




































Forearm and hand - deep dissection
Order for more €200.00 and you will receive your order free of shipping costs (valid for deliveries within Germany).
Product information "Forearm and hand - deep dissection"
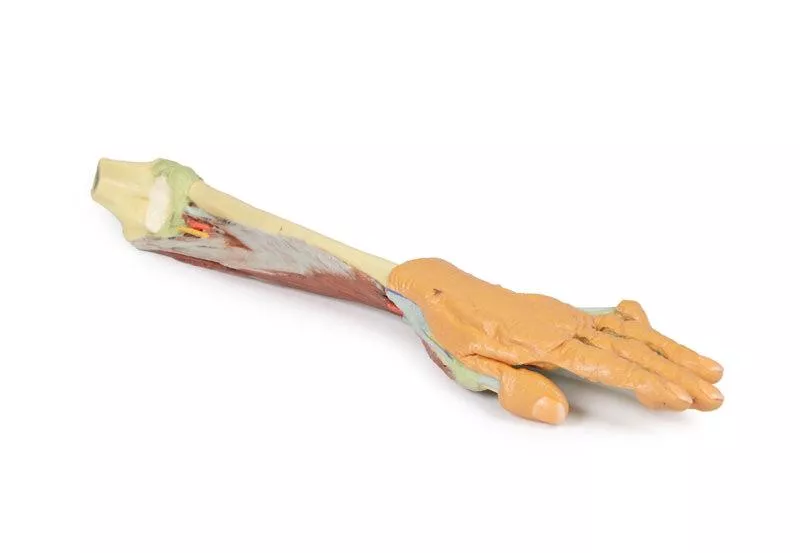
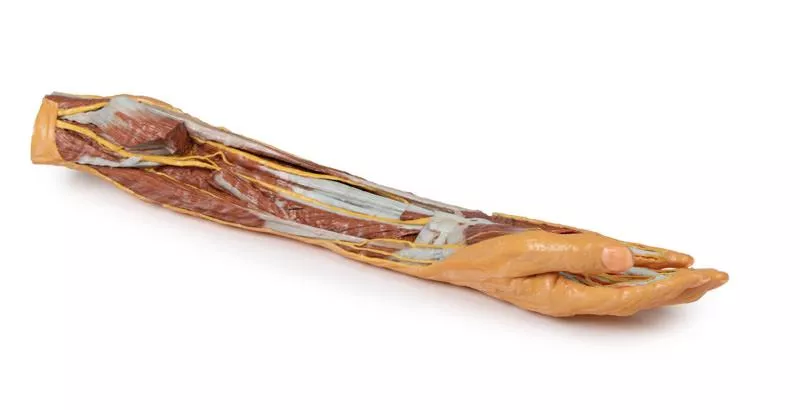
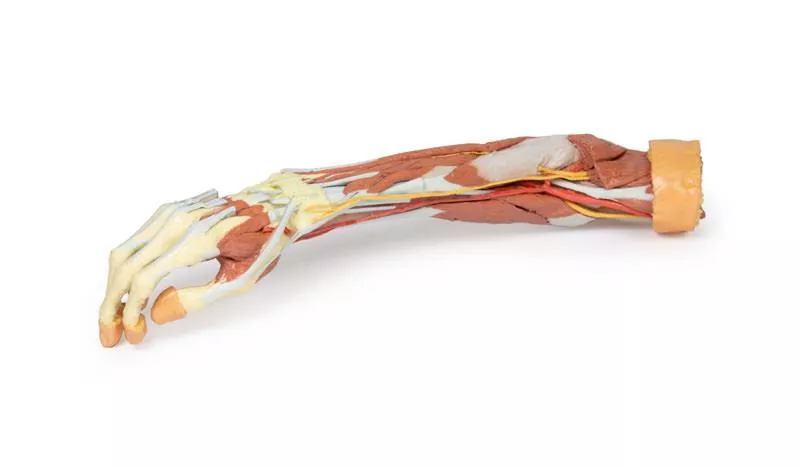
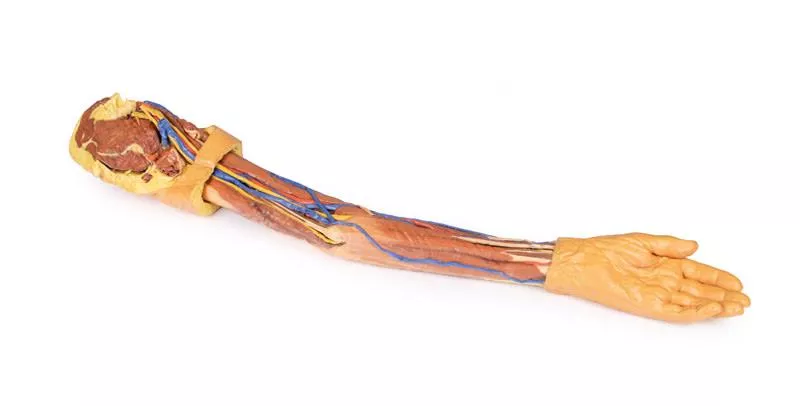
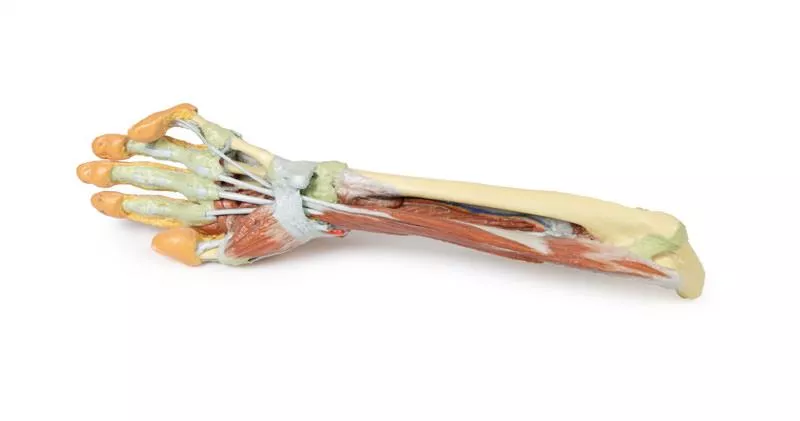
This 3D printed specimen presents a deep dissection of the left upper limb, from the distal humerus to the palmar surface of the hand, offering detailed insights into the osseous, muscular, vascular, and neural structures.
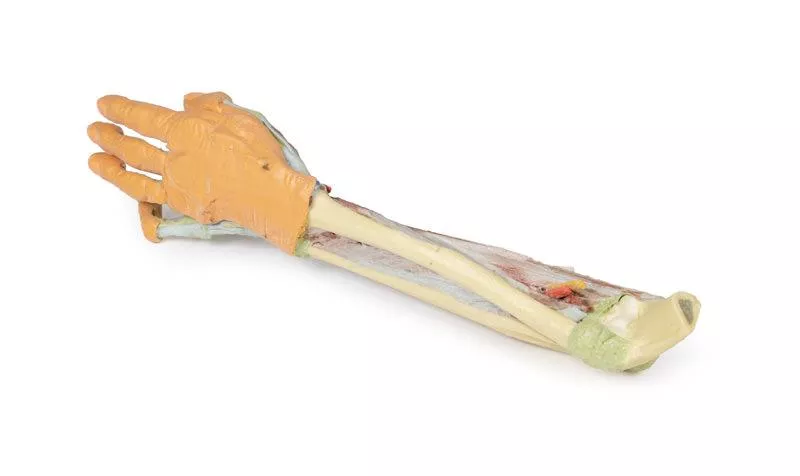
Elbow and Forearm
Around the distal humerus, most musculature has been removed except the humeral origin of the flexor digitorum superficialis. The anterior joint capsule is opened, showing the articulation of the humerus, radius, and ulna.
In the cubital fossa, the biceps brachii tendon, brachialis, brachial artery and vein, and median nerve are visible. Most surrounding forearm structures are removed to expose the anterior interosseous artery, vein, and nerve lying on the interosseous membrane, extending toward pronator quadratus.
Wrist and Carpal Tunnel
The flexor digitorum superficialis origin on the radius is exposed, with its tendons passing under the flexor retinaculum into the hand. Also visible at the wrist are the distal insertions of key forearm muscles (e.g. brachioradialis, FCR, FCU, ECRL, ECRB) and the radial artery.
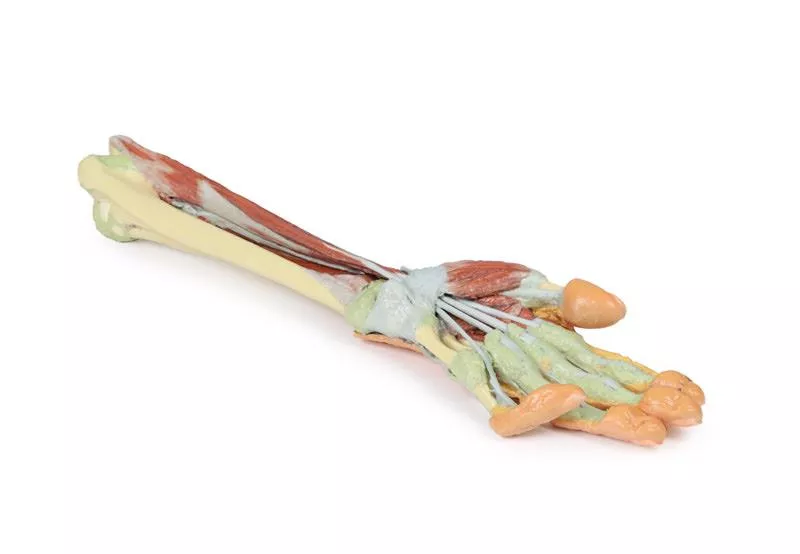
Palmar Hand Anatomy
Within the hand, tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus continue into the fingers via fibrous digital sheaths. The flexor pollicis longus tendon runs to the thumb, while the sheath of the fifth digit is opened medially.
The dissection reveals deep muscles including the adductor pollicis (both heads) and the first dorsal interosseous.
Dorsal Hand
The dorsal skin is largely intact but dissected medially to show the extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, and the extensor expansion.
This model offers a focused, high-resolution look at the deep anterior anatomy of the distal upper limb—ideal for anatomical education and demonstration.
Elbow and Forearm
Around the distal humerus, most musculature has been removed except the humeral origin of the flexor digitorum superficialis. The anterior joint capsule is opened, showing the articulation of the humerus, radius, and ulna.
In the cubital fossa, the biceps brachii tendon, brachialis, brachial artery and vein, and median nerve are visible. Most surrounding forearm structures are removed to expose the anterior interosseous artery, vein, and nerve lying on the interosseous membrane, extending toward pronator quadratus.
Wrist and Carpal Tunnel
The flexor digitorum superficialis origin on the radius is exposed, with its tendons passing under the flexor retinaculum into the hand. Also visible at the wrist are the distal insertions of key forearm muscles (e.g. brachioradialis, FCR, FCU, ECRL, ECRB) and the radial artery.
Palmar Hand Anatomy
Within the hand, tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus continue into the fingers via fibrous digital sheaths. The flexor pollicis longus tendon runs to the thumb, while the sheath of the fifth digit is opened medially.
The dissection reveals deep muscles including the adductor pollicis (both heads) and the first dorsal interosseous.
Dorsal Hand
The dorsal skin is largely intact but dissected medially to show the extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, and the extensor expansion.
This model offers a focused, high-resolution look at the deep anterior anatomy of the distal upper limb—ideal for anatomical education and demonstration.
Documents
| Datasheet MP1514 | Download |
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.
Documents
| Datasheet MP1514 | Download |
Other customers also bought
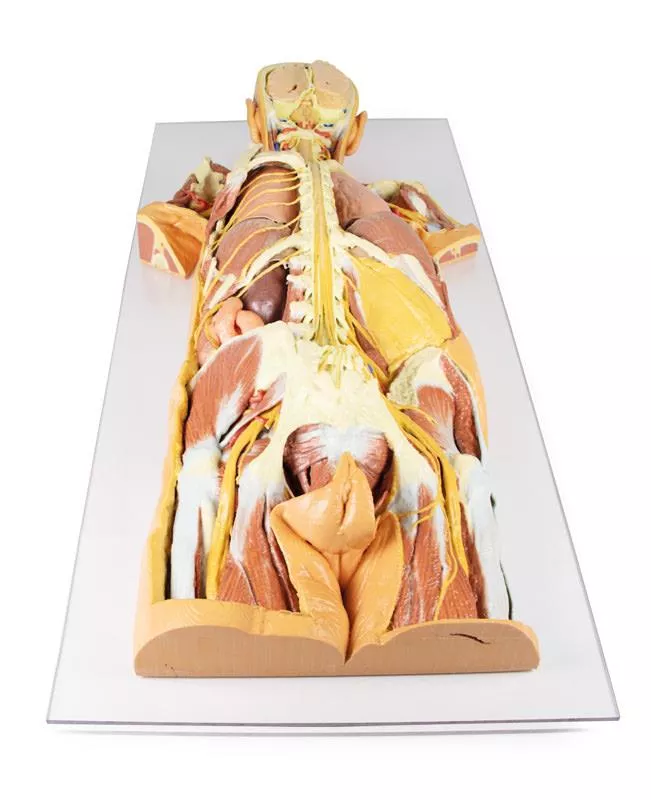
This large, multipart 3D printed specimen showcases detailed anatomy of the head, neck, thorax, axillae, and upper limbs.Head and Neck:The calotte has been removed ~2?cm above the orbits to expose the brain and endocranial cavity. A transverse cerebral section shows grey and white matter, lateral ventricles, and choroid plexus. The right side retains skin and fascia, false-coloured to highlight facial and neck angiosomes. The left side reveals facial expression and mastication muscles, and infratemporal structures including the lingual nerve and terminal branches of the external carotid artery. The carotid sheaths are opened bilaterally, exposing the common, internal, and external carotid arteries, and vagus nerves. The sternocleidomastoid and internal jugular veins are mostly removed. On the right, the great auricular and hypoglossal nerves are visible, along with the stylohyoid ligament and supra-/infrahyoid muscles. The thyroid gland is prominent, with preserved superior and inferior thyroid vessels.Root of the Neck and Axilla:On the left, partial clavicle removal reveals the first rib, anterior scalene, and brachial plexus roots (C5–T1) forming trunks between scalene muscles. The subclavian artery passes posterior to scalenus anterior, transitioning to the axillary artery, closely related to the brachial plexus cords.The left axilla displays brachial plexus divisions and cords. The formation of the median nerve around the axillary artery is distinct. The ulnar, musculocutaneous, axillary, thoracodorsal, and long thoracic nerves are clearly identified with their courses and muscular targets.On the right, the clavicle and subclavius muscle are intact, showing the cervico-axillary canal. Pectoralis major and minor have been reflected, exposing deeper structures.Thorax:A window in the left thoracic wall reveals the mediastinum. The left lung has been removed. Intercostal spaces are visible beneath the parietal pleura; neurovascular bundles are identifiable posteriorly. The heart is exposed without pericardium, showing the left atrium and ventricle, pulmonary vessels, aorta, and both left vagus and recurrent laryngeal nerves. The right thoracic wall remains intact, displaying intercostal and upper limb muscles. From below, the right lung, pleural cavities, and diaphragmatic heart surface are visible. Posterior thoracic skin and fascia are intact, showing cutaneous nerve distribution.Size: 50 x 20 x 41 cm
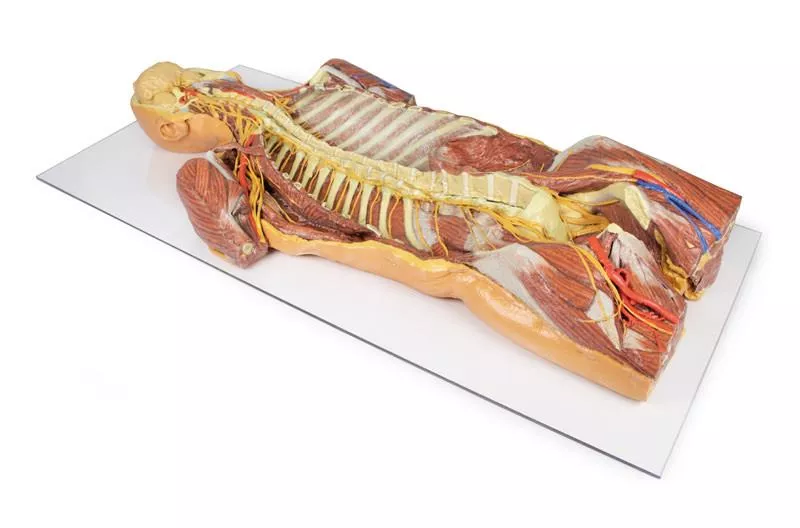
This detailed 3D printed specimen provides a unique dorsal view of the head, neck, thorax, abdomen, and gluteal regions, highlighting the central nervous system and segmental nerves in anatomical context. The model reveals deep structures through extensive removal of posterior elements, including the posterior cranium, vertebral arches, and parts of the thoracic and gluteal walls.Cranial and Cervical StructuresThe posterior skull is removed to display a coronal section of the cerebral hemispheres, separated by the falx cerebri and bordered by a preserved superior sagittal sinus. The cerebellum is removed, exposing the fourth ventricle, pons, medulla oblongata, and cranial nerves VII–XII. The vertebral arteries are visible ascending through the transverse foramina and curving toward the foramen magnum. The cervical and brachial plexus roots are shown resting on scalene muscles and major vessels, extending into the axilla. Axilla and Upper ThoraxThe scapulae are partially (left) or fully (right) removed, allowing visualization of the brachial plexus and axillary vessels.On the left, parts of deltoid, infraspinatus, and teres minor remain, while the long thoracic nerve, lateral thoracic artery, and subscapular branches are preserved.On the right, the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery are shown passing toward the surgical neck of the humerus. Thoracic Spine and Intercostal NervesA laminectomy reveals the spinal cord, dorsal roots, and ganglia.On the right, the posterior thoracic wall is removed (ribs 2–12), exposing the lung and diaphragm.On the left, ribs 3–5 are retained to show intercostal musculature and nerve positioning, with the full set of intercostal nerves preserved.Lumbar Region and AbdomenThe lumbar spinal cord is opened to show the conus medullaris and cauda equina.On the right, the quadratus lumborum is removed, exposing subcostal and lumbar nerves along the psoas.On the left, the subcostal nerve, kidney, and jejunum are visible through an opened peritoneal cavity. Gluteal and Pelvic DissectionIn the gluteal region, gluteus maximus is removed bilaterally:Left side: Gluteus medius is preserved; the superior and inferior gluteal arteries and nerves, internal pudendal vessels, and the sciatic nerve are visible relative to the piriformis and lateral rotators.Right side: Deeper dissection reveals the lumbar and sacral plexuses within the true pelvis. This model offers a rare, continuous view of deep axial anatomy, perfect for advanced anatomical study, neuroanatomy training, and surgical reference.
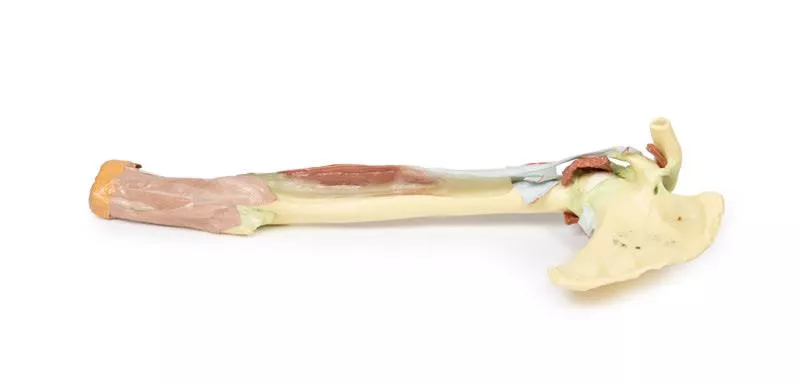
This 3D printed specimen highlights the origin, course, and insertion of the biceps brachii muscle, while most other arm and shoulder muscle bellies have been removed to enhance visibility.Biceps Brachii: Origins and InsertionThe long head of the biceps originates from the supraglenoid tubercle (not visible) and travels through the bicipital groove, while the short head arises from the coracoid process. The bifid insertion is clearly shown: the bicipital aponeurosis and the round tendon wrapping around the radius to insert on the radial tuberosity. Shoulder Region StructuresSeveral preserved elements are visible around the shoulder joint, including partial stumps or tendons of the subclavius, subscapularis, pectoralis major, teres minor, infraspinatus, long head of triceps, and latissimus dorsi. The teres major tendon lies along the medial lip, and the pectoralis major tendon along the lateral lip of the bicipital groove. Also preserved are key shoulder ligaments:- Coracoclavicular ligament- Coracoacromial ligament- Coracohumeral ligament- Capsules of the shoulder and acromioclavicular jointsThe supraspinatus is the only complete rotator cuff muscle retained, and the suprascapular ligament is seen bridging the suprascapular notch. Elbow Joint AnatomyAt the elbow, the joint capsule, annular ligament of the radius, and radial collateral ligaments are visible. The ulnar collateral ligament is not shown due to retention of both heads of flexor carpi ulnaris.This model is ideal for studying biceps anatomy, shoulder tendon insertions, and key ligamentous structures of the shoulder and elbow joints, making it a valuable tool for anatomical education and demonstration.
This 3D printed model provides a detailed ventral view of the head, neck, thorax, abdomen, and proximal thighs, offering insight into the central nervous system, nerve plexuses, and major vascular structures. It serves as a complementary piece to the dorsal dissection model (MP1400).Brain and Upper SpineThe facial skeleton is removed, exposing both cerebral hemispheres, parts of the Circle of Willis, and key arteries (vertebral, basilar, AICA, labyrinthine). Several cranial nerves (II, III, V, VI) and the right internal carotid artery are preserved. Below, the anterior spinal cord, vertebral arteries, and cervical and brachial plexus roots are visible, along with CN X, CN XII, and the sympathetic trunks. Axillae and Upper LimbsThe anterior thoracic wall, clavicles, and first ribs are removed to expose both axillae, with clear views of the brachial plexus, axillary arteries, and surrounding musculature. The proximal upper limbs are preserved to mid-arm level. Thorax and Lumbar RegionThe spinal cord extends to the conus medullaris, with ventral nerve roots and sympathetic chains visible throughout. Splanchnic nerves, intercostal nerves, and abdominal wall nerves (e.g., ilioinguinal, genitofemoral, femoral) are preserved. On the right, removal of the psoas muscle exposes the lumbar plexus.Pelvis and Proximal ThighThe pelvic viscera are removed, but the pelvic floor, rectum, and lumbosacral plexus remain. Obturator nerves are visible entering the obturator canals, and the femoral vessels are retained in both femoral triangles. This model is ideal for studying ventral CNS access, neurovascular pathways, and regional anatomical relationships across the entire torso.
This high-detail 3D printed specimen presents a combined superficial and deep dissection of the anterior right distal arm, forearm, and hand, offering a comprehensive view of key muscular, neural, and tendinous structures.Proximal Forearm & Cubital RegionMedially, the ulnar nerve is shown passing through the cubital tunnel and deep to the flexor carpi ulnaris. The cubital fossa has been opened by removing most flexor muscles, clearly exposing the biceps brachii and brachialis insertions, as well as the courses of the median, ulnar, and superficial radial nerves in the anterior compartment. Forearm: Muscle and Nerve DetailMuscular branches of the median nerve are visible entering the pronator teres and flexor digitorum profundus. The pronator teres insertion lies between the partially exposed supinator and flexor pollicis longus.Near the wrist, tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus are preserved, passing through the carpal tunnel alongside the median nerve. The pronator quadratus is partially visible deep to these structures.The flexor retinaculum is covered by the palmaris longus tendon, palmar aponeurosis, and palmaris brevis muscle. Wrist & Anatomical SnuffboxLaterally, the superficial radial nerve crosses over the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons, entering the roof of the anatomical snuffbox, aiding in topographic orientation.Palm & Digital StructuresThe hand is superficially dissected between the thenar and hypothenar eminences, removing only skin and fascia. The tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus extend through the palm, surrounded by lumbricals and terminal branches of the median and ulnar nerves, forming common and proper digital nerves.Although most arterial structures have been removed for clarity, one common palmar digital artery and several proper palmar digital arteries are retained along the fingers.This model is ideal for detailed anatomical study of anterior forearm structures, neurovascular paths, and hand anatomy, particularly the carpal tunnel and digital innervation.
This detailed 3D print displays the left upper limb from the distal arm to the hand, highlighting key muscular, vascular, and neural structures through deep dissection. Elbow Region & Distal ArmThe cubital fossa reveals the classic lateral-to-medial layout: biceps tendon, brachial artery, and median nerve, with the bicipital aponeurosis removed. The ulnar nerve passes behind the medial epicondyle, and the superficial radial nerve is visible between brachioradialis and brachialis. Anterior & Posterior ForearmAnteriorly, the superficial flexors—pronator teres, FCR, FDS, and FCU—are clearly shown (no palmaris longus present). The radial and ulnar arteries, as well as the superficial radial nerve, are identifiable.Posteriorly, extensor muscles from the common extensor origin are preserved, including ECU, extensor digitorum, and ECRB/ECRL. The anatomical snuffbox is visible with the radial artery and cutaneous radial nerve. Palm & Carpal TunnelThe thenar/hypothenar muscles, flexor retinaculum, long tendons, and lumbricals are exposed. The median nerve runs beneath the retinaculum, and the superficial palmar arch (from the ulnar artery) is intact. Digital nerves and vessels are clearly seen, along with the recurrent median nerve branch and the extensor expansion on the middle finger.This model is ideal for studying upper limb anatomy, with special focus on the elbow, forearm, and hand structures.
This 3D printed model presents a superficial dissection of the right distal arm, forearm, and hand, showcasing key vascular, nervous, and muscular anatomy.Distal Arm & Cubital FossaThe arrangement of the biceps tendon, brachial artery, and median nerve is visible from lateral to medial. The bicipital aponeurosis has been removed to expose deeper structures. The ulnar nerve is reflected from the cubital tunnel, and the radial nerve with its branches is visible near the supinator muscle. Forearm AnatomyOn the anterior forearm, superficial flexors (pronator teres, FCR, FDS, FCU) are preserved; palmaris longus is absent. The radial artery is exposed; the ulnar artery is not visible. Posteriorly, extensors from the common origin are visible, including ECRB, ED, EDM, and ECU. The APL, EPB, and EPL are also shown wrapping around the radius. Hand & SnuffboxThe anatomical snuffbox reveals the radial artery in its floor and cutaneous branches of the radial nerve. The palmar side displays thenar/hypothenar muscles, lumbricals, flexor tendons, and the median nerve beneath the flexor retinaculum. A superficial branch of the radial artery crosses the retinaculum.Ideal for anatomical education, this print offers a clear view of key structures in the distal upper limb.
This detailed 3D printed model presents the male posterior abdominal wall from the diaphragm down to the pelvic brim, including the pelvis and proximal thigh.A focused pelvic and thigh version is also available (MP1770).Muscular Anatomy & DiaphragmThe parietal peritoneum is removed to expose the key muscles of the posterior abdominal wall: psoas major, quadratus lumborum, transversus abdominis, and iliacus below the iliac crest. The diaphragm shows distinct muscular fibers originating from the thoracic cage and lumbar vertebrae (right crus L1–L3, left crus L1–L2), connected by the median arcuate ligament. Major diaphragmatic openings for the esophagus, aorta, and inferior vena cava are visible, although the aorta is removed. NervesSomatic nerves are clearly identifiable, including the subcostal, iliohypogastric, and ilioinguinal nerves (which arise together in this specimen), the lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh, the genitofemoral nerve (on psoas), and the femoral nerve situated between psoas and iliacus. The sympathetic trunks run alongside the lumbar vertebrae. Vessels & KidneysThe aorta and inferior vena cava are transected at L3, with the aortic bifurcation positioned slightly higher than usual. The renal arteries and veins are preserved, though their full origin is partly obscured by the absence of the great vessels. Both kidneys are dissected free from surrounding fat, showing the typical lower position of the right kidney. The ureters are visible descending from the renal hilum, passing medial to the psoas before crossing the pelvic brim into the true pelvis. This model offers an exceptional view of the complex anatomy of the posterior abdominal wall, pelvis, and proximal thigh, making it ideal for advanced anatomical study, surgical planning, and clinical reference.
This 3D printed model presents a detailed anatomical view of the left upper limb, extending from the scapula to the hand. Most of the skin and fascia have been removed to expose the muscles, vessels, and nerves, while select regions (such as the dorsum of the scapula, proximal arm, and hand) retain superficial coverings for reference. Veins and Superficial StructuresThe cephalic, basilic, and median cubital veins are preserved, clearly demonstrating the superficial venous system from the wrist to the deltopectoral groove and brachial vein. Axilla and ShoulderIn the axillary region, the deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor and major, and subscapularis muscles are shown in cross-section. Key tendons — including those of the latissimus dorsi, coracobrachialis, and pectoralis major — are also retained.Portions of the axillary artery and vein are visible, along with the lateral cords of the brachial plexus. Several terminal branches are displayed, including the ulnar, median, musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, and upper subscapular nerves. Arm and Forearm DissectionThe model continues distally with a full view of the anterior and posterior compartments of the arm, displaying both muscle structure and the deep neurovascular pathways. In the cubital fossa, part of the bicipital aponeurosis remains intact.In the forearm, superficial flexor and extensor muscles are dissected from their origins to their tendinous insertions. A section of deep forearm fascia over the extensor compartment is retained for structural orientation. At the distal forearm, the radial and ulnar arteries and the median nerve are clearly visible. This model is ideal for teaching and studying upper limb anatomy, offering detailed views of musculature, vascular structures, and nerve pathways with a focus on both surface and deep anatomical relationships.

Continuous innovation

Social responsibility

Active customer orientation

Understanding quality

Sustainable actions

ISO 9001 certification
Your last viewed products