Product information "Foot - Structures of the plantar surface"
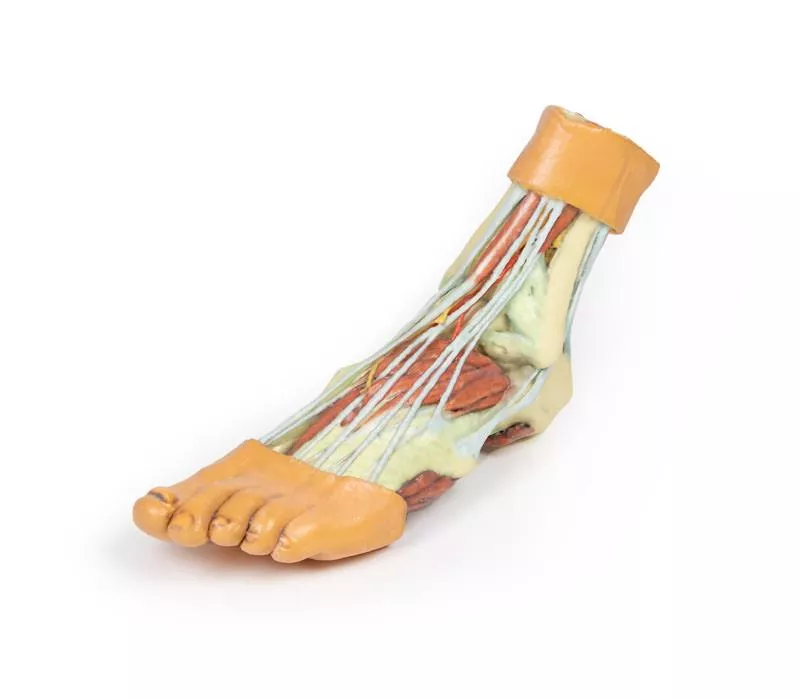
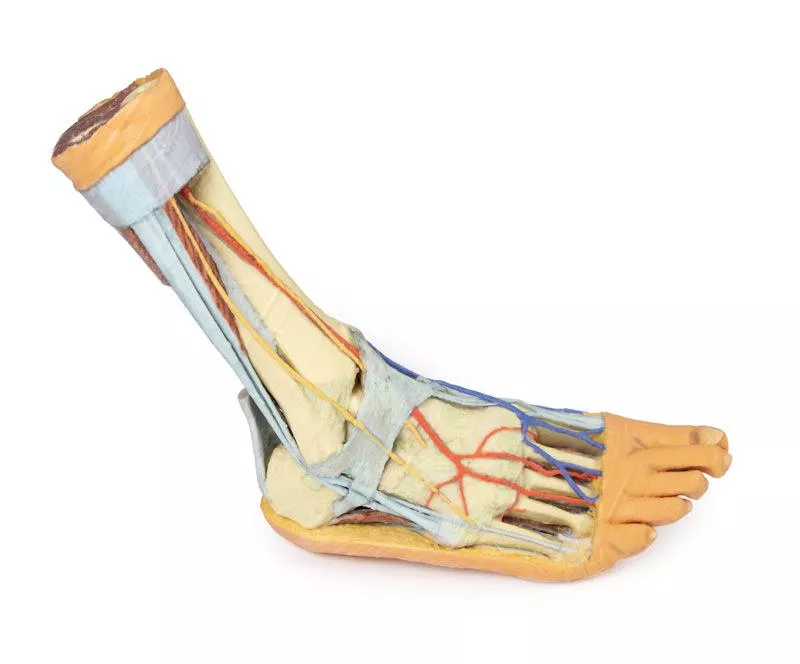
This 3D printed specimen highlights the anatomy of the right distal leg and foot, including deep plantar structures.
Proximal Leg Structures
In cross-section, the tibia, fibula, interosseous membrane, and leg muscles are clearly visible. At the medial ankle, the long tendons of the dorsiflexors and plantarflexors pass superficial to capsular and extracapsular ligaments. The posterior tibial artery, veins, and tibial nerve are traced from the posterior leg to the plantar surface. Laterally, the fibularis muscles (longus, brevis, tertius) and their insertions are displayed.
Dorsal Foot Structures
On the dorsum of the foot, the anterior tibial artery and deep fibular nerve emerge deep to the extensor hallucis longus, lying superficial to the extensor hallucis brevis and extensor digitorum brevis.
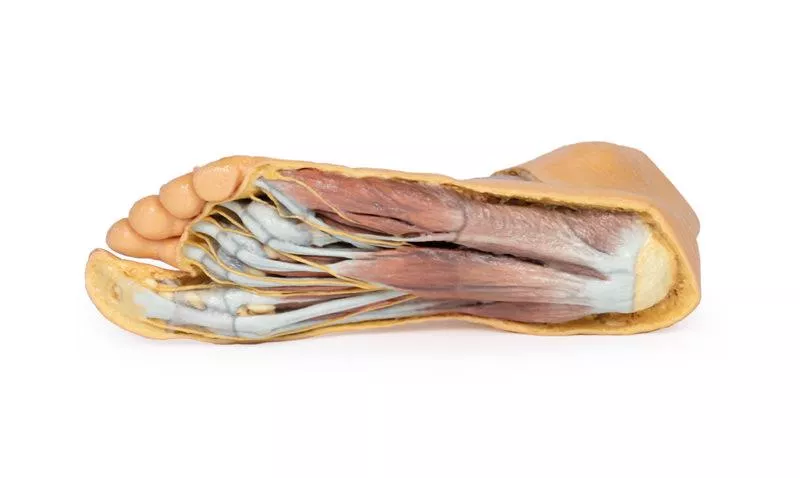
Plantar Surface Anatomy
The plantar aponeurosis and portions of superficial and deep muscles—flexor digitorum brevis, abductor hallucis, abductor digiti minimi, quadratus plantae—have been removed to reveal the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, and fibularis longus tendons. The origins of the flexor hallucis brevis and flexor digiti minimi brevis, as well as the lumbricals arising from the flexor digitorum longus tendons, are also visible.
Proximal Leg Structures
In cross-section, the tibia, fibula, interosseous membrane, and leg muscles are clearly visible. At the medial ankle, the long tendons of the dorsiflexors and plantarflexors pass superficial to capsular and extracapsular ligaments. The posterior tibial artery, veins, and tibial nerve are traced from the posterior leg to the plantar surface. Laterally, the fibularis muscles (longus, brevis, tertius) and their insertions are displayed.
Dorsal Foot Structures
On the dorsum of the foot, the anterior tibial artery and deep fibular nerve emerge deep to the extensor hallucis longus, lying superficial to the extensor hallucis brevis and extensor digitorum brevis.
Plantar Surface Anatomy
The plantar aponeurosis and portions of superficial and deep muscles—flexor digitorum brevis, abductor hallucis, abductor digiti minimi, quadratus plantae—have been removed to reveal the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, and fibularis longus tendons. The origins of the flexor hallucis brevis and flexor digiti minimi brevis, as well as the lumbricals arising from the flexor digitorum longus tendons, are also visible.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.