Product information "Superficial Face"
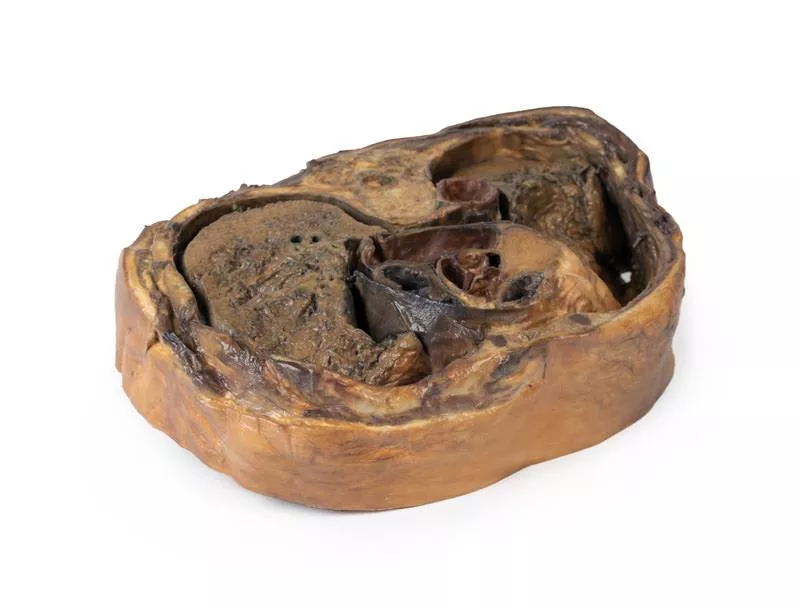
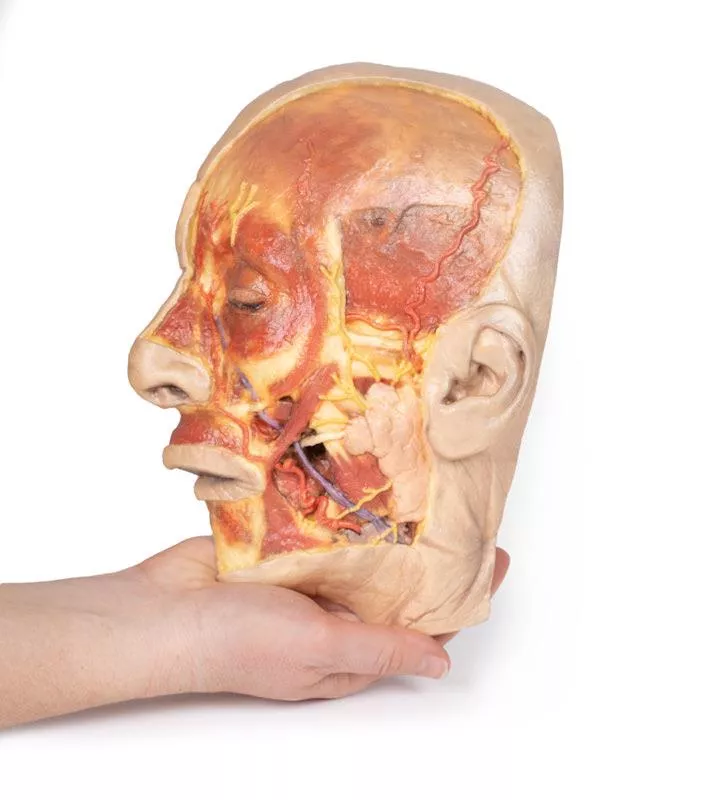
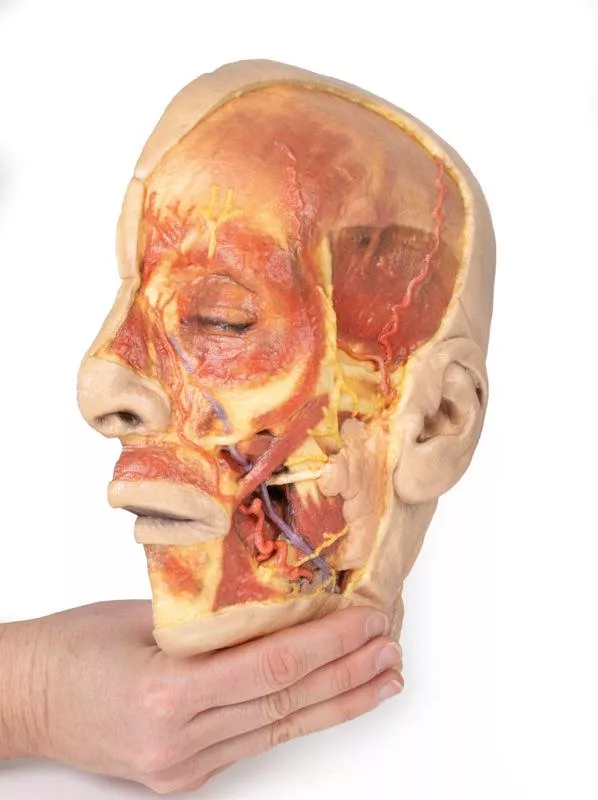
This detailed 3D model features a superficial dissection of the left face just anterior to the ear, with false colouring highlighting key neurovascular structures and muscles of facial expression.
It serves as a focused complement to the broader dissection in our HW 45 model. Undissected areas have been digitally removed for clarity.
Key Features:
Parotid Region & Facial Nerve Branches:
Exposes the parotid gland and duct, along with terminal branches of the facial nerve (CN VII): cervical, mandibular, buccal, zygomatic, and temporal.
Facial Vessels & Nerve-Vessel Relationships:
Shows the facial artery and vein in relation to CN VII branches. Vessels are traced from the mandible to the orbit, offering anatomical landmarks.
Muscles of Facial Expression (Highlighted):
Includes masseter, depressor anguli oris, zygomaticus major & minor, orbicularis oris, nasalis, levator labii superioris alaeque nasi, procerus, and orbicularis oculi.
Temporal & Forehead Structures:
Displays the auriculotemporal nerve and superficial temporal artery over the temporal fascia, with part of the temporalis muscle visible.
Superiorly, the supraorbital nerve and vessels ascend on the epicranial aponeurosis, overlying the frontalis muscle.
This model offers a concise yet richly detailed view of facial anatomy, ideal for teaching nerve-muscle-vascular relationships in the superficial face.
It serves as a focused complement to the broader dissection in our HW 45 model. Undissected areas have been digitally removed for clarity.
Key Features:
Parotid Region & Facial Nerve Branches:
Exposes the parotid gland and duct, along with terminal branches of the facial nerve (CN VII): cervical, mandibular, buccal, zygomatic, and temporal.
Facial Vessels & Nerve-Vessel Relationships:
Shows the facial artery and vein in relation to CN VII branches. Vessels are traced from the mandible to the orbit, offering anatomical landmarks.
Muscles of Facial Expression (Highlighted):
Includes masseter, depressor anguli oris, zygomaticus major & minor, orbicularis oris, nasalis, levator labii superioris alaeque nasi, procerus, and orbicularis oculi.
Temporal & Forehead Structures:
Displays the auriculotemporal nerve and superficial temporal artery over the temporal fascia, with part of the temporalis muscle visible.
Superiorly, the supraorbital nerve and vessels ascend on the epicranial aponeurosis, overlying the frontalis muscle.
This model offers a concise yet richly detailed view of facial anatomy, ideal for teaching nerve-muscle-vascular relationships in the superficial face.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.