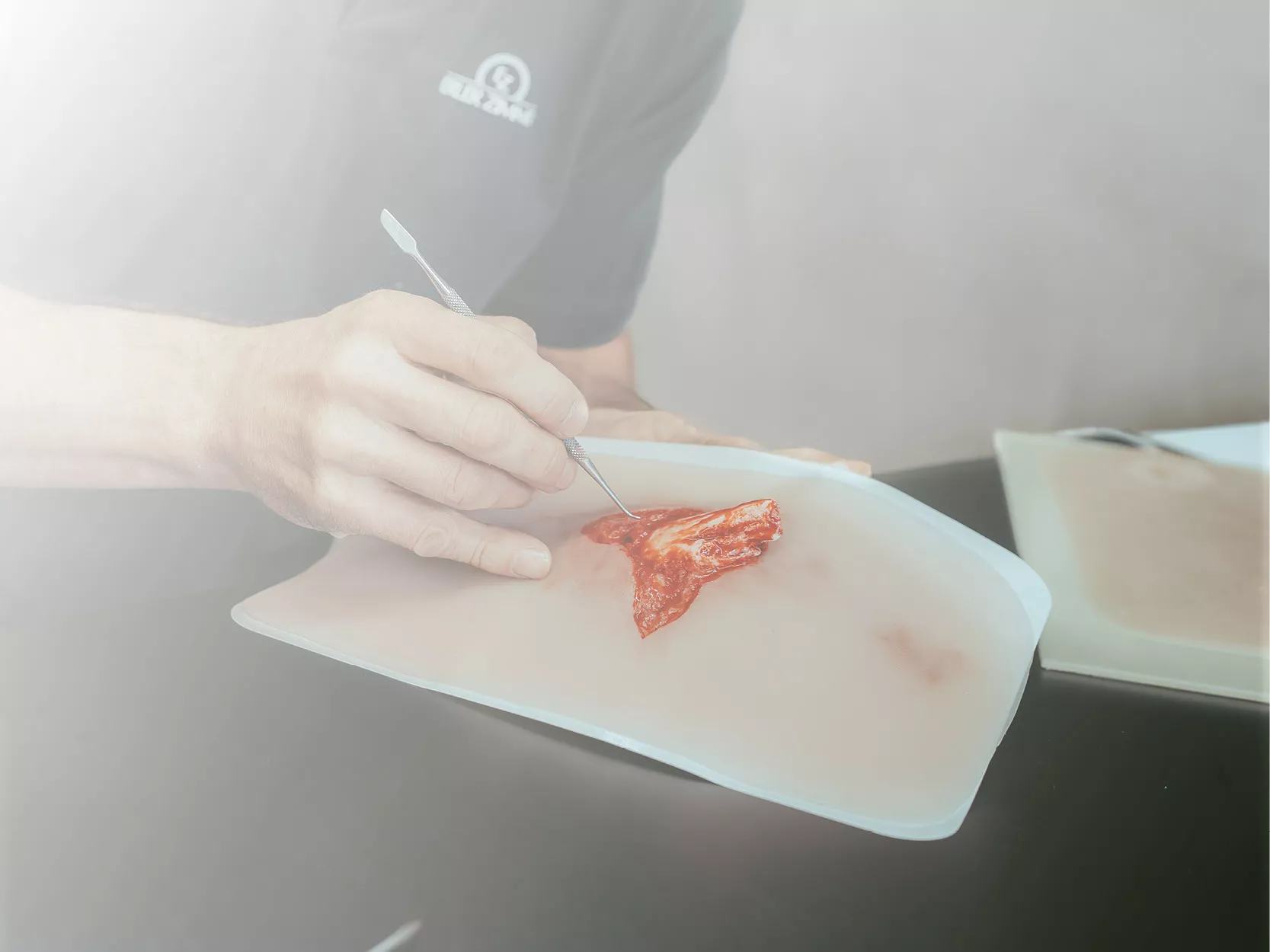
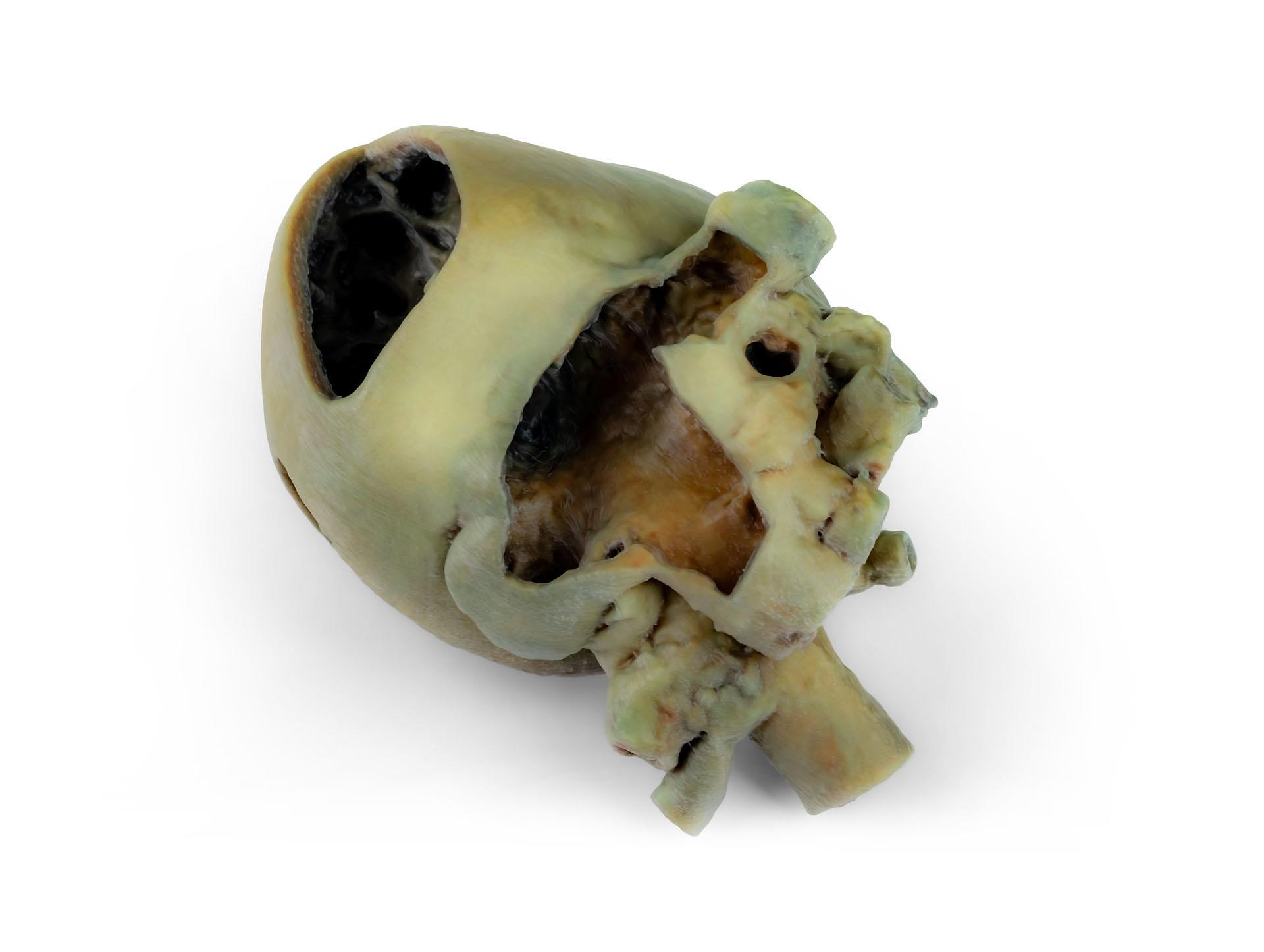
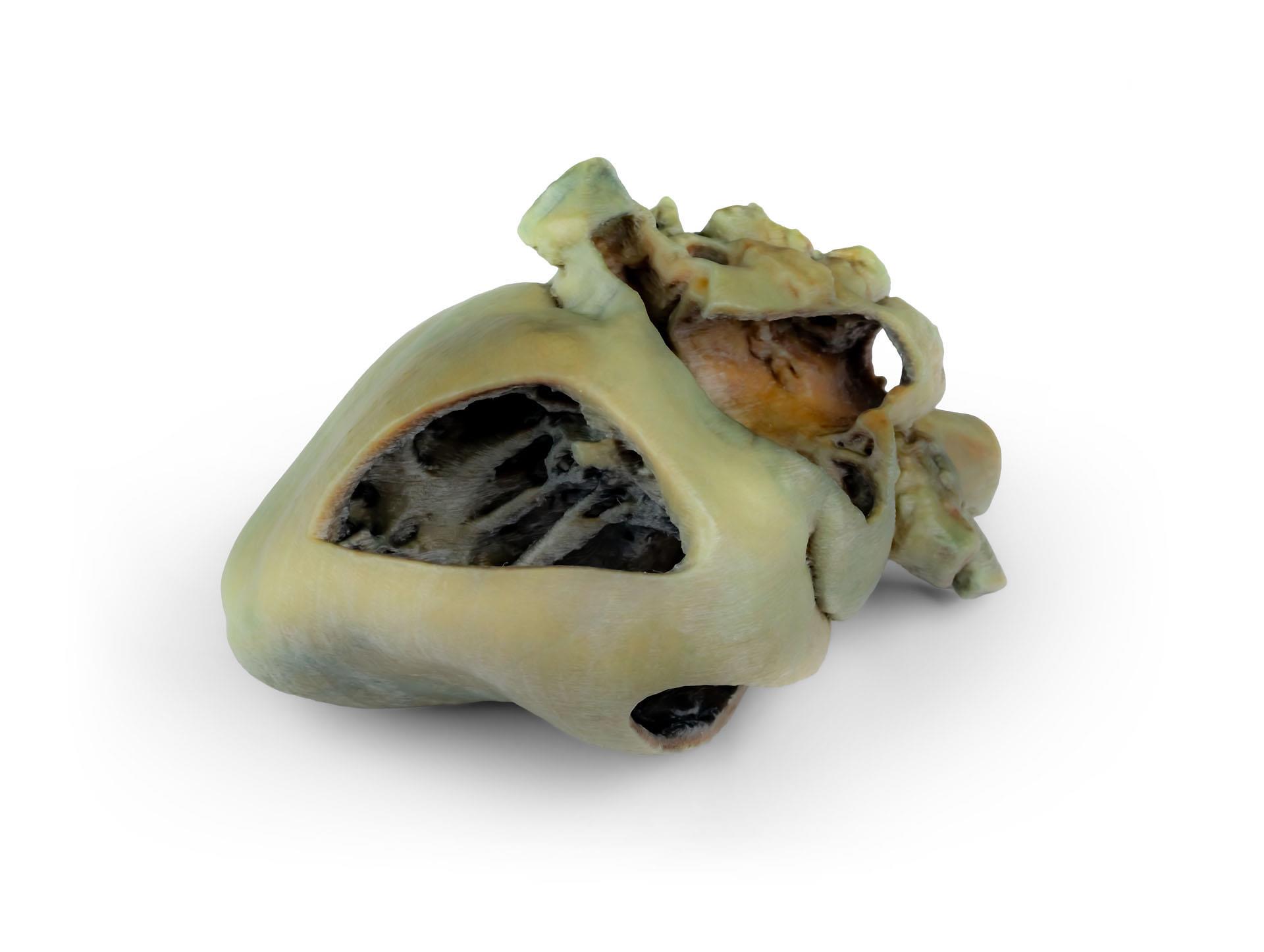
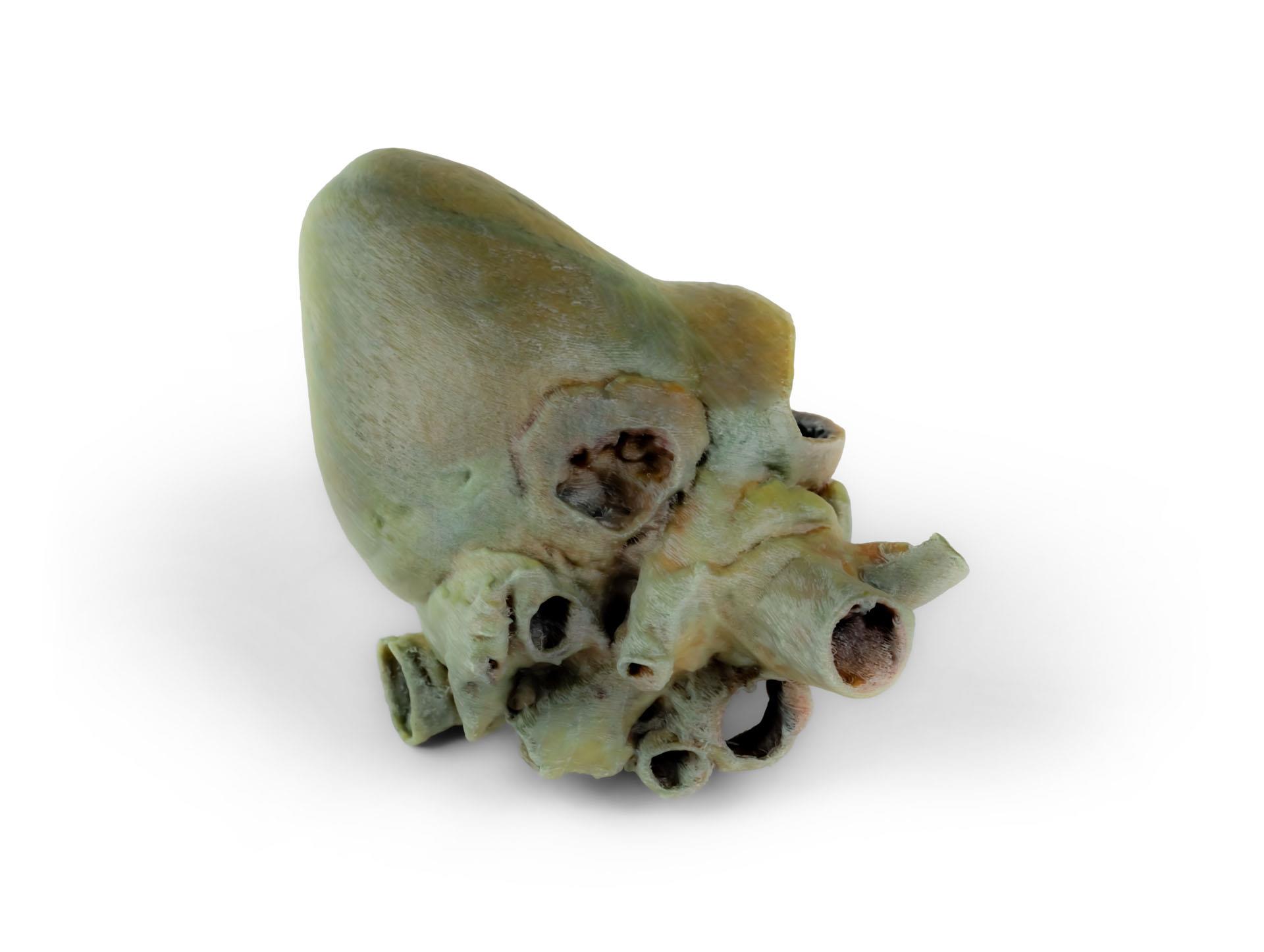
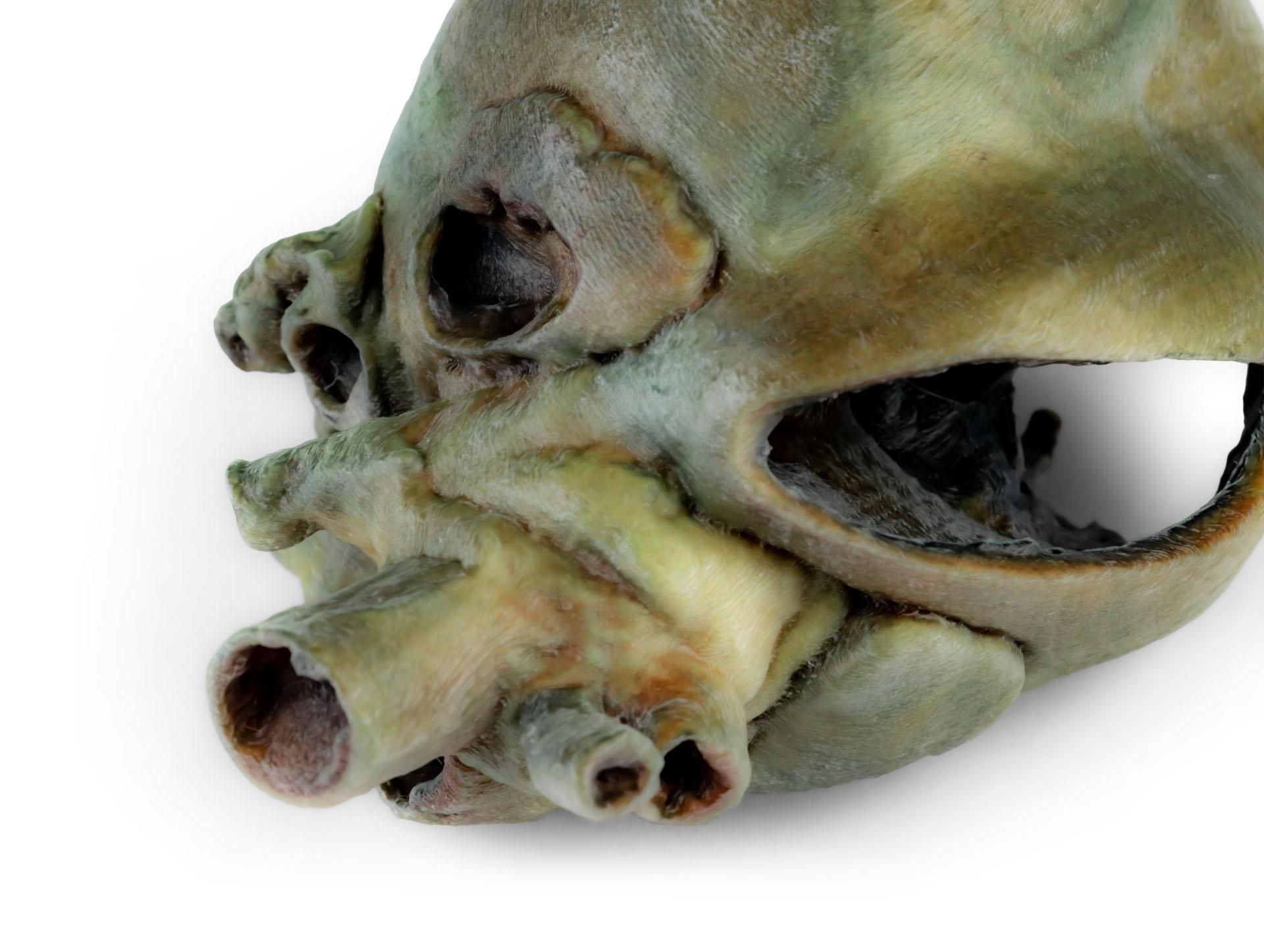
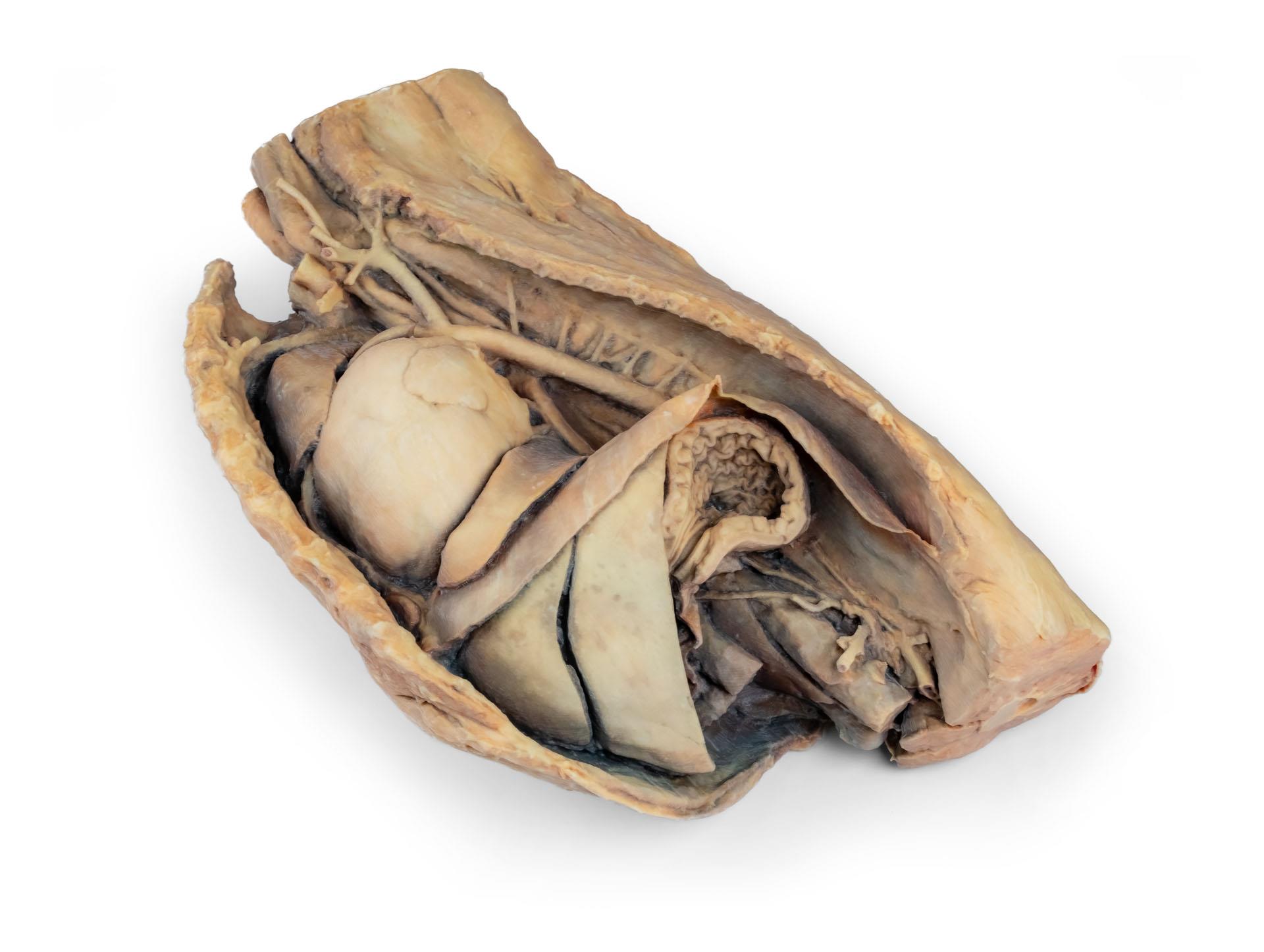
Dissected Dog Heart showing the Cardiac Cavities.
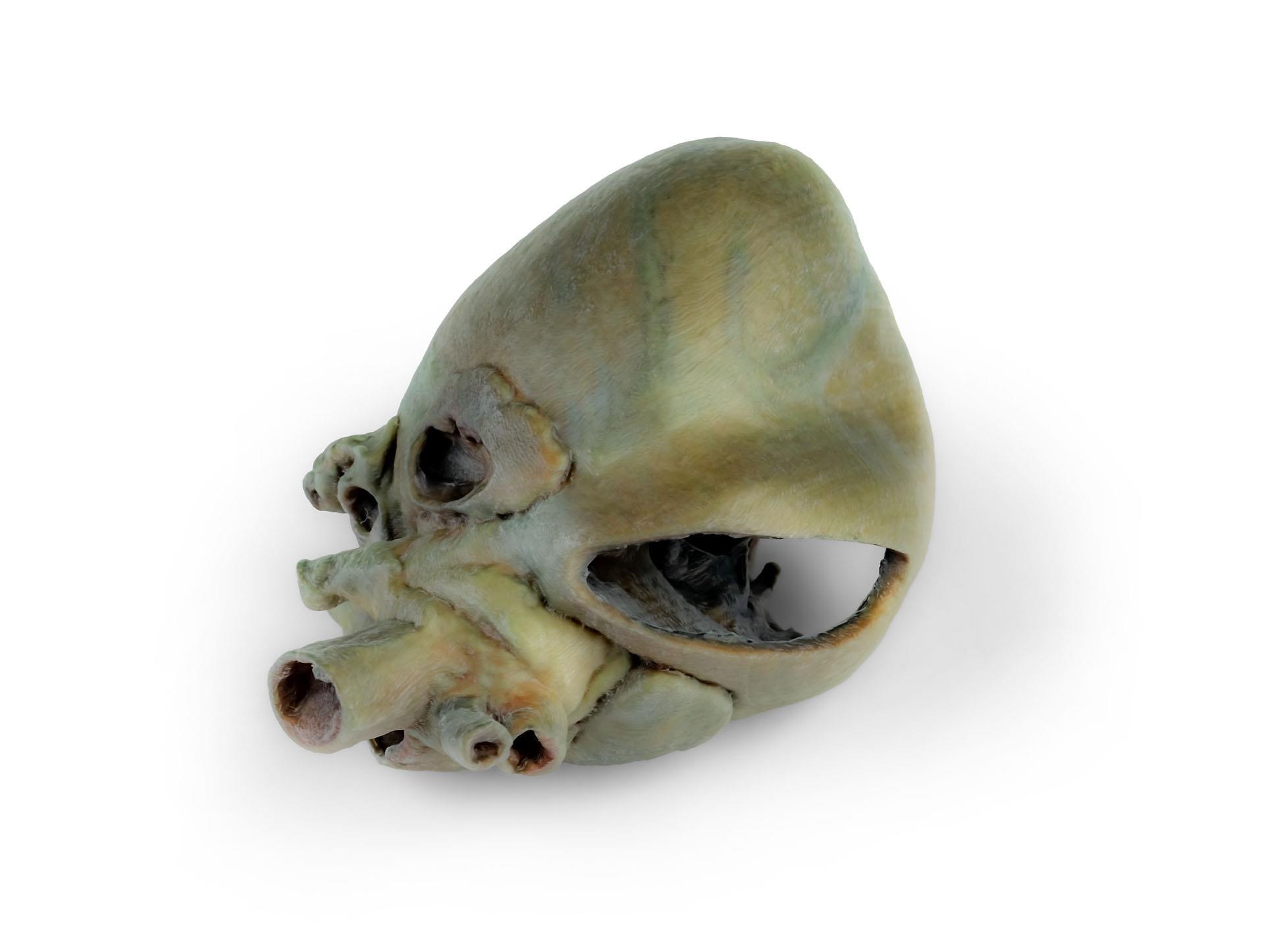
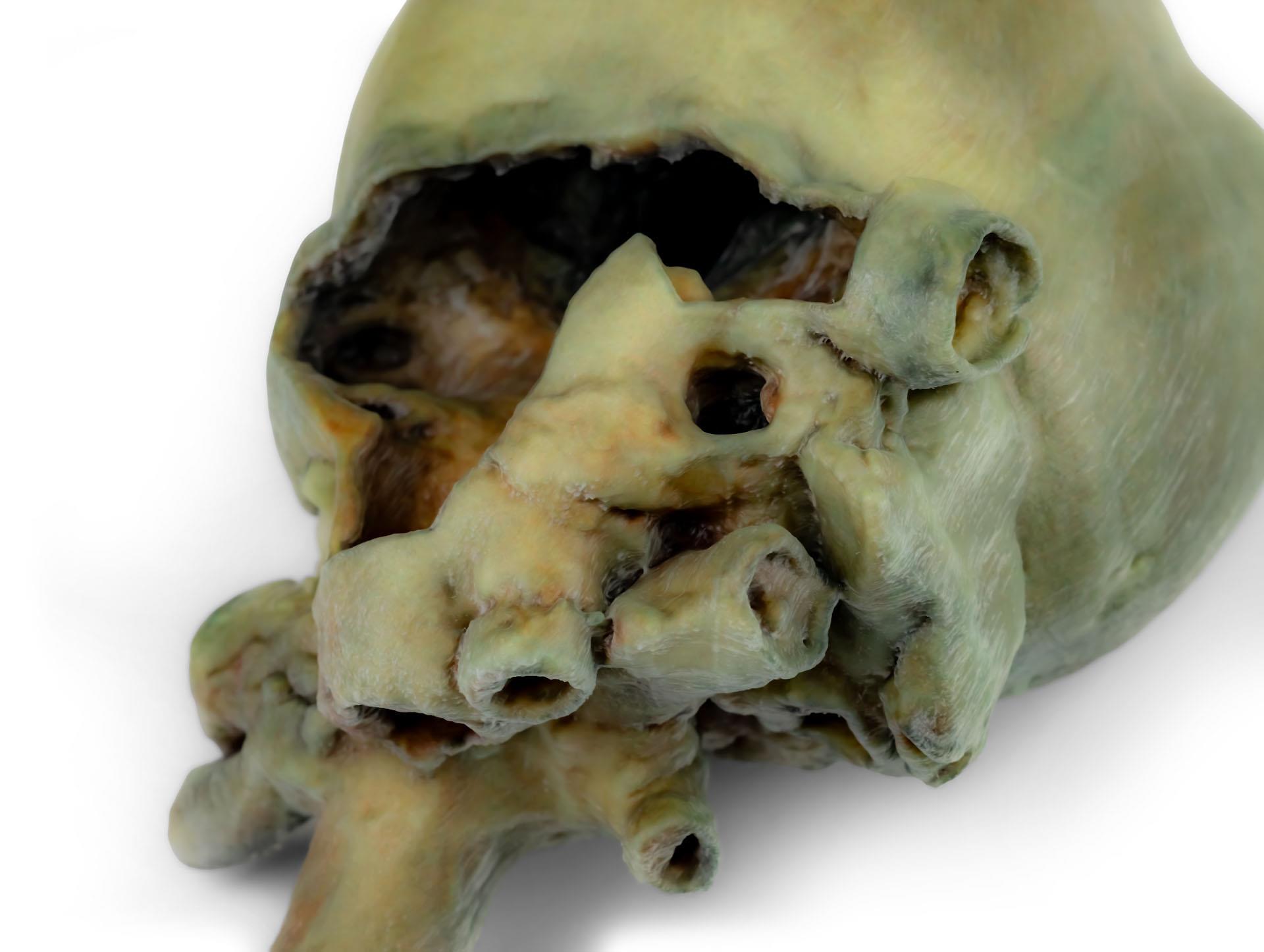
This specimen displays the anatomical features of the external surface of the heart, including both the atrial and auricular faces. At the base of the heart, the ascending aorta and its relationship with the pulmonary trunk are clearly visible, along with the sites of entry of the cranial and caudal venae cavae into the right atrium. The bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk into the pulmonary arteries can be observed, as well as the termination of the pulmonary veins into the left atrium. Both the interventricular and coronary grooves are visible.
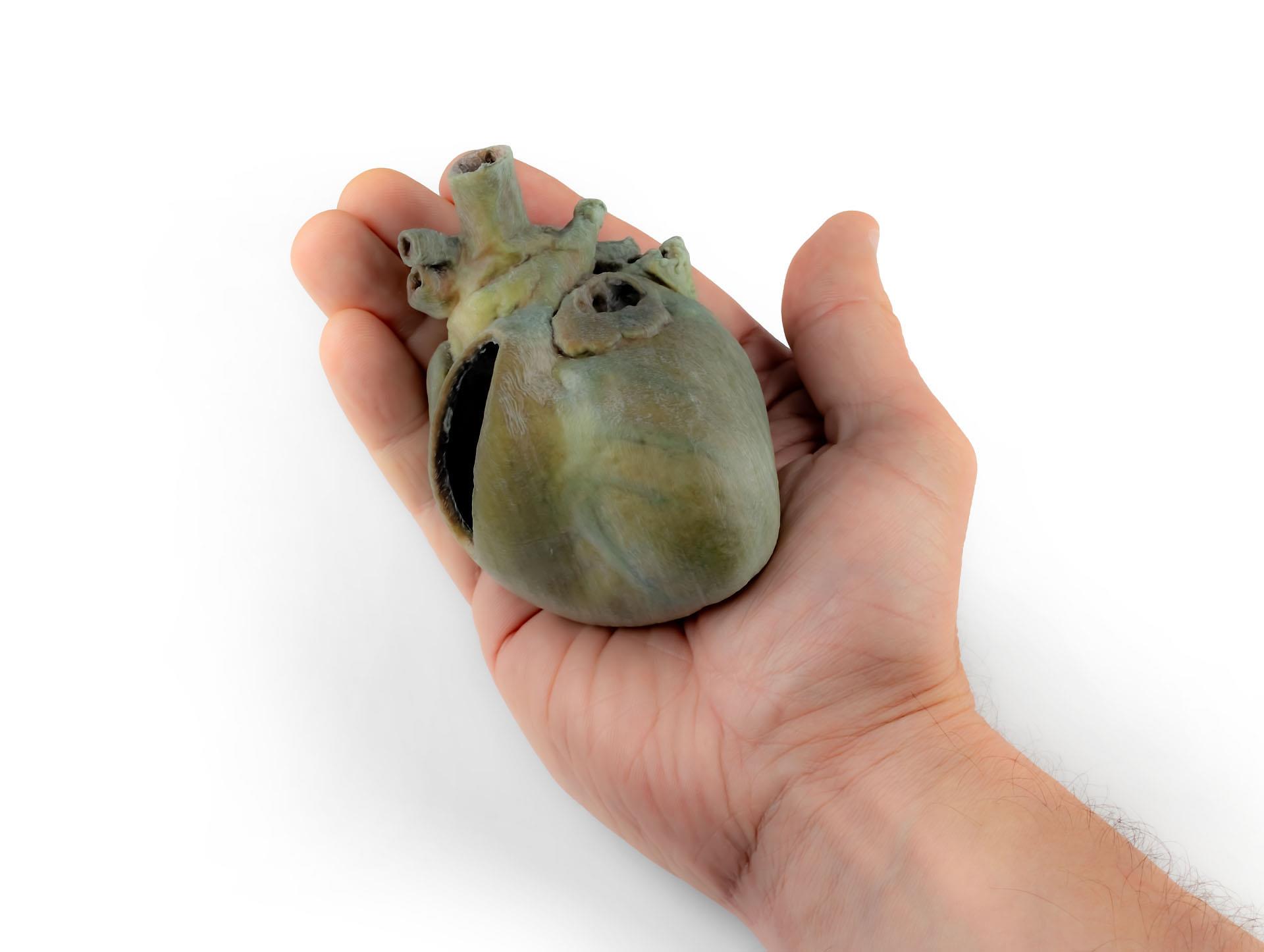
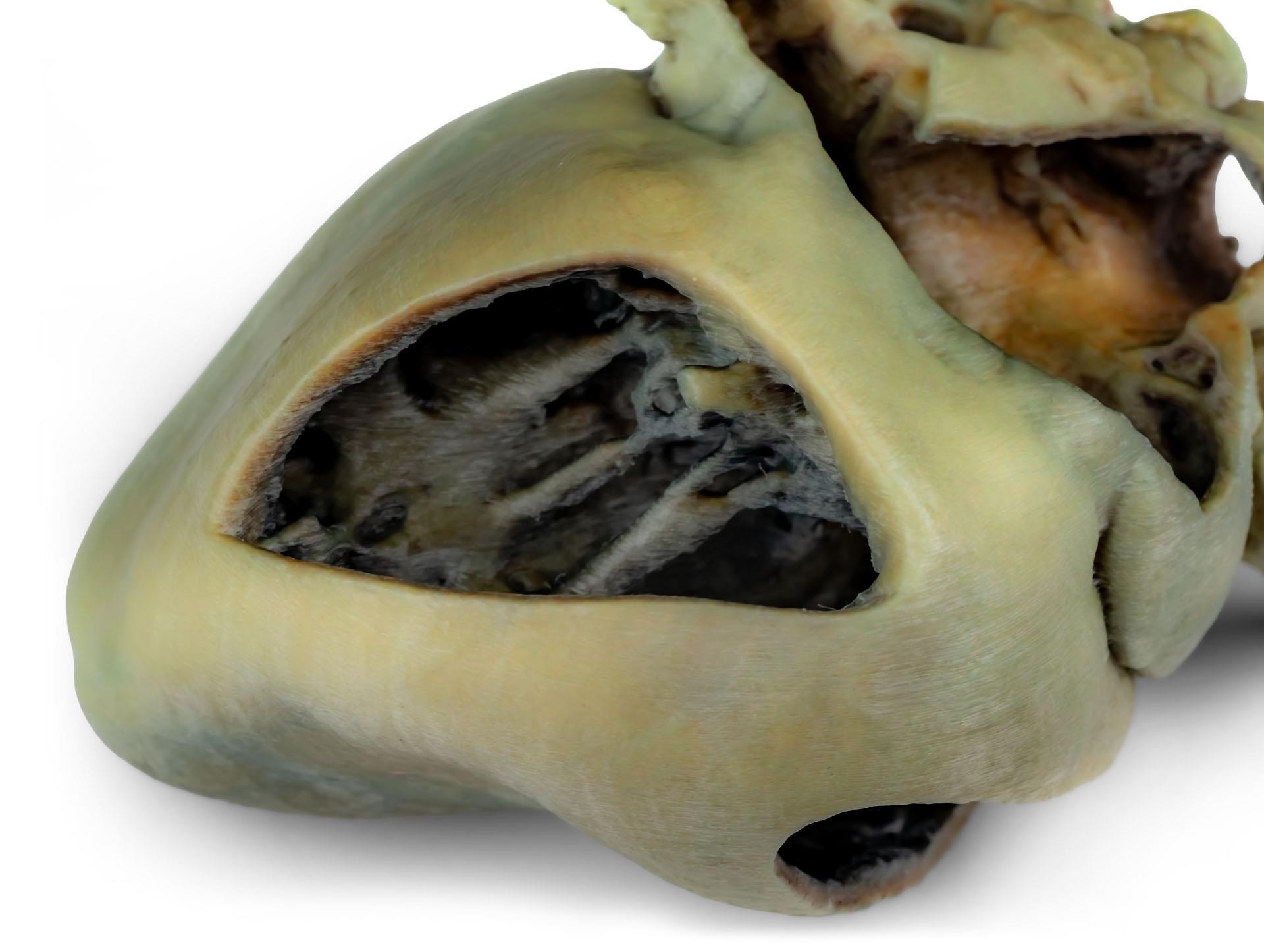
A portion of the right atrial wall has been removed to expose the right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve, including the chordae tendineae and papillary muscles.
Additionally, the septomarginal trabecula (moderator band) is visible within the right ventricle, as well as the trajectory from the ventricle to the pulmonary trunk. The left atrial wall is also open to display its lumen.
This specimen displays the anatomical features of the external surface of the heart, including both the atrial and auricular faces. At the base of the heart, the ascending aorta and its relationship with the pulmonary trunk are clearly visible, along with the sites of entry of the cranial and caudal venae cavae into the right atrium. The bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk into the pulmonary arteries can be observed, as well as the termination of the pulmonary veins into the left atrium. Both the interventricular and coronary grooves are visible.
A portion of the right atrial wall has been removed to expose the right atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve, including the chordae tendineae and papillary muscles.
Additionally, the septomarginal trabecula (moderator band) is visible within the right ventricle, as well as the trajectory from the ventricle to the pulmonary trunk. The left atrial wall is also open to display its lumen.