Product information "Foot - Superficial and deep structures of the distal leg and foot"
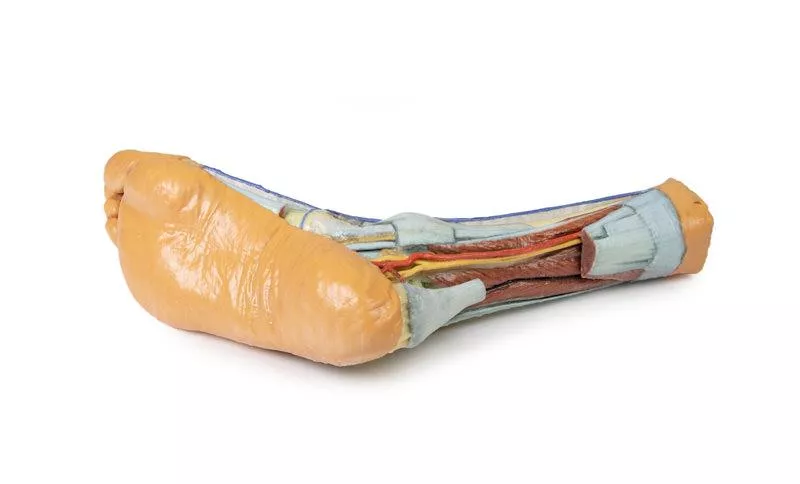
This 3D printed anatomical specimen showcases both superficial and deep structures of the distal leg and foot.
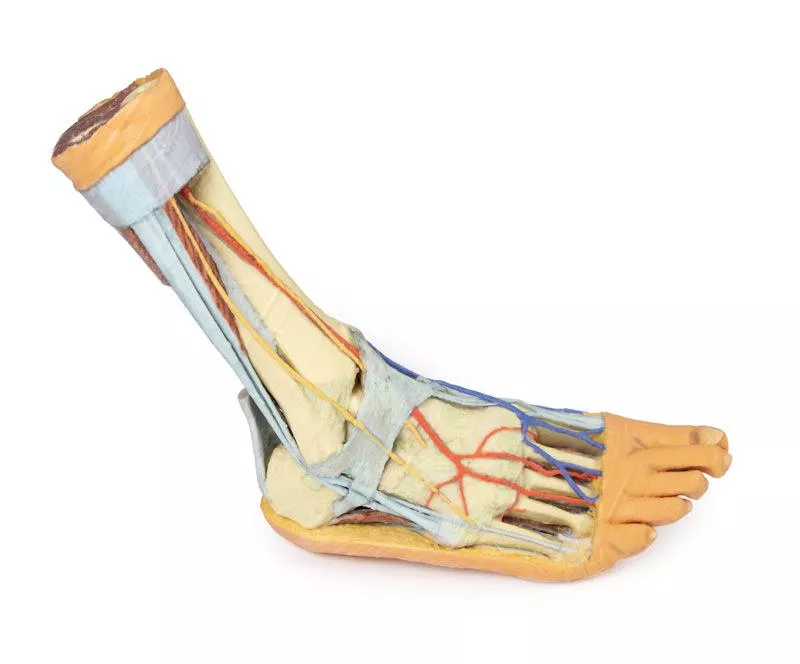
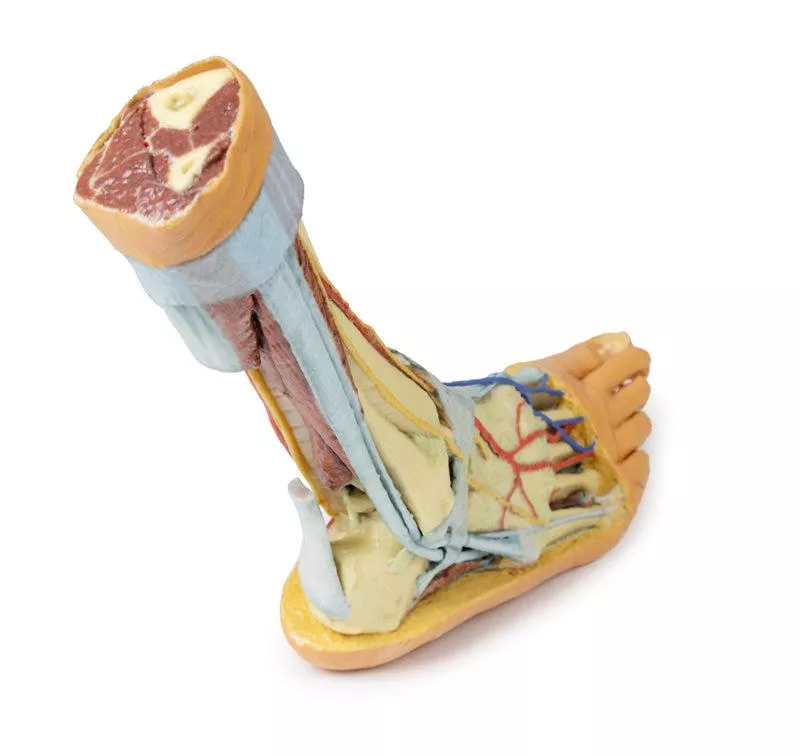
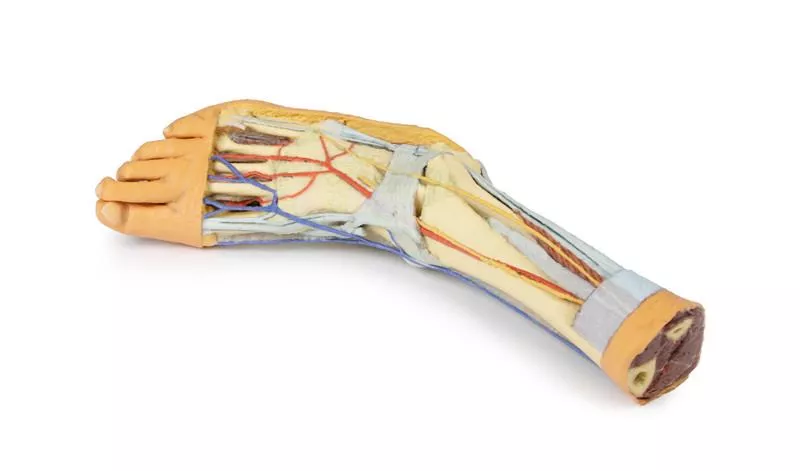
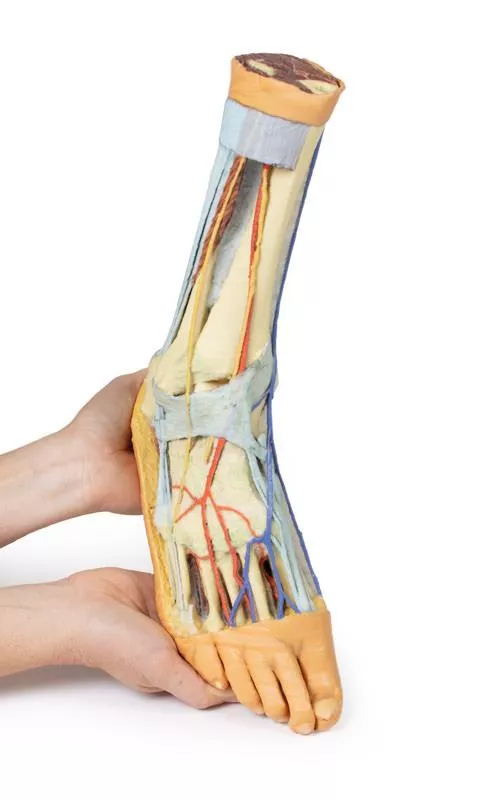
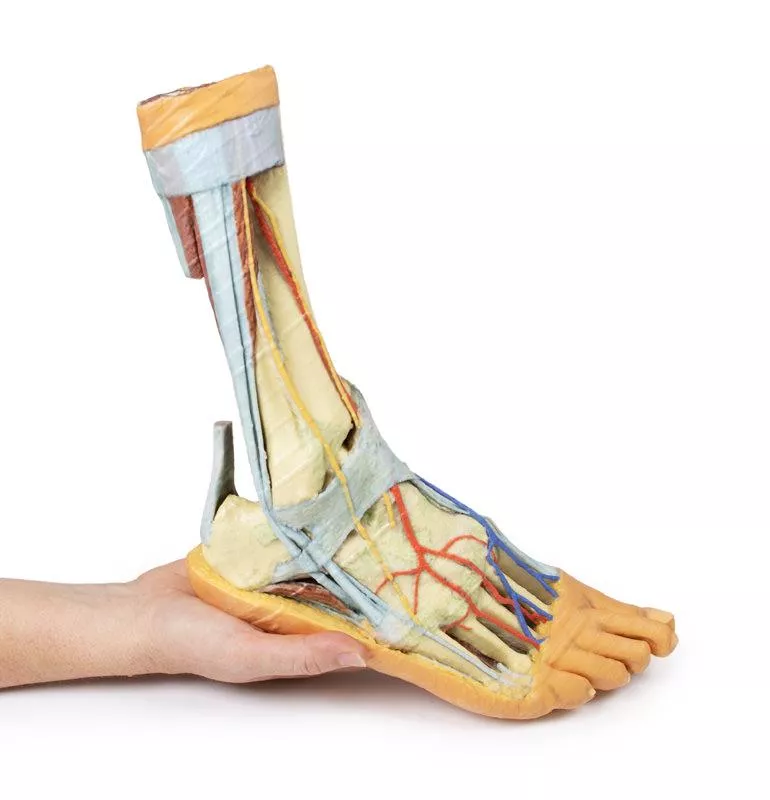
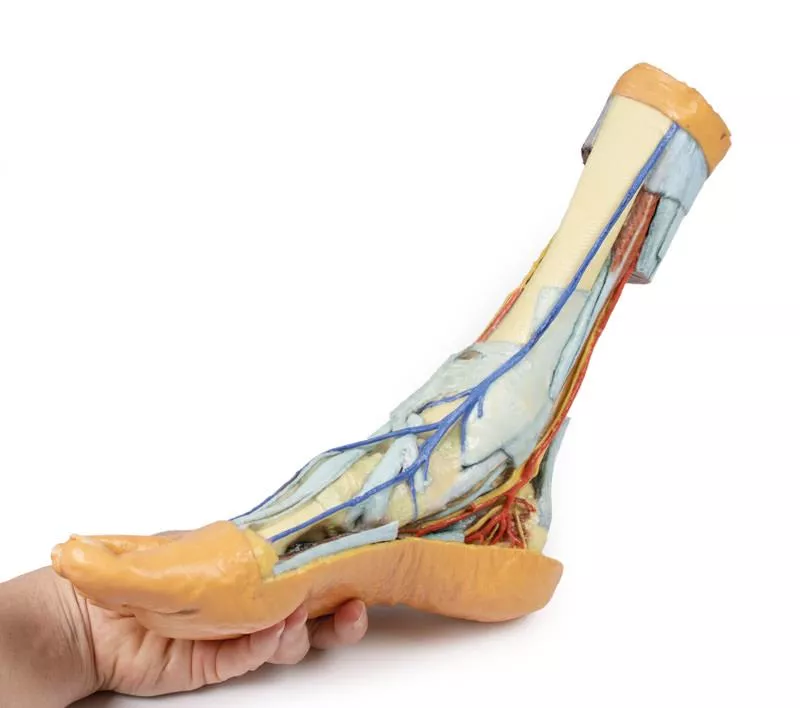
Posterior Compartment: Deep Musculature and Neurovascular Structures
The posterior compartment of the leg has been dissected proximally to remove the triceps surae muscles and the tendocalcaneus, revealing the deep muscles: tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus. The tibial nerve and posterior tibial artery can be traced down to their medial and lateral plantar branches at the level of the flexor retinaculum. To enhance visibility, the origin of the abductor hallucis brevis has been removed.
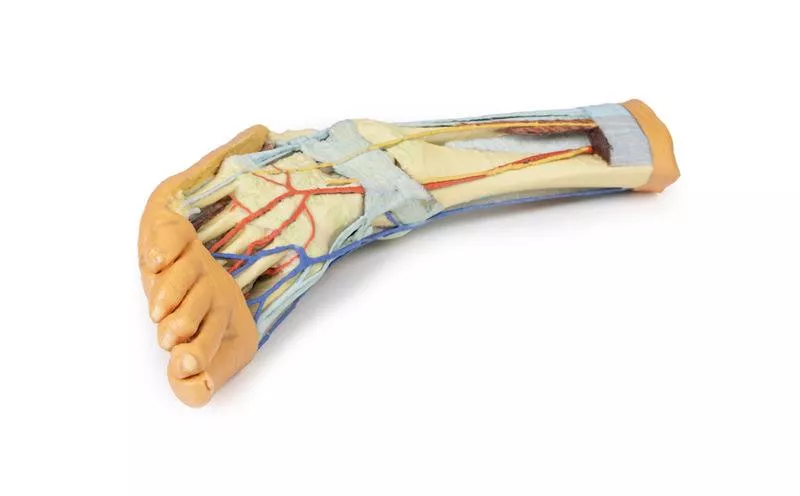
Venous Anatomy and Anterior Compartment Highlights
The great saphenous vein is preserved as it originates from the medial side of the dorsal venous arch, extending to the edge of the specimen. While the anterior compartment muscles have been removed to expose the interosseous membrane, the anterior tibial artery, and the deep fibular nerve, key tendons remain intact. These include the insertions of tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, and the hallucal tendon of extensor digitorum longus, all passing deep to the inferior extensor retinaculum. The anterior tibial artery continues as dorsalis pedis, giving rise to the arcuate artery and dorsal metatarsal arteries. Removal of the dorsal interossei allows visualization of their terminal branches as they approach the plantar interossei.
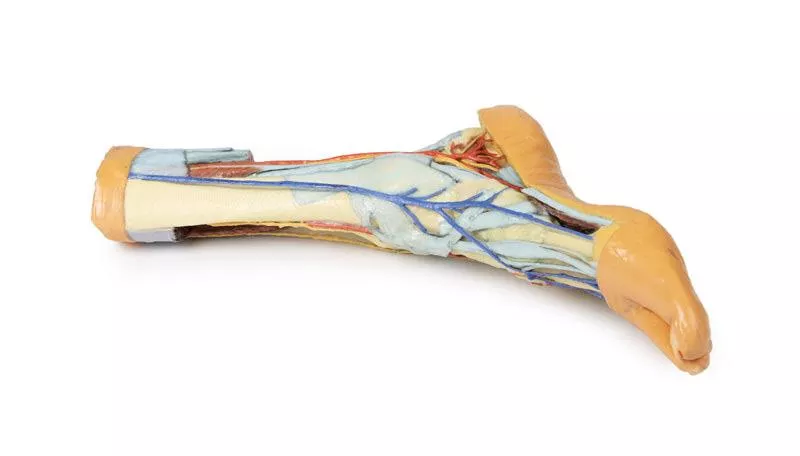
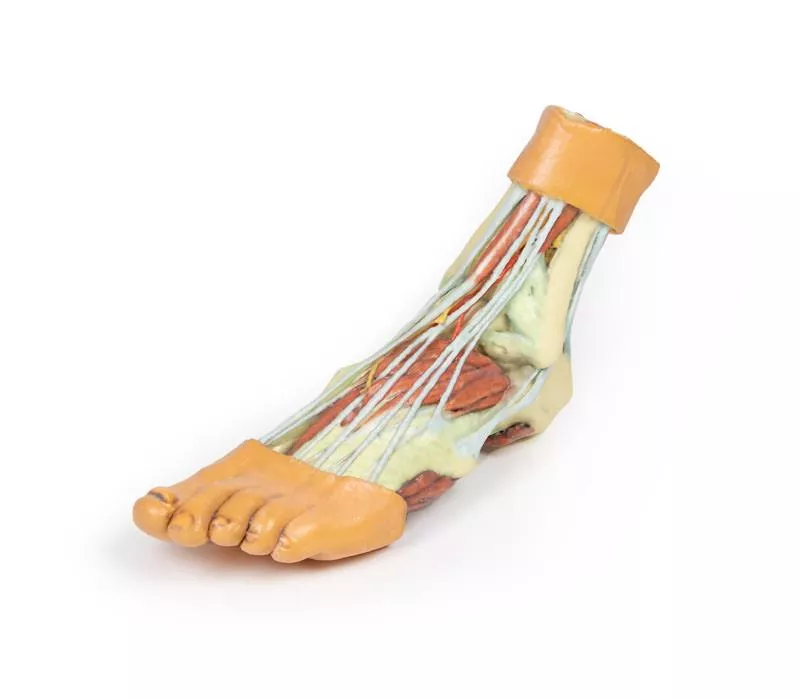
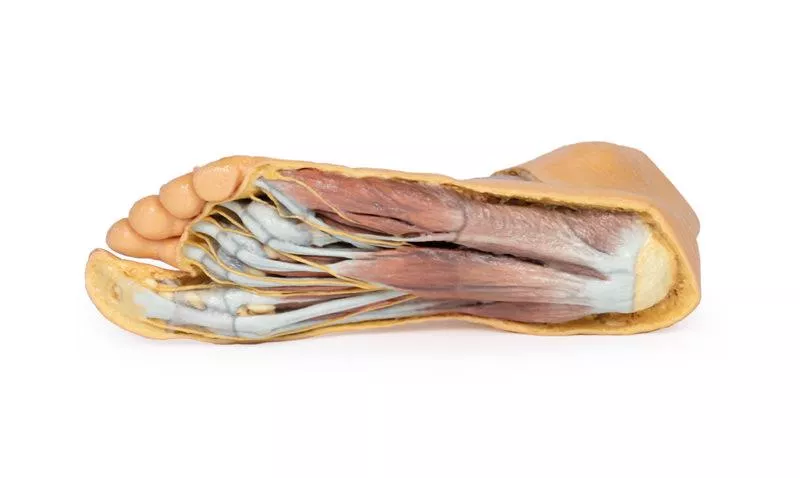
Lateral View: Muscles, Tendons, and Nerve Terminations
On the lateral aspect, the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles and their tendons are clearly visible. The tendons pass beneath the superior fibular retinaculum (cut edge) and the intact inferior fibular retinaculum. Also visible are the extensor digitorum longus tendon to the fifth digit and the termination of the superficial fibular nerve. Near the entry of the fibularis longus tendon into the plantar foot, the abductor digiti minimi muscle origin is preserved.
Ligamentous Structures
Deep structures include key ligaments of the distal leg and foot, such as the anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments, calcaneofibular ligament, dorsal and posterior talonavicular ligaments, and the deltoid ligament, all providing essential support and insight into joint stability.
Posterior Compartment: Deep Musculature and Neurovascular Structures
The posterior compartment of the leg has been dissected proximally to remove the triceps surae muscles and the tendocalcaneus, revealing the deep muscles: tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus. The tibial nerve and posterior tibial artery can be traced down to their medial and lateral plantar branches at the level of the flexor retinaculum. To enhance visibility, the origin of the abductor hallucis brevis has been removed.
Venous Anatomy and Anterior Compartment Highlights
The great saphenous vein is preserved as it originates from the medial side of the dorsal venous arch, extending to the edge of the specimen. While the anterior compartment muscles have been removed to expose the interosseous membrane, the anterior tibial artery, and the deep fibular nerve, key tendons remain intact. These include the insertions of tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, and the hallucal tendon of extensor digitorum longus, all passing deep to the inferior extensor retinaculum. The anterior tibial artery continues as dorsalis pedis, giving rise to the arcuate artery and dorsal metatarsal arteries. Removal of the dorsal interossei allows visualization of their terminal branches as they approach the plantar interossei.
Lateral View: Muscles, Tendons, and Nerve Terminations
On the lateral aspect, the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles and their tendons are clearly visible. The tendons pass beneath the superior fibular retinaculum (cut edge) and the intact inferior fibular retinaculum. Also visible are the extensor digitorum longus tendon to the fifth digit and the termination of the superficial fibular nerve. Near the entry of the fibularis longus tendon into the plantar foot, the abductor digiti minimi muscle origin is preserved.
Ligamentous Structures
Deep structures include key ligaments of the distal leg and foot, such as the anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments, calcaneofibular ligament, dorsal and posterior talonavicular ligaments, and the deltoid ligament, all providing essential support and insight into joint stability.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.