Product information "Brain (Cerebrum)"
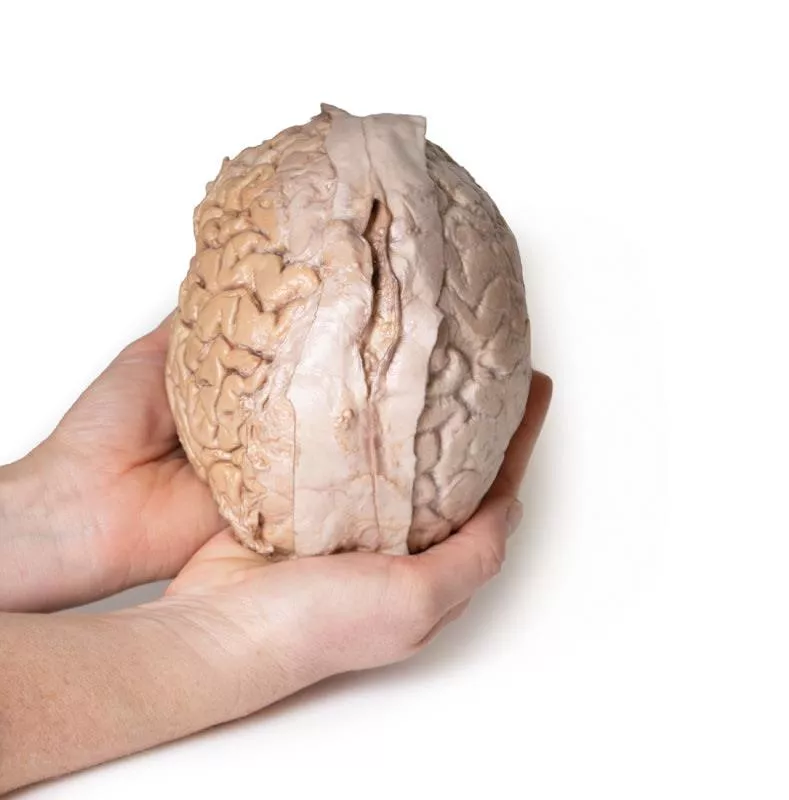
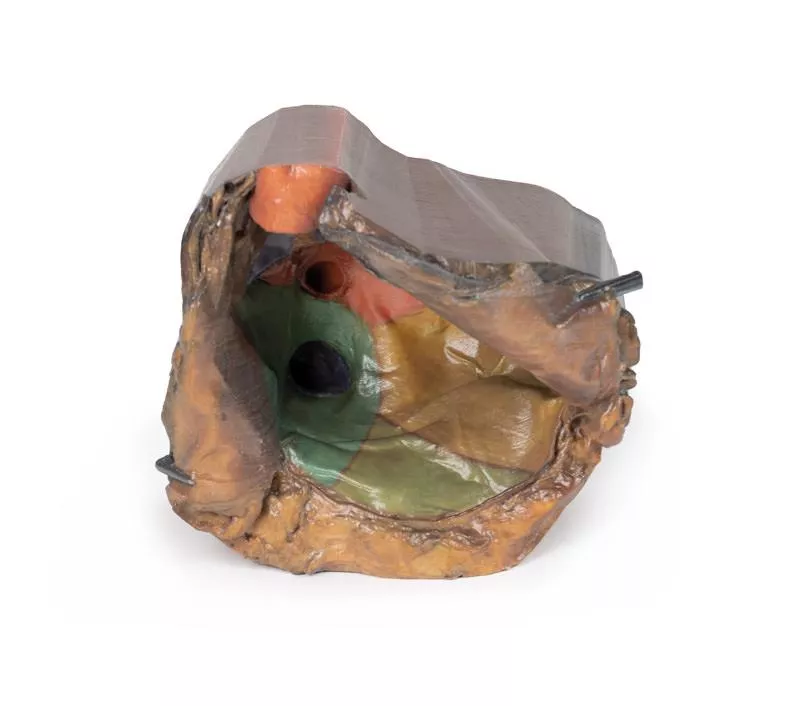
This 3D model provides a unique perspective on the anatomy of the cerebrum relative to the meninges.
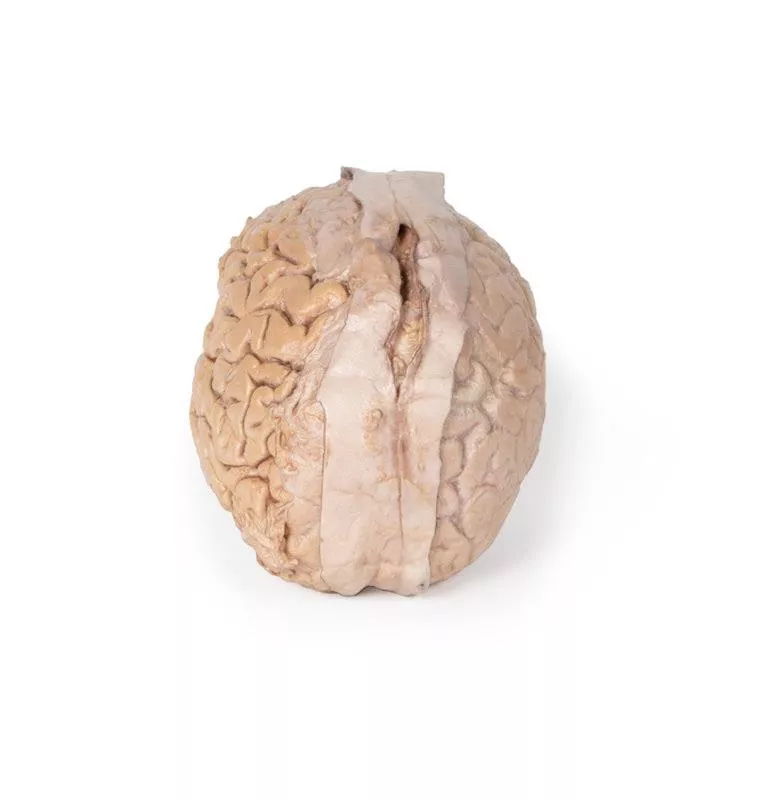
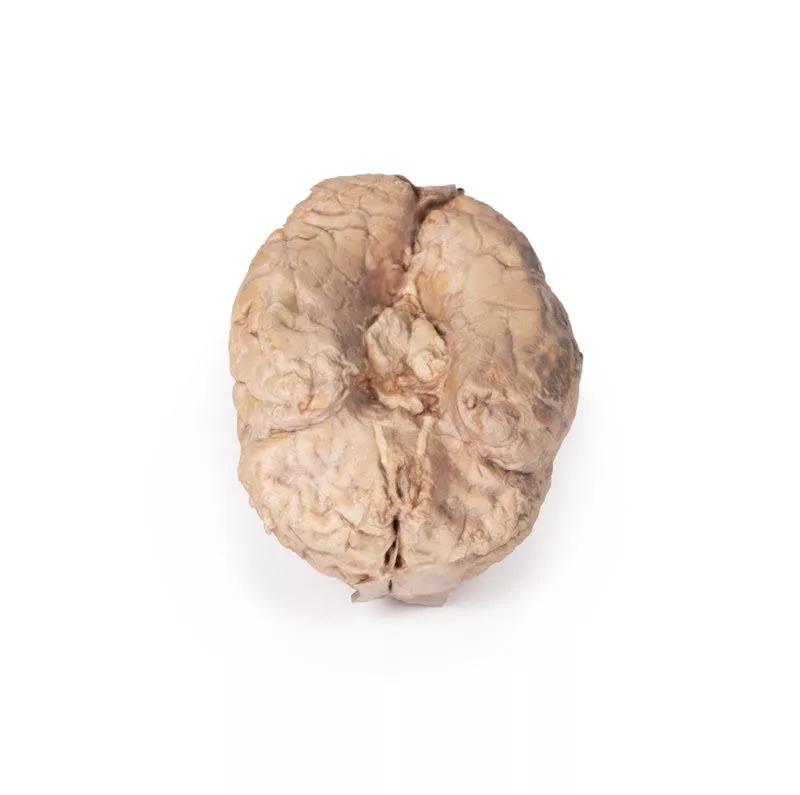
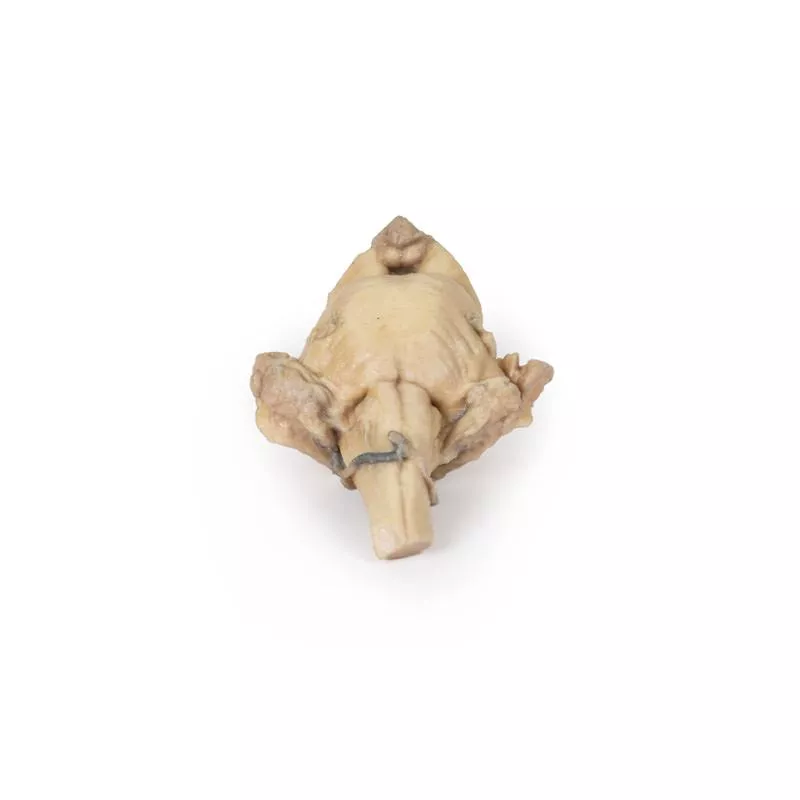
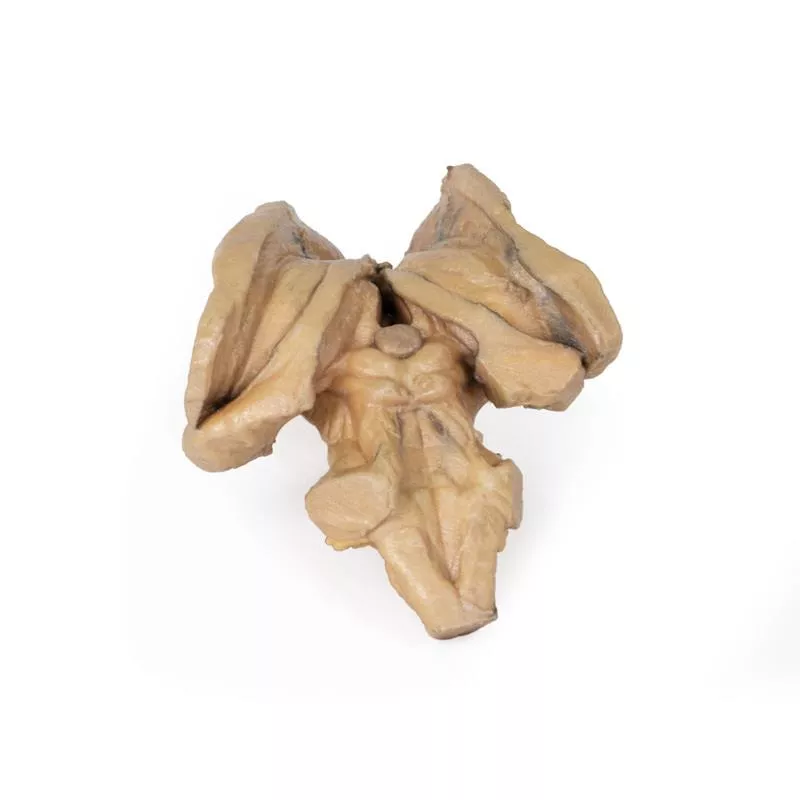
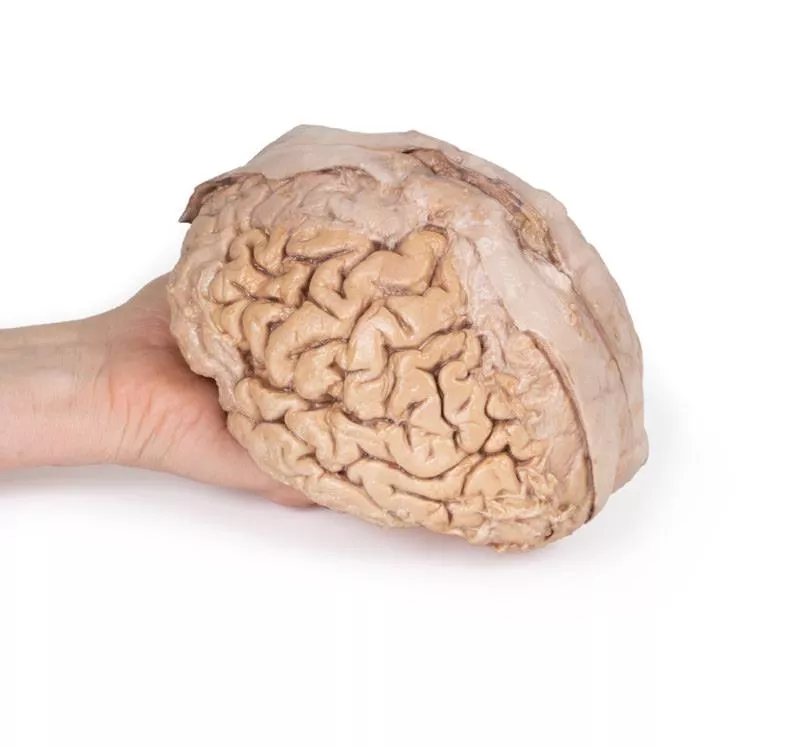
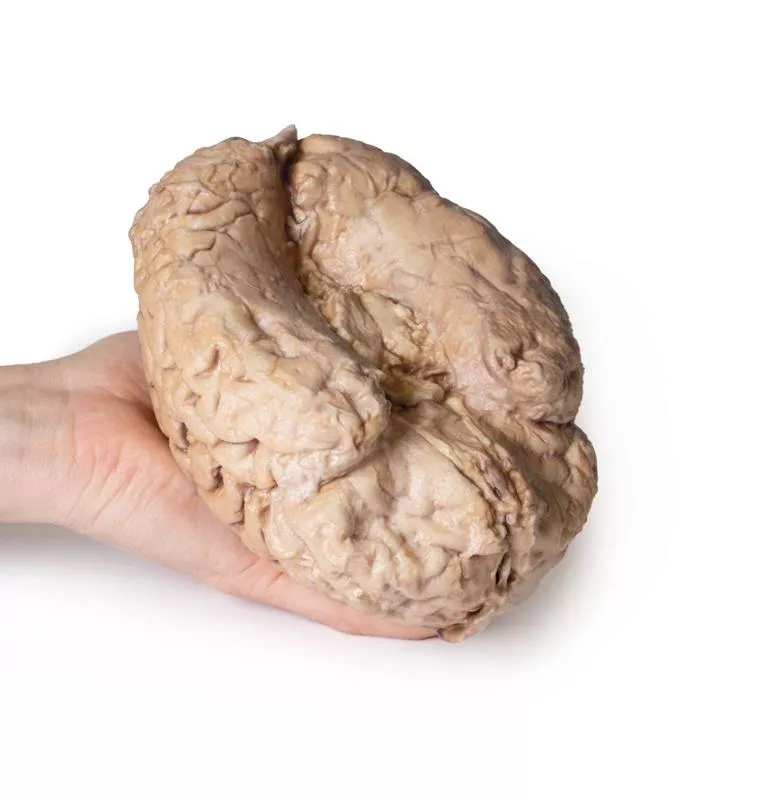
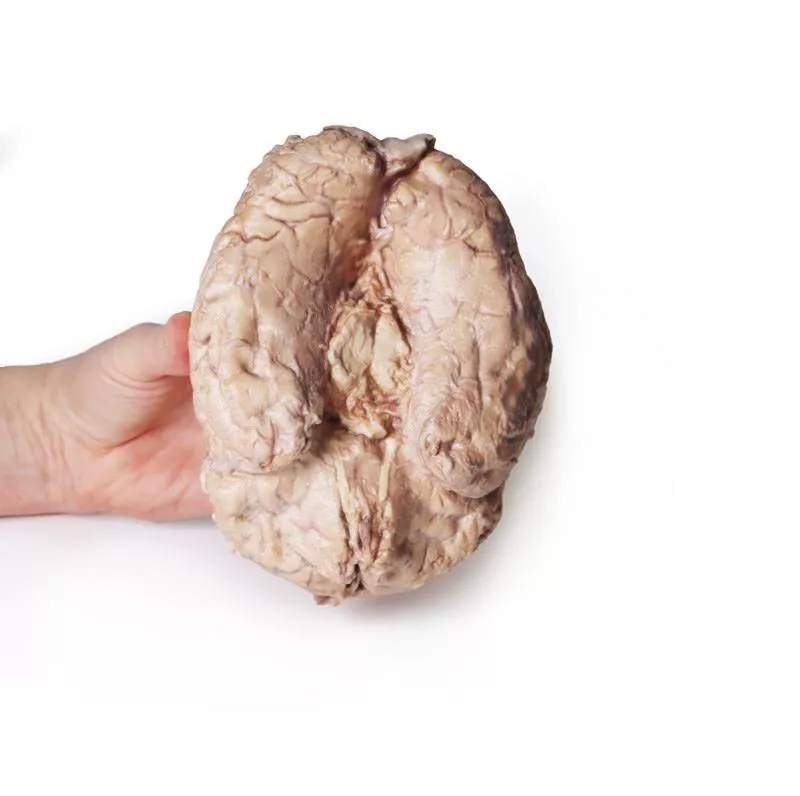
The cerebrum has been separated from the brainstem and cerebellum, with only parts of the midbrain and cerebral peduncles visible on the inferior surface. Adjacent to the cut section the olfactory tracts and bulbs can be seen extending along the inferior margin of the frontal lobes of the cerebrum.
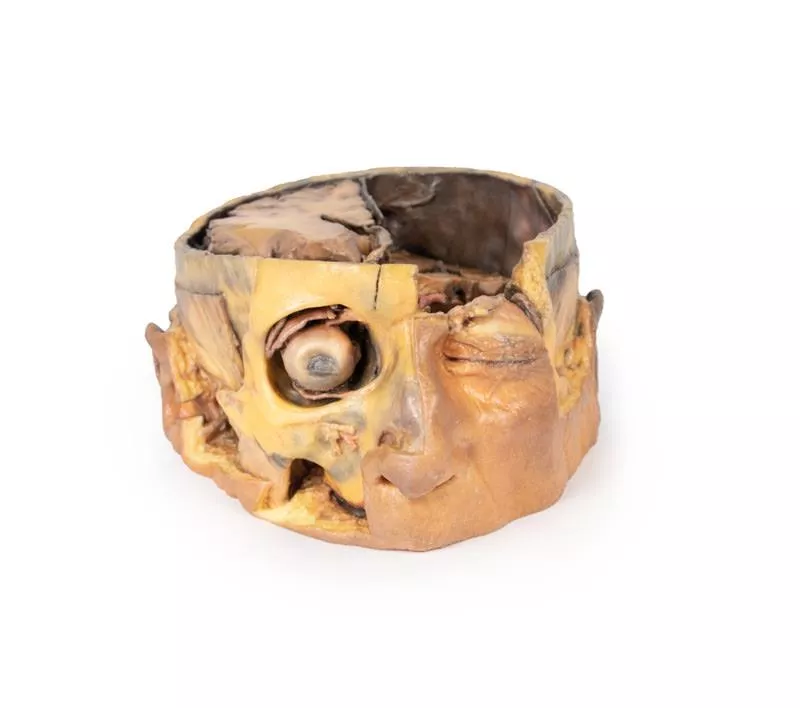
Varying dissection between the left and right cerebral hemispheres allows an appreciation for the organisation of the brain and meninges as it would normally appear within the cranial cavity. In the midline, the dura mater has been preserved from anterior (rostral) to posterior. The central portion of the true (endosteal) dura opened to expose the superior sagittal sinus (between endosteal and meningeal layers of dura mater).
Numerous arachnoid granulations (clusters of arachnoid villi) are visible within the opened superior sagittal sinus – as well as across the margins of the preserved dura. On the right cerebral hemisphere, the dura mater has been completely removed to expose the underlying arachnoid mater, which obscures the appearance of the underlying cerebral gyri and sulci as well as the terminal branches of cerebral arteries. In contrast, the arachnoid mater has dissected across most of the hemisphere (excepting a margin for reference) to expose the gyri and sulci covered in pia mater. This allows a clear view of the lateral sulcus and the central sulcus, with the latter defining the boundaries of the frontal and parietal lobes - and separating the primary sensory and motor cortical areas on the gyri on either side of the sulcus.
The cerebrum has been separated from the brainstem and cerebellum, with only parts of the midbrain and cerebral peduncles visible on the inferior surface. Adjacent to the cut section the olfactory tracts and bulbs can be seen extending along the inferior margin of the frontal lobes of the cerebrum.
Varying dissection between the left and right cerebral hemispheres allows an appreciation for the organisation of the brain and meninges as it would normally appear within the cranial cavity. In the midline, the dura mater has been preserved from anterior (rostral) to posterior. The central portion of the true (endosteal) dura opened to expose the superior sagittal sinus (between endosteal and meningeal layers of dura mater).
Numerous arachnoid granulations (clusters of arachnoid villi) are visible within the opened superior sagittal sinus – as well as across the margins of the preserved dura. On the right cerebral hemisphere, the dura mater has been completely removed to expose the underlying arachnoid mater, which obscures the appearance of the underlying cerebral gyri and sulci as well as the terminal branches of cerebral arteries. In contrast, the arachnoid mater has dissected across most of the hemisphere (excepting a margin for reference) to expose the gyri and sulci covered in pia mater. This allows a clear view of the lateral sulcus and the central sulcus, with the latter defining the boundaries of the frontal and parietal lobes - and separating the primary sensory and motor cortical areas on the gyri on either side of the sulcus.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.