Product information "Ruptured Berry Aneurysm"
Clinical History
A 38-year-old woman developed sudden pain behind the right eye, followed by progressive weakness of the left leg. On examination, she was confused and hypertensive with left-sided hemiparesis, right homonymous hemianopia, and a right VIth cranial nerve palsy. Reflexes were brisk on the left side, with an upgoing plantar reflex. Lumbar puncture revealed raised pressure and blood-stained CSF. Angiography identified an intracerebral aneurysm, which was clipped surgically. Unfortunately, the patient died suddenly the day after surgery.
Pathology
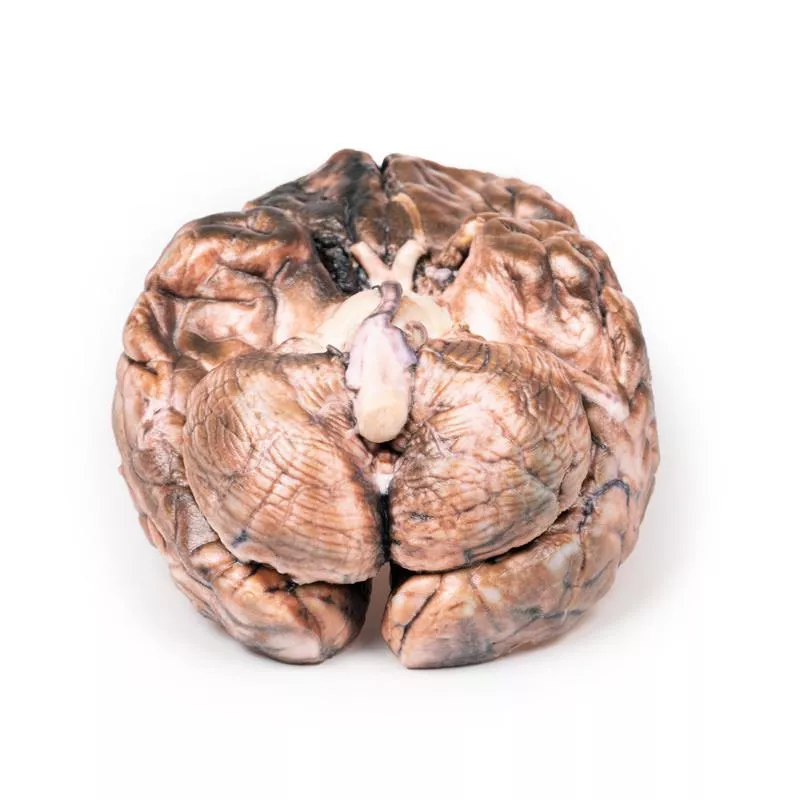
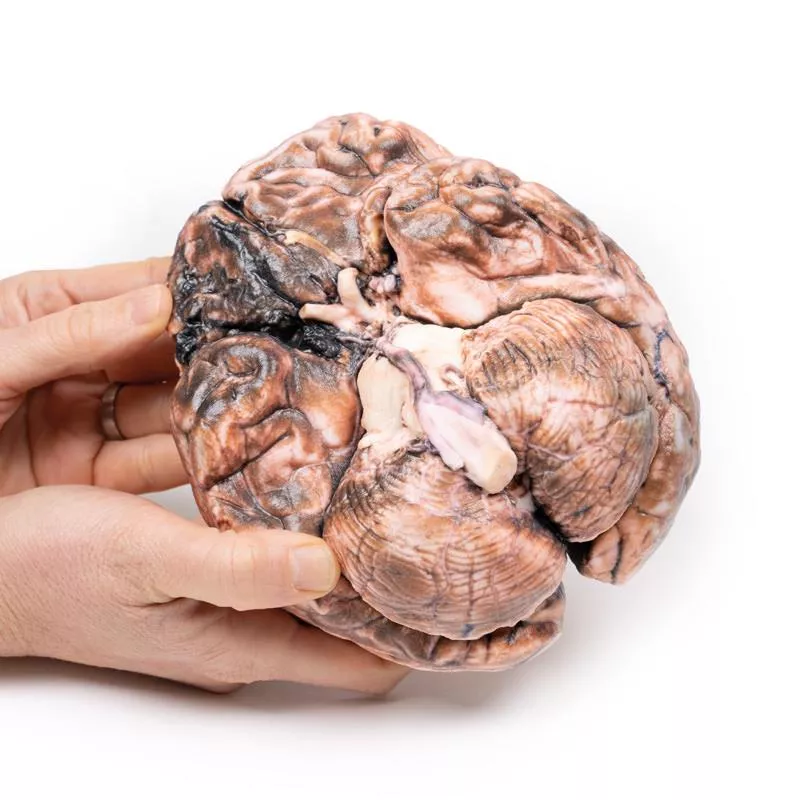
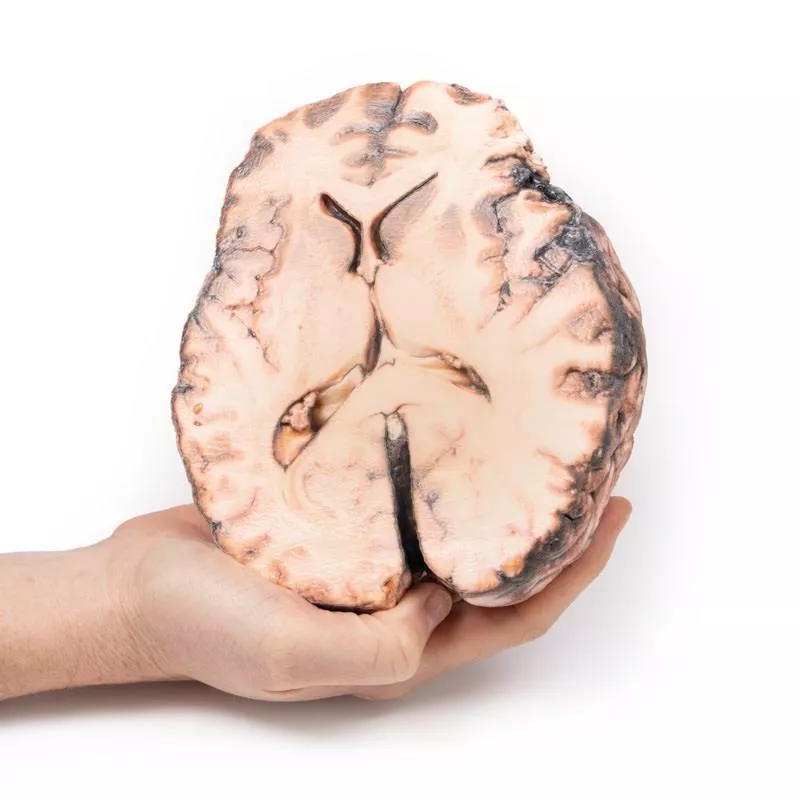
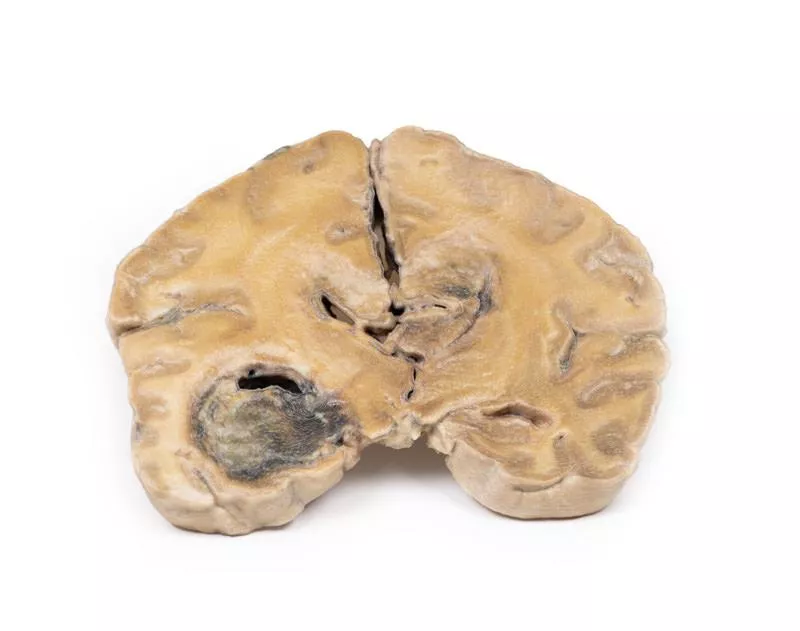
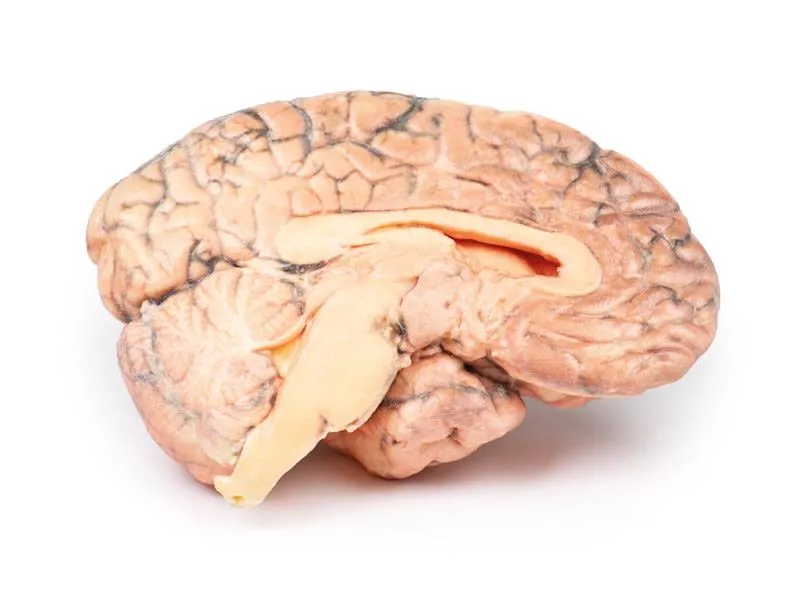
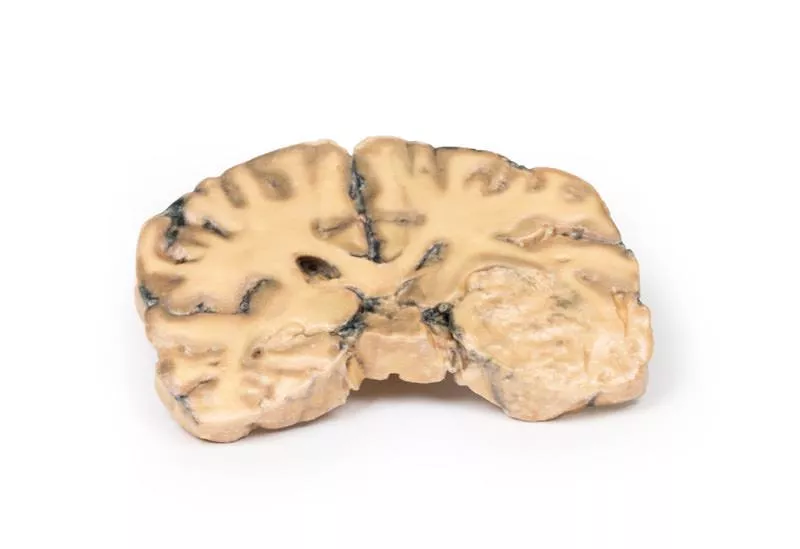
The basal brain surface shows a 5 mm saccular aneurysm at the junction of the right internal carotid and posterior communicating artery, which had ruptured. Subarachnoid haemorrhage is visible in the cisterna magna and on the inferior right frontal lobe. A similar unruptured aneurysm is also present on the left. The right frontal lobe appears soft and friable.
Further Information
Posterior communicating artery aneurysms are the third most common among Circle of Willis aneurysms and can compress nearby cranial nerves, such as the abducens (VI). The patient’s retro-orbital pain may relate to irritation of the trigeminal nerve, while the visual field defect likely resulted from pressure on the right optic tract. Neurological symptoms depend on the affected vascular territory of the cerebral cortex.
A 38-year-old woman developed sudden pain behind the right eye, followed by progressive weakness of the left leg. On examination, she was confused and hypertensive with left-sided hemiparesis, right homonymous hemianopia, and a right VIth cranial nerve palsy. Reflexes were brisk on the left side, with an upgoing plantar reflex. Lumbar puncture revealed raised pressure and blood-stained CSF. Angiography identified an intracerebral aneurysm, which was clipped surgically. Unfortunately, the patient died suddenly the day after surgery.
Pathology
The basal brain surface shows a 5 mm saccular aneurysm at the junction of the right internal carotid and posterior communicating artery, which had ruptured. Subarachnoid haemorrhage is visible in the cisterna magna and on the inferior right frontal lobe. A similar unruptured aneurysm is also present on the left. The right frontal lobe appears soft and friable.
Further Information
Posterior communicating artery aneurysms are the third most common among Circle of Willis aneurysms and can compress nearby cranial nerves, such as the abducens (VI). The patient’s retro-orbital pain may relate to irritation of the trigeminal nerve, while the visual field defect likely resulted from pressure on the right optic tract. Neurological symptoms depend on the affected vascular territory of the cerebral cortex.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.