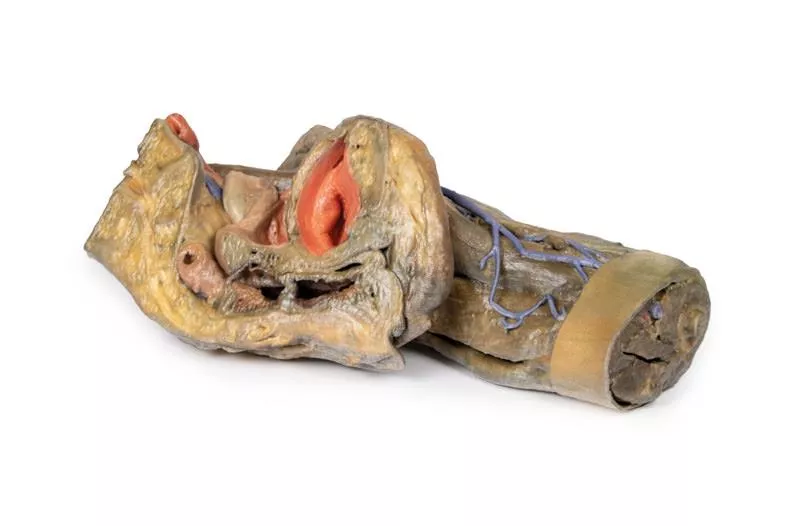
Product information "Abdomen with bilateral Hernias"
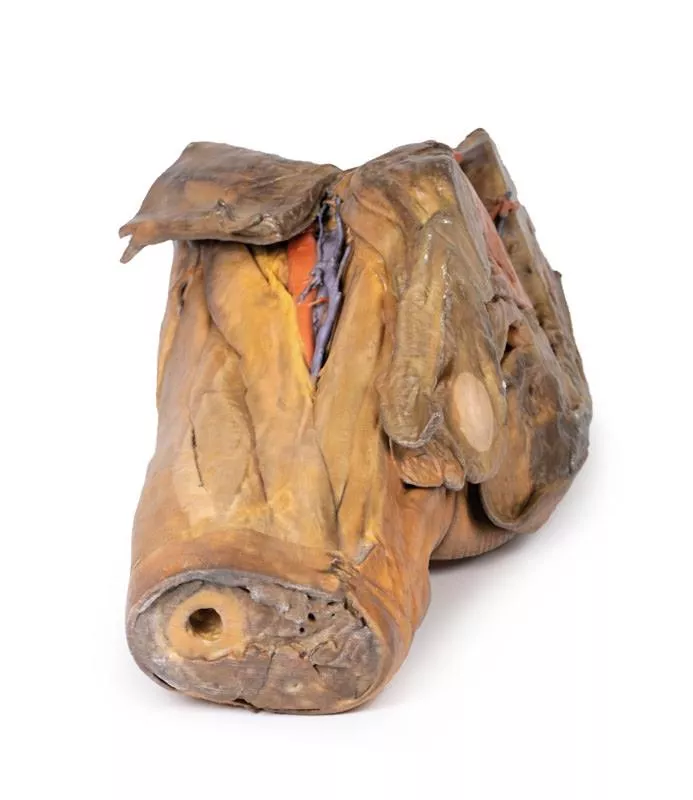
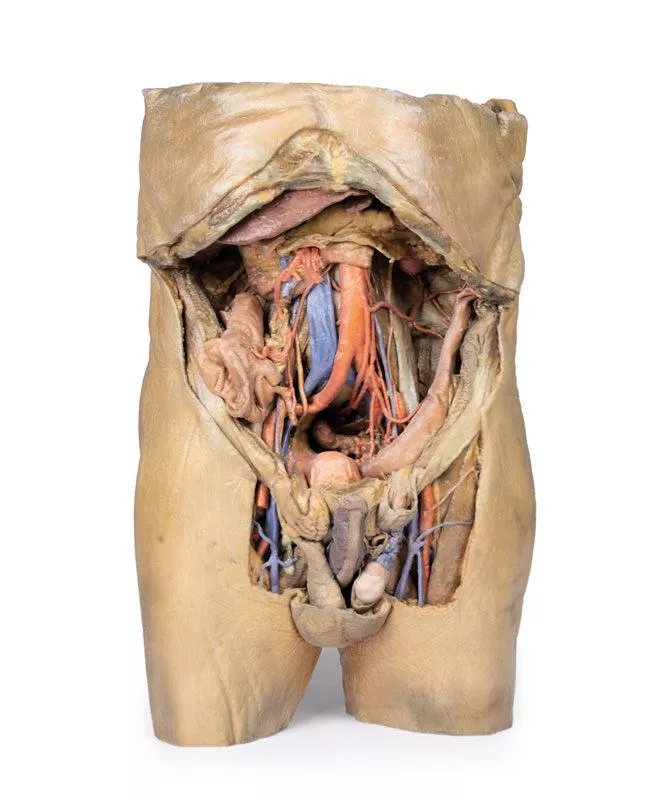
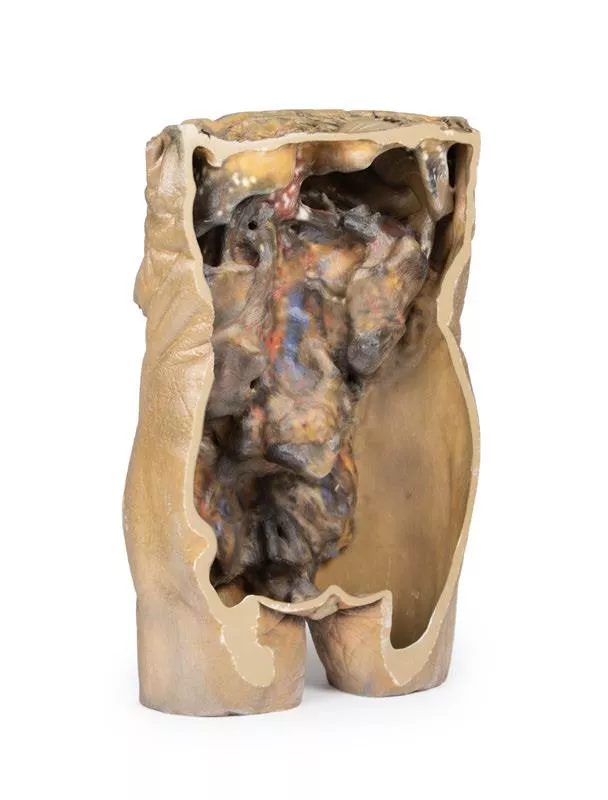
This 3D model represents one of the largest and most complex in the series, consisting of a partial torso from the diaphragm to the proximal thigh with a complete abdominal cavity preserving varying levels of dissection. This 3D model also records the rare, simultaneous occurrence of indirect and direct inguinal hernias allowing for a consideration of the anatomical underpinnings for both conditions. Given the scale of the dissection this 3D model description is divided into discrete parts based on views and regions.
The diaphragm
The diaphragm is preserved on the model’s superior aspect, with both domes and costodiaphragmatic recesses visible despite some distortion from rib removal. The fibrous pericardium rests on the central tendon, with the terminal inferior vena cava seen in the caval foramen. Lateral to this lies the oesophagus in the oesophageal hiatus, and the descending thoracic aorta approaching the aortic hiatus near the vertebrae.
The epigastric and hypochondriac regions
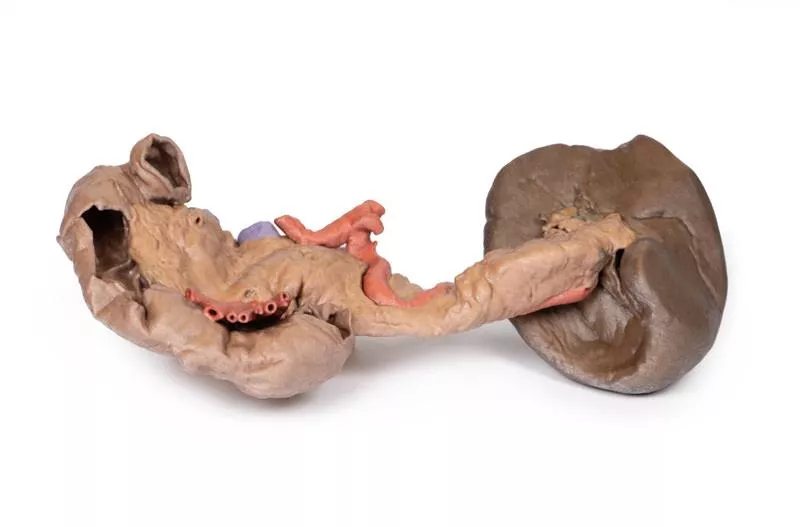
In the abdomen, removal of the anterior wall, greater omentum, and much of the GI tract reveals retroperitoneal structures. The terminal oesophagus enters just left of the liver. With the stomach removed, the pancreas is fully exposed from head to tail, reaching the spleen in the left hypochondrium. Above it, the splenic and common hepatic arteries span the narrow space between pancreas, diaphragm, and liver. The tortuous splenic artery divides near the splenic vein; the common hepatic gives rise to the gastroduodenal and right gastric arteries, superficial to the portal vein. The superior mesenteric vessels pass near the pancreatic head, and the ileocolic artery leads to the caecum. The inferior mesenteric vein arises from the superior rectal vein and crosses the descending aorta.
Below the liver, the gallbladder lies between the lobes. On the left, renal vessels pass deep to the pancreas, with ureters descending across the psoas muscles.
The umbilical and lumbar regions
Most abdominal organs in the umbilical and lumbar regions have been removed to reveal the posterior abdominal wall. Centrally, the descending aorta and inferior vena cava are prominent, with testicular vessels traceable toward the inguinal region. Two right lumbar arteries branch from the aorta, and the inferior mesenteric artery gives rise to the left colic, sigmoid, and superior rectal arteries. On the right, subcostal, iliohypogastric, and ilioinguinal nerves are visible, along with the circumflex iliac artery.
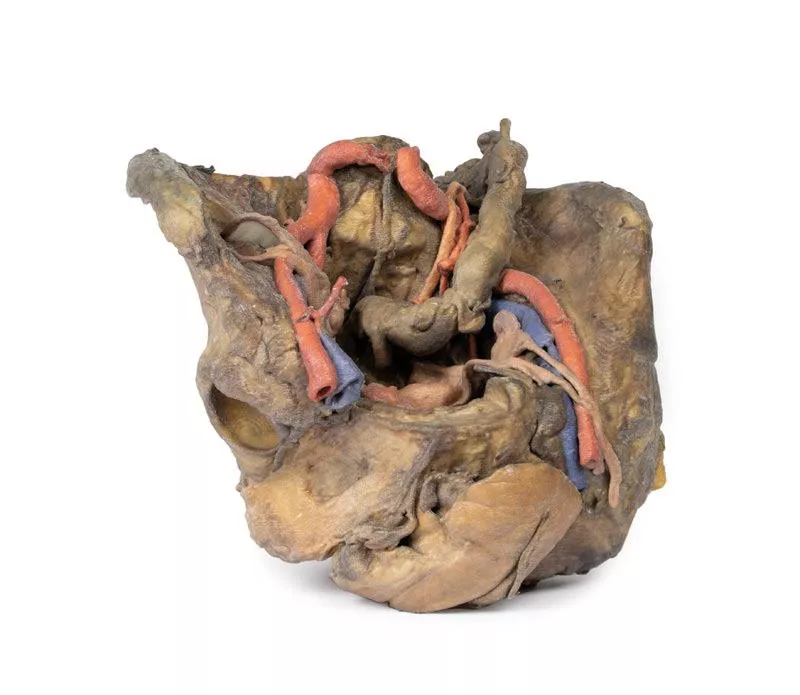
The hypogastrium and iliac regions
The abdominal aorta bifurcates into the common, internal, and external iliac arteries, with matching iliac veins merging into the inferior vena cava. The obturator artery, ureters, and testicular vessels are visible. In the true pelvis, the peritoneum covers the bladder, while the rectum remains obscured. The right iliac fossa contains the terminal ileum, caecum, and appendix, with nearby vessels and nerves. On the left, the sigmoid colon crosses the iliac fossa, where an epiploic appendage extends into an indirect hernia near the inferior epigastric artery.
The inguinal region and perineum
This model uniquely preserves both direct (right) and indirect (left) inguinal hernias, with the inferior epigastric vessels retained for anatomical orientation. The right hernia lies medial to these vessels; the left hernia sac extends laterally into the spermatic cord, containing an epiploic appendage. The perineum reveals the penis, testes, and spermatic cords. On the right, the cord remains intact; on the left, it’s opened, showing a varicose testicular vein linked to the indirect hernia.
The thigh
The femoral triangle has been dissected on both thighs. On the right, the femoral sheath was removed to reveal the femoral artery, vein, deep inguinal lymph nodes, and femoral nerve. On the left, a broader view exposes anterior and medial thigh muscles, with the femoral artery, profunda femoris, and circumflex iliac artery visible. The model ends mid-thigh, showing cross-sectional anatomy including the femoral shaft, vessels, and muscles in the subsartorial canal.
The diaphragm
The diaphragm is preserved on the model’s superior aspect, with both domes and costodiaphragmatic recesses visible despite some distortion from rib removal. The fibrous pericardium rests on the central tendon, with the terminal inferior vena cava seen in the caval foramen. Lateral to this lies the oesophagus in the oesophageal hiatus, and the descending thoracic aorta approaching the aortic hiatus near the vertebrae.
The epigastric and hypochondriac regions
In the abdomen, removal of the anterior wall, greater omentum, and much of the GI tract reveals retroperitoneal structures. The terminal oesophagus enters just left of the liver. With the stomach removed, the pancreas is fully exposed from head to tail, reaching the spleen in the left hypochondrium. Above it, the splenic and common hepatic arteries span the narrow space between pancreas, diaphragm, and liver. The tortuous splenic artery divides near the splenic vein; the common hepatic gives rise to the gastroduodenal and right gastric arteries, superficial to the portal vein. The superior mesenteric vessels pass near the pancreatic head, and the ileocolic artery leads to the caecum. The inferior mesenteric vein arises from the superior rectal vein and crosses the descending aorta.
Below the liver, the gallbladder lies between the lobes. On the left, renal vessels pass deep to the pancreas, with ureters descending across the psoas muscles.
The umbilical and lumbar regions
Most abdominal organs in the umbilical and lumbar regions have been removed to reveal the posterior abdominal wall. Centrally, the descending aorta and inferior vena cava are prominent, with testicular vessels traceable toward the inguinal region. Two right lumbar arteries branch from the aorta, and the inferior mesenteric artery gives rise to the left colic, sigmoid, and superior rectal arteries. On the right, subcostal, iliohypogastric, and ilioinguinal nerves are visible, along with the circumflex iliac artery.
The hypogastrium and iliac regions
The abdominal aorta bifurcates into the common, internal, and external iliac arteries, with matching iliac veins merging into the inferior vena cava. The obturator artery, ureters, and testicular vessels are visible. In the true pelvis, the peritoneum covers the bladder, while the rectum remains obscured. The right iliac fossa contains the terminal ileum, caecum, and appendix, with nearby vessels and nerves. On the left, the sigmoid colon crosses the iliac fossa, where an epiploic appendage extends into an indirect hernia near the inferior epigastric artery.
The inguinal region and perineum
This model uniquely preserves both direct (right) and indirect (left) inguinal hernias, with the inferior epigastric vessels retained for anatomical orientation. The right hernia lies medial to these vessels; the left hernia sac extends laterally into the spermatic cord, containing an epiploic appendage. The perineum reveals the penis, testes, and spermatic cords. On the right, the cord remains intact; on the left, it’s opened, showing a varicose testicular vein linked to the indirect hernia.
The thigh
The femoral triangle has been dissected on both thighs. On the right, the femoral sheath was removed to reveal the femoral artery, vein, deep inguinal lymph nodes, and femoral nerve. On the left, a broader view exposes anterior and medial thigh muscles, with the femoral artery, profunda femoris, and circumflex iliac artery visible. The model ends mid-thigh, showing cross-sectional anatomy including the femoral shaft, vessels, and muscles in the subsartorial canal.
🔬 3D Anatomy Series - Human Body Replicas to Enhance Teaching!
August 26, 2025
Discover exclusive 3D-printed models of the human body – created directly from radiological data or real specimens.
Erler-Zimmer
Erler-Zimmer GmbH & Co.KG
Hauptstrasse 27
77886 Lauf
Germany
info@erler-zimmer.de
Achtung! Medizinisches Ausbildungsmaterial, kein Spielzeug. Nicht geeignet für Personen unter 14 Jahren.
Attention! Medical training material, not a toy. Not suitable for persons under 14 years of age.