Product information "Nodular hyperplasia of the Prostate"
Clinical History
A 63-year-old man presented with acute abdominal pain and had been unable to urinate for five days. He reported a two-year history of urinary frequency, hesitancy, double voiding, nocturia, and poor stream. Examination revealed a distended bladder and an enlarged prostate. Bladder scan showed >1?L urine retention; labs confirmed acute renal failure. Catheterisation attempts failed, leading to a total prostatectomy. He recovered well post-op.
Pathology
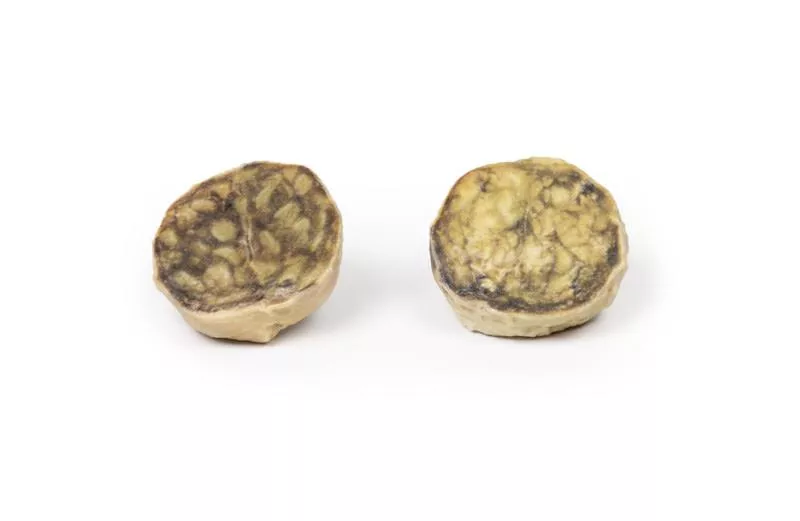
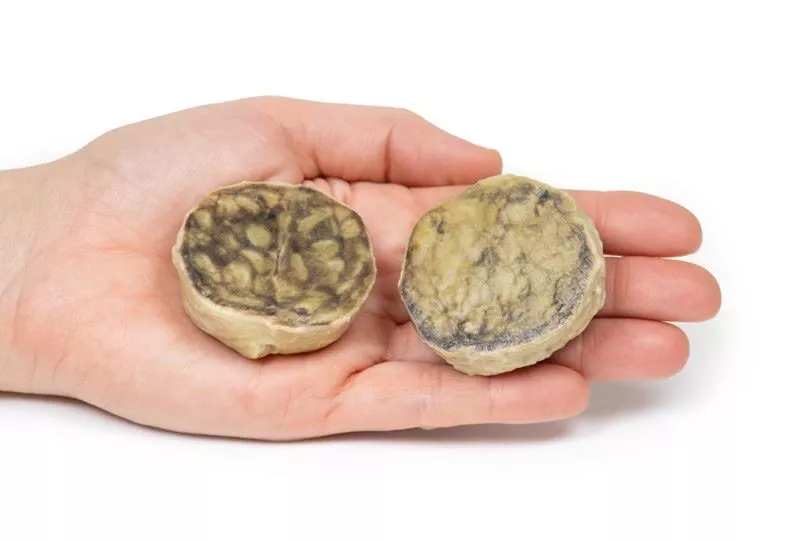
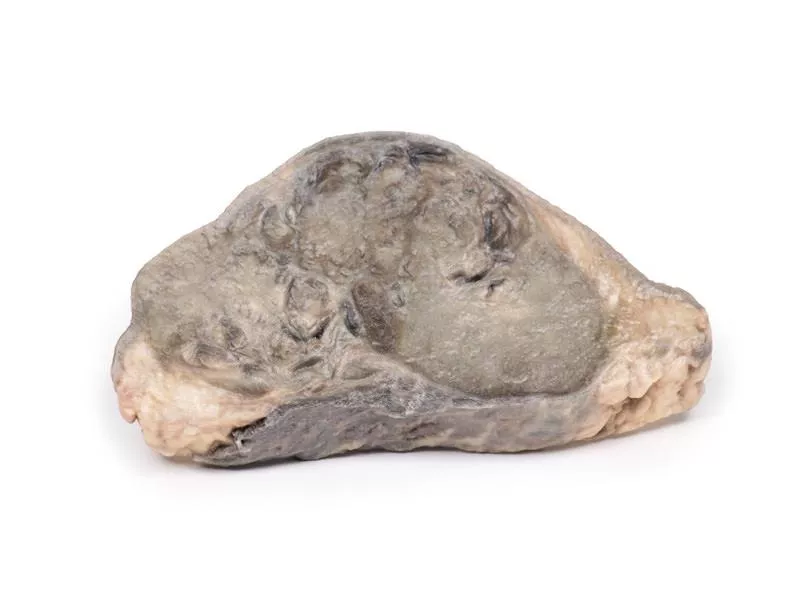
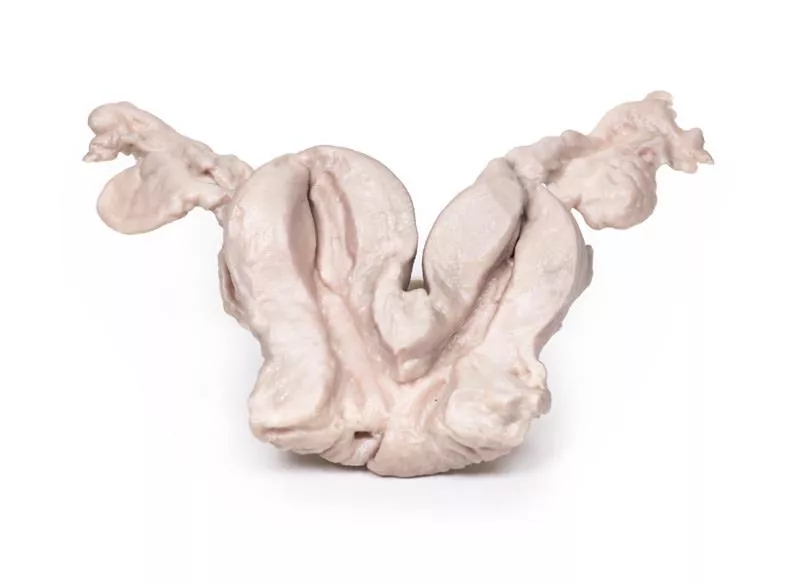
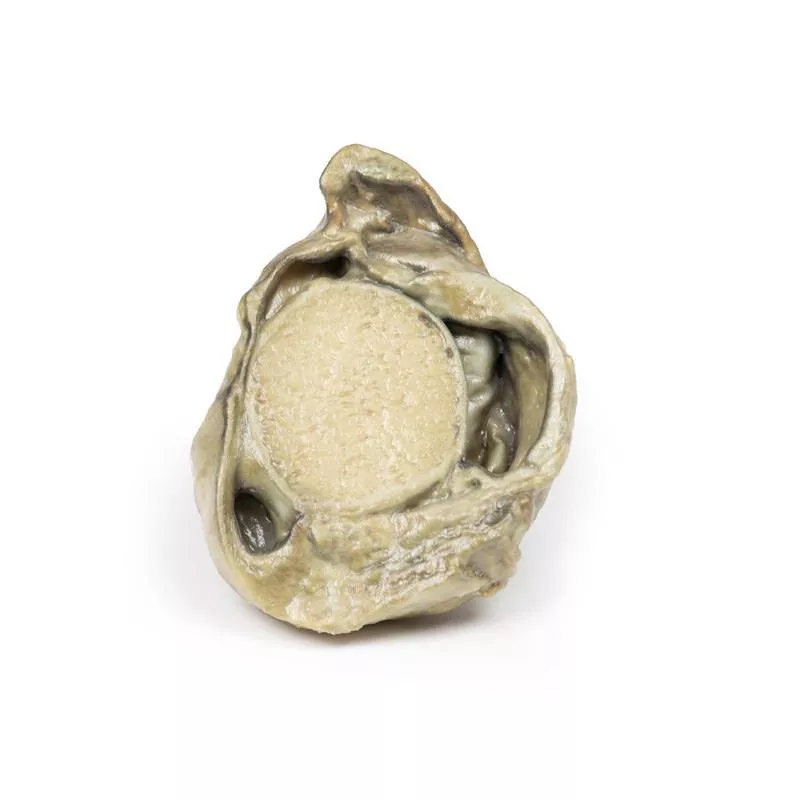
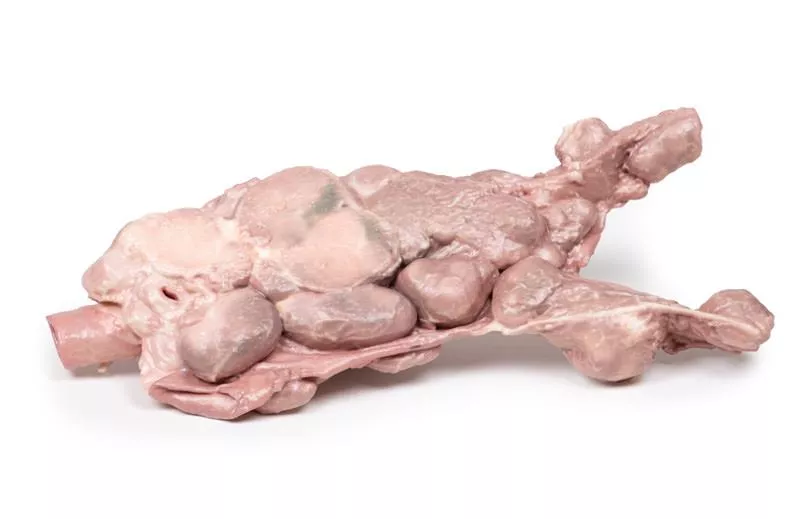
The enlarged prostate, sliced transversely, shows multiple nodules (2–10?mm) consistent with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Further Information
BPH is a common condition in older men, caused by nodular overgrowth of stromal and epithelial cells in the periurethral zone, stimulated by dihydrotestosterone. The median lobe may enlarge disproportionately and obstruct the urethra.
Prevalence increases with age: 20% by 40, 70% by 60, 90% by 80. Risk factors include family history, obesity, and androgenic steroids.
Typical symptoms: urinary frequency, nocturia, hesitancy, double voiding, dribbling. Acute urinary retention can lead to UTIs and kidney damage.
Diagnosis includes history, digital rectal exam (DRE), PSA test, and imaging. Treatments: alpha-blockers, 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, or in severe cases transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). Total prostatectomy is rarely used due to complications.
A 63-year-old man presented with acute abdominal pain and had been unable to urinate for five days. He reported a two-year history of urinary frequency, hesitancy, double voiding, nocturia, and poor stream. Examination revealed a distended bladder and an enlarged prostate. Bladder scan showed >1?L urine retention; labs confirmed acute renal failure. Catheterisation attempts failed, leading to a total prostatectomy. He recovered well post-op.
Pathology
The enlarged prostate, sliced transversely, shows multiple nodules (2–10?mm) consistent with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Further Information
BPH is a common condition in older men, caused by nodular overgrowth of stromal and epithelial cells in the periurethral zone, stimulated by dihydrotestosterone. The median lobe may enlarge disproportionately and obstruct the urethra.
Prevalence increases with age: 20% by 40, 70% by 60, 90% by 80. Risk factors include family history, obesity, and androgenic steroids.
Typical symptoms: urinary frequency, nocturia, hesitancy, double voiding, dribbling. Acute urinary retention can lead to UTIs and kidney damage.
Diagnosis includes history, digital rectal exam (DRE), PSA test, and imaging. Treatments: alpha-blockers, 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, or in severe cases transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). Total prostatectomy is rarely used due to complications.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.